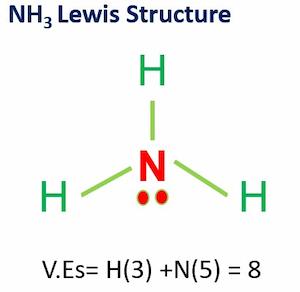
Ammonia (NH3) comprises one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms. NH3 is a neutral compound because the sum of individual oxidation numbers of the atoms nitrogen (oxidation number = -3) and hydrogen ( oxidation number = 1 ) is zero. The oxidation number of a compound is never addressed. However, the oxidation numbers of the different components that comprise the compound are added to determine the charge of an ion or molecule.
Table of Contents
Arrangement of atoms in Ammonia
The ammonia molecule is an inorganic compound with a trigonal pyramidal shape.
It contains three hydrogen atoms and an unshared pair of electrons attached to the nitrogen atom.
Strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding makes it highly associated.
It is a polar molecule. The compound ammonia is formed when three hydrogen atoms interact with one nitrogen atom.
Three hydrogen atoms share electrons with nitrogen’s five outer electrons, thereby giving all four atoms entire outer shells. Each hydrogen atom is one electron short of a noble gas structure (complete shell), while nitrogen is three electrons short of a complete outer shell (of 8).
Three hydrogen atoms and one nitrogen atom combine to make NH3, giving the hydrogen atoms electrical properties similar to helium and the nitrogen atom those similar to neon.
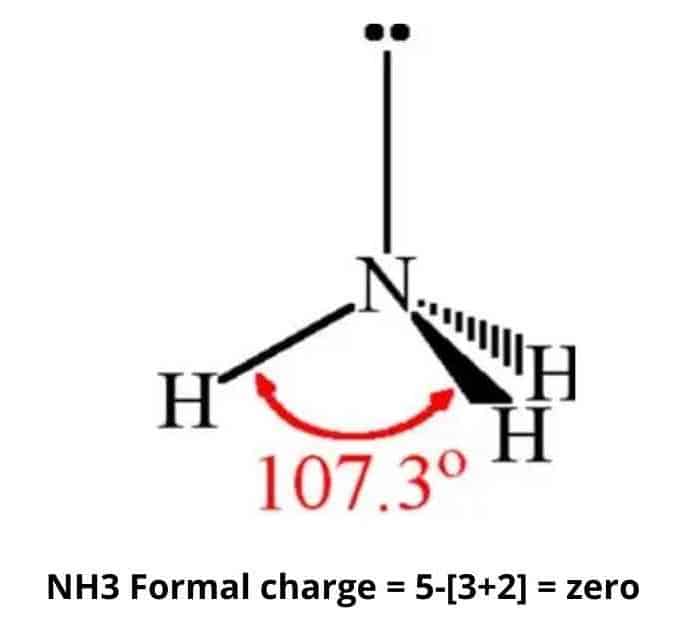
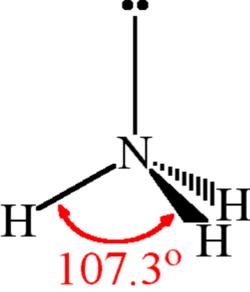
The NH3 molecule is held together by the strong N–H nitrogen–hydrogen single covalent bonds by sharing electrons. The H–N–H bond angle is 107o.
Molecular Geometry of NH3
NH3 molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal.
The nitrogen atom carries a single non-bonding lone pair of electrons that acts as a repulsive force on the bonding orbitals.
Three hydrogen atoms are connected to a central nitrogen atom.
Because nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell, it must interact with three hydrogen atoms to meet the octet rule and generate ammonia, a stable molecule.
Molar Mass of Ammonia
Molar mass of Nitrogen = 14.0067 g/mol.
Hydrogen Molar mass = 1.00794 g/mol.
Molar mass of Ammonia (NH3)= 14.0067 g/mol + (3× 1.00794) g/mol = =17.03052 g/mol
=17.03052 g/mol
Summary
- NH3 is a neutral compound with oxidation number zero.
- A compound’s oxidation number is never reported. To calculate the charge of an ion or molecule, the oxidation numbers of all those components that form the substance are added.
- The NH3 oxidation number is the sum of individual oxidation numbers of the atoms nitrogen (oxidation number = -3) and hydrogen (oxidation number = 1) is zero.
Related Links
| Is HCl Polar or Nonpolar? | CLF3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry |
| SF4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry | Sublimation Examples| Process & Case Study |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How to draw the lewis structure of SO2?
SO2 Lewis structure would comprise two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both S and O atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 12.
- The molecular geometry of SO2 is a trigonal planner.
- The three pairs of bonding electrons are arranged in the plane at an angle of 120-degree.
- The sulfur’s valence electron = 6
- valence electrons of oxygen in SO2 are 6
2. What are unbonded pairs of electrons?
Unbonded pairs of electrons are unshared valence electrons.
They are also called lone pairs of electrons.
They are found in the outermost electron shell of atoms and can be identified by drawing lewis’s structure.
3. What is SO2?
SO2 (Sulfur dioxide) is the entity of a bond between Sulfur and Oxygen atoms.
It is a colorless, toxic, and inorganic gas with a pungent smell like Nitric acid.
SO2 gives a weak acid solution when dissolved in water.
It is naturally found in small amounts in the atmosphere and is a primary precursor of Sulfuric acid.
4. What are the uses of oxygen?
Steel, plastics, and textiles production, steel and other metals brazing, welding, and cutting, rocket propellant, oxygen therapy, and life support systems in airplanes, submarines, spaceflight, and diving are all examples of common oxygen applications.
5. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar molecule. The central boron atom in BF3 contains sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an empty p orbital and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Any net dipole in that plane is canceled out since the Boron-Fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart. Even though each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero since the bond vectors cancel out. Check the full article “Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”
6. NH3 is a polar or nonpolar molecule?
Ammonia (NH3) is a polar molecule. Since the molecule contains three N-H bond dipoles that do not cancel out. In each bond, nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. This unequal distribution of charges among both nitrogen and hydrogen atoms makes NH3 a polar molecule.
7. NH3 oxidation number?
The NH3 oxidation number is the sum of individual oxidation numbers of the atoms nitrogen (oxidation number = -3) and hydrogen (oxidation number = 1) is zero.
8. What is nitrogen trifluoride gas?
Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is an odorless, colorless gas. When inhaled, it is exceedingly poisonous. Containers may burst violently if exposed to fire or heat for a lengthy period of time.
9. What is perchloric acid used for?
Perchloric acid (HCLO4) is used to separate potassium from sodium in many laboratory tests and industrial processes. It is also used as an oxidizing agent, especially in the determination of chromium in steel, ferrochrome, chromite, and leather.
10. CH4 polar or nonpolar?
Methane (CH4) is a nonpolar molecule.
11. What is the oxidation number of NH3?
Ammonia is made up of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms (NH3). The NH3 oxidation number is zero because the sum of the individual oxidation values of the atoms nitrogen (oxidation number = -3) and hydrogen (oxidation number = 1) is zero.
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar?| Simple Explanation
SO2 Polar or Nonpolar
SiCl4 Polar or Nonpolar
Ionic Compounds| Properties, and Examples
Is MgCl2 Ionic or Covalent?
SO2 Ionic or Covalent?
Is Ammonium Ion (NH4+) Polar or Nonpolar?
HCN Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
SiO2 Lewis Structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
Charge of Ammonia (NH3)| Simple Steps
| Is Titanium Magnetic? | N2 Lewis Structure| Hybridization & Molecular Geometry |
| CH4 Polarity | Is Air a Homogeneous Mixture? |
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023