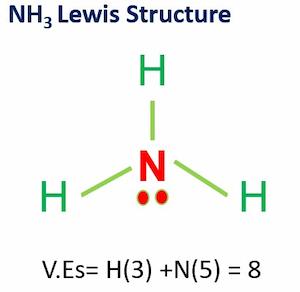
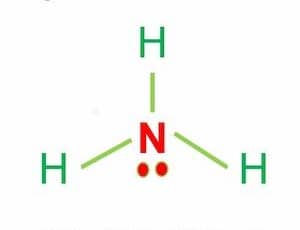
NH3 is a polar molecule because it has three nitrogen-hydrogen bond dipoles that do not cancel out. In each bond, nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. The polarity comes from the unequal distribution of charges among both nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
| Name of molecule | Ammonia (NH3) |
| Bond Angles | 107.3 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of NH3 | Pyramidal planar |
| Hybridization of NH3 | SP3 hybridization |
| Electronic configuration | 1S22S22P3. |
| NH3 oxidation number | zero |
| Is NH3 polar? | Polar |
Table of Contents
What is the Polarity of a Molecule?
When the electronegativity of the bound atoms differs, polar molecules form. Nonpolar molecules are formed when electrons are shared equally between atoms in a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a bigger molecule cancel each other out. Examples of polar molecules include water, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and ethanol.
Examples of nonpolar molecules include helium, argon, krypton, and xenon.
Please refer to another interesting article, “Why is water a polar molecule?”.
Ammonia Molecular Geometry
NH3 molecular geometry is trigonal-pyramidal.
Since the nitrogen atom has a single non-bonding lone pair of electrons, it acts as a repulsive force on the bonding orbitals.
The three hydrogen atoms are joined in the middle by a nitrogen atom.
Because nitrogen’s valence shell has five electrons, it must interact with three hydrogen atoms to meet the octet rule and generate ammonia, a stable molecule.
What is polarity?
The distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond causes polarity.
Specifically, it is found that bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent. In hydrogen chloride, for instance, the H atom is slightly positively charged whereas the Cl atom is slightly negatively charged.
Partial charges are the little electrical charges that exist on different atoms, and the existence of partial charges indicates the presence of a polar bond.
Examples of polar molecules
Some examples of polar molecules are water (H2O), Ethanol, Ammonia, and SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide).
HCL Polar or Nonpolar
HCl (hydrochloric acid) is a polar molecule. Since chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, it pulls the bonded electron pair closer to it and obtains a partial negative charge, whereas hydrogen gains a partial positive charge. HCl has a dipole moment of 1.03 D.
CO2 Polar or Nonpolar
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is nonpolar because of its linear and symmetrical structure. The two oxygen atoms from either direction of the carbon atom pull the electrons equally from both sides. Due to unequal sharing of valence electrons, CO2 is nonpolar in nature.
SO2 Polar or Nonpolar
The gas sulfur dioxide (SO2) has a polar character. It’s a polar molecule because of the electronegativity difference between the sulfur (2.58) and oxygen (3.44) atoms. SO2 has a bent form due to unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
The polarity of Ammonia (NH3)
The electronegativity difference between nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) causes the polarity of the NH3 molecule.
This mismatch in electronegativity results in three dipole moments in one direction.
As a result, ammonia has a net dipole moment, making it a polar molecule.
In addition, the NH3 Lewis structure shows that there is a lone pair of electrons present in nitrogen.
This exerts an outward force on the bond due to which the shape of NH3 becomes unsymmetrical.
Polarity of H2S
H2S is a slightly polar molecule because of the minor difference in electronegativity values of hydrogen (2.2) and sulfur (2.58) atoms. Furthermore, the existence of two lone pairs on the opposite side of the two hydrogen atoms makes the molecule more polar and causes the H2S molecule to have a bent shape geometrical structure.
Summary
The answer to the question “Is NH3 Polar or Nonpolar?” is, that NH3 is a polar molecule because it has three nitrogen-hydrogen bond dipoles that do not cancel out. Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen in each bond. Polarity is caused by the unequal distribution of charges among nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
Related Topics
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
HCN Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
SiO2 Lewis Structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
Valence Electrons in Nitrogen
Charge of Ammonia (NH3)| Simple Steps
Frequently Asked Question
1. Polar covalent bond?
Polar molecules form when the electronegativity of the connected atoms changes. When electrons are evenly divided between atoms in a diatomic molecule or when polar molecules in a larger molecule cancel each other out, nonpolar molecules arise.
2. What is a hydrogen bond?
A hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a dipole-dipole interaction. It is not an actual chemical bond.
It develops when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a strongly electronegative atom.
(fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen ) exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons.
This type of bond is weaker than an ionic or covalent bond but stronger than van der Waals forces.
3. What is the electronegativity difference?
Electronegativity refers to an atom’s tendency to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond.
The greater the difference between electronegativity values, the more polar the chemical bond formed between them.
4. Define dipole moments
A dipole moment is simply a measurement of the net polarity of a molecule.
When polar bonds are irregularly scattered around the core of a molecule, the charge distribution throughout the entire molecule is uneven, resulting in a polar molecule.
Ammonia is an example of a polar molecule (Nh3).
The electrons they share are drawn to nitrogen because nitrogen attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen.
5. CH4 polar or nonpolar?
Methane (CH4) is a nonpolar molecule.
6. What is a polar covalent bond?
The polar covalent bond is a kind of covalent bond that lies between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Such bonds are formed when the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7.
6. What is the oxidation number of NH3?
Ammonia is made up of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms (NH3). The NH3 oxidation number is zero because the sum of the individual oxidation values of the atoms nitrogen (oxidation number =-3) and hydrogen (oxidation number =1) is zero.
More Topics
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023


