The molar mass of nitrogen (N) is approximately 14.01 grams per mole of nitrogen atoms.
Nitrogen is a chemical element with the symbol N, the atomic number 7, and an atomic mass of 14.00674 µ. A nitrogen molecule has a molar mass of 28 atomic mass units (AMU).
| Name of molecule | Nitrogen |
| Bond Angles | 180 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of Nitrogen | Linear |
| The polarity of the N2 molecule | Nonpolar |
| Nitrogen valence electrons | 5 electrons (10 for N2) |
| The molar mass of nitrogen | 28 atomic mass units |
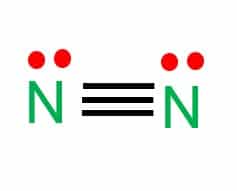
Table of Contents
Steps to Find Molar Mass
- Determine the compound or molecule’s formula.
- Determine the number of atoms in each element of the compound or molecule using the formula.
- Divide the atomic weight of each element by the number of atoms in that element.
- Do the same for all of the elements in the molecule or compound.
- Add all of the values obtained in the preceding step.
- The molecular mass of a substance is calculated by multiplying its molecular mass by its unit of measurement, grams per mole.
The molecular mass of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element with the symbol N, atomic number 7, and atomic mass of 14.00674 u.
For nitrogen, the mass of the N2 molecule is
The molecular mass of a nitrogen molecule (N2) = 14.01 u + 14.01 u = 28.02 u.
General Characteristics of Nitrogen
- Nitrogen is present in the free state in the air as a major constituent (78% by volume).
- It is a nonmetal and a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
- Its compounds are covalent in nature.
- N2 is an inactive gas in comparison with oxygen, which is the next major constituent of air.
- Inorganic compounds of nitrogen are not commonly found as minerals.
- In its combined state, nitrogen is found in all living matter, including, animals and plants, in the form of proteins, urea, and amino acids.
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In a nitrogen molecule, a triple covalent bond is represented by three lines between two atoms of nitrogen.
- The bond angle is 180 degrees, and there are 10 valence electrons.
- N2 is a nonpolar molecule with linear geometry.
- The molar mass of nitrogen is 28 atomic mass units (AMU).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below. If you have any other questions, please feel free to comment.
1. What are polar and nonpolar bonds?
Polar When the electronegativity of the bonded atoms differs, molecules are formed. When electrons are shared equally between atoms in a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other out, nonpolar molecules form.
2. Why Is Nitrous Oxide Called Laughing Gas?
If a mixture of nitrogen oxide and a little oxygen is inhaled for a sufficiently long time, it produces hysterical laughter. Hence, nitrogen oxide is also known as “laughing gas”. That’s why nitrous oxide is called laughing gas.
3. Explain the N2 dot structure in the simplest form
N2 dot structure would comprise two atoms of nitrogen (N) atoms. There is a triple bond between both nitrogen atoms.
Each N is surrounded by two dots, which are called lone pairs of electrons.
It is a diatomic nonpolar molecule with a bond angle of 180 degrees.
4. Explain o2 lewis structure in the simplest form
Two oxygen atoms are joined by a double bond in the O2 Lewis structure. There are 12 valence electrons, and the bond angle is 180 degrees. O2 is a nonpolar, linear-geometry molecule.
5. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar compound. In BF3, the central boron atom has sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an unfilled p orbital on the Bron atom and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Because the boron-fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart, any net dipole in that plane is canceled out. Even if each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero because adding the bond vectors cancels everything out.
Check out the full article here“Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”.
More Interested Links
How many electrons does Helium have?
Sodium Valence Electrons
Silicon Mass Number
The Density of Oxygen| Commonly Used Units
Silicon Valence Electrons
Electron Configuration for Calcium
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023