Methane (CH4) is the simplest hydrocarbon and the main element of natural gas. It is colorless, odorless, and combustible. CH4 is a nonpolar molecule because of its symmetric tetrahedral geometrical form and four identical C-H bonds. Carbon and hydrogen have electronegativity values of 2.55 and 2.2, respectively, resulting in almost zero partial charges.
Table of Contents
Is CH4 Polar or Nonpolar?
CH4 is a nonpolar molecule having a symmetric tetrahedral geometrical structure and four identical C-H bonds. Carbon and hydrogen have electronegativity values of 2.55 and 2.2, respectively, resulting in an equal distribution of electrons between carbon and hydrogen.
Methane (CH4) is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable gas that is used to create energy and heat homes worldwide. It is used in chemical processes to produce other important gases, including hydrogen and carbon monoxide, as well as carbon black, a chemical component found in some types of rubber used in vehicle tires.
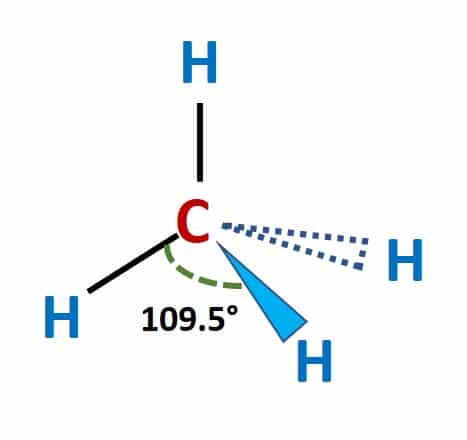
| Name of molecule | Methane (CH4) |
| Bond Angles | 109.5° degrees |
| CH4 Molecular geometry | Tetrahedral |
| Hybridization of Methane | sp3 hybridization |
| Number of Valence Electrons in the molecule | 8 |
| Is CH4 Polar or Nonpolar? | nonpolar |
CH4 Molecular Geometry
Methane’s molecular geometry is tetrahedral, with bond angles of 109.5°. In the Methane molecule, four covalent bonds exist between hydrogen atoms and core carbon atoms.
The theory of Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) states that electron pairs of the same kind repel each other. Because there are four electron bonding pairs, they adopt a tetrahedral molecule structure to decrease repulsive forces.
CH4 Polarity- Key Points
- The nonpolar, colorless, and odorless gas
- It is extremely combustible and is utilized to generate energy.
- also known as marsh gas
- Density = 0.657 kg/m³
- Boiling point:-161.6 °C
- Freezing point: -182 °C
- The molar mass of CH4 is 16.04 g/mol.
- In the CH4 lewis structure, there is a single bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms
CH4 Hybridization
There are four sigma bonds between C and H. The carbon atom in the center is sp3 hybridized. This is because, in the valence shell of carbon, one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals combine to produce four sp3 hybrid orbitals of equal energy and shape. In addition, four H atoms utilize these four carbon sp3 hybrid orbitals to create C-H sigma bonds, which leads to the creation of the methane molecule.
Molar Mass of CH4
Molar mass of Hydrogen = 1.00794 g/mol
Carbon molar mass = 12.011 g/mol
CH4 molar mass is 16.04 g/mol
Methane Effects
Methane (CH4) poisoning can develop as a result of prolonged exposure to high levels of methane. While it is widely thought to be non-toxic, its major hazard is that it works as an asphyxiant, similar to carbon monoxide exposure.
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SiO2 Lewis Structure
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
Is HCl Polar or Nonpolar?
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
Is Nh3 Polar?
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- CH4 is a nonpolar molecule because of its symmetric tetrahedral geometrical shape and four identical C-H bonds.
- The bond angle is 109.5 degrees, and there are 8 valence electrons.
- Exposure to Methane can be dangerous.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below:
1. Why Methane is nonpolar?
Natural gas’s primary component, methane, is a nonpolar molecule. In a three-dimensional configuration fashioned like a four-sided pyramid, four hydrogen atoms encircle a single carbon atom. The symmetry of the hydrogens on the pyramid’s corners distributes electric charge uniformly across the molecule, making it nonpolar.
2. Explain Methane Lewis Structure in simple words
The methane (CH4) molecule has four single shared covalent bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Furthermore, because there are no lone pairs of electrons on an atom, the bond angle is the ideal tetrahedral angle of 109.5°.
3. What is Methane?
Natural gas, which is largely made up of methane, is the most environmentally friendly fossil fuel. Methane that is discharged into the atmosphere before being burnt, on the other hand, is hazardous to the environment. Methane contributes to climate change because of its ability to trap heat in the atmosphere.
4. What is the dot structure of Hydrogen Sulfide?
On both sides of the central sulfur atom in the H2S Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms.
The molecule bends due to the existence of two unbonded pairs of electrons.
Because sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen, the molecule is somewhat polar.
The vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments in the instance of H2S results in a non-zero total dipole moment. As a result, dipole-dipole interactions in hydrogen sulfide are detected.
5. Is CH4 polar?
Because the ch4 molecule is symmetrical and lacks a loan pair, it is a nonpolar molecule. This is referred to as a nonpolar molecule.
6. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar compound. In BF3, the central boron atom has sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an unfilled p orbital on the Bron atom and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Because the Boron-Fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart, any net dipole in that plane is canceled out. Even if each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero because adding the bond vectors cancels everything out.
Check out the full article “Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”.
7. Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?
SiCl4 (silicon tetrachloride) is a nonpolar molecule. Because the four chemical bonds between silicon and chlorine are uniformly distributed, SiCl4 is non-polar. A polar covalent bond is a type of covalent link that is intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. When the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7, such bonds occur.
Check the full article “Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?”.
8. Is carbon dioxide a pure substance?
Carbon dioxide is a pure substance since its composition remains constant regardless of where it is collected. Carbon Dioxide is a greenhouse gas that is naturally occurring and innocuous in small amounts, but as levels grow, it can have an impact on productivity and sleep. CO2 levels concentrate inside with less ventilation since they are most typically created by the air we exhale.
Each carbon dioxide molecule will always have one carbon and two oxygens.
Check the full article “Is carbon dioxide a pure substance?”.
9. What is nitrogen trifluoride gas?
Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is an odorless, colorless gas. When inhaled, it is exceedingly poisonous. Containers may burst violently if exposed to fire or heat for a lengthy period of time.
10. What is perchloric acid used for?
Perchloric acid (HCLO4) is used to separate potassium from sodium in many laboratory tests and industrial processes. It is also used as an oxidizing agent, especially in the determination of chromium in steel, ferrochrome, chromite, and leather.
More Interesting Topics
Is Titanium Magnetic?
Power Units- The Basics
Electromagnetic Force
Sulfur Electron Configuration
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar?
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Master’s degree in Materials Science.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



