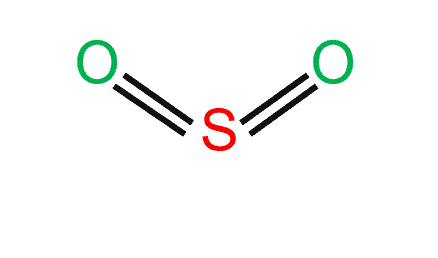
The SO2 Lewis structure would be comprised of two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both sulfur and oxygen atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 18.
| Name of molecule | Sulfur dioxide (SO2) |
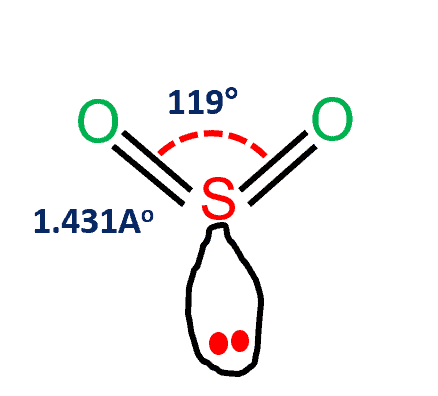
| Bond Angles | 119 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of SO2 | Bent-V shaped |
| Hybridization of SO2 | sp2 hybridization |
| No of Valence Electrons in the molecule | 18 |
| The dipole moment of SO2 | 1.62 debye |
Table of Contents
Step By Step Construction of Lewis Structure
The electron geometry of Sulfur dioxide is in the shape of a trigonal planar (as per lewis structure ). The three pairs of bonding electrons lie at an angle of 119o. Two double pairs are bonded together and there is one lone pair as well, which further gives it a bent shape.
Step-1: Count the valence electrons of atoms
First, we need to figure out the number of valence electrons in individual atoms as shown in the Table.
| Atom | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons (VEs) |
| 8O | 1S2 2S2 2P4 | 6 |
| 16S | 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P4 | 6 |
VEs= VEs in 1 Sulfur atom + VEs in 2 Oxygen atoms
Valence electrons in SO2 = 1(6)+2(6) =18
Sulfur dioxide has a total of 18 valence electrons, with six electrons contributed by each of the atoms in the compound.
Step-2: Determine the central atom
For the sulfur dioxide molecule, sulfur has less electronegativity value than oxygen. As per the rule, the element with the least electronegativity is placed at the center.
Therefore, place sulfur in the center and then the oxygen on either side.
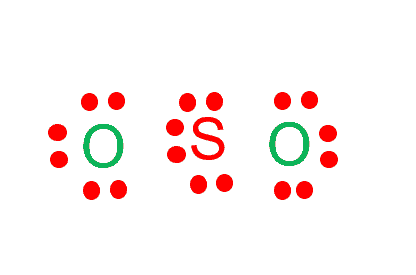
Step-3: Place electron pairs between the atoms
Draw six dots around each atom.
In the figure, one electron pair between two atoms is equivalent to one line. Out of 18 electrons, 4 will be used in pairs between atoms. Now we have 14 valence electrons to distribute.
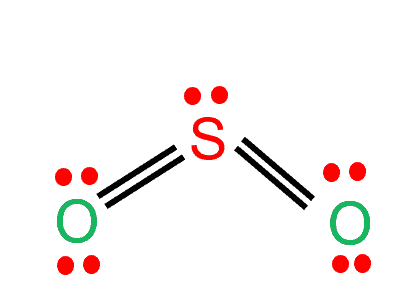
Step 4: Place remaining electrons around the other atoms
To complete the octet of the molecule, the sulfur atom will donate its four electrons to both oxygen atoms to form a double bond. As shown in the image, there is one lone pair remaining on Sulfur. This lone pair on the central sulfur atom makes a bent molecular geometry.
What is sulfur dioxide (SO2)?
Sulfur Dioxide (American English), also known as Sulfur Dioxide (Commonwealth English), is the entity of a bond between sulfur and oxygen atoms.
It is a colorless, toxic, inorganic gas with a pungent smell like nitric acid.
It is naturally released by volcanic activity.
It gives a weak acid solution when dissolved in water.
Sulfur dioxide is naturally found in small amounts in the atmosphere and is a primary precursor of sulfuric acid.
The molar mass of Sulfur dioxide
The molecular mass of sulfur is 32.066 g/mol.
O2 molar mass = 16.00 x 2 = 32.00 g/mol.
The molar mass of SO2 is 64.066 g/mol.
SO2 Lewis Structure-Key Points
- The electron geometry of SO2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner.
- The three pairs of bonding electrons are arranged in the plane at an angle of 120 degrees.
- The sulfur valence electron is equal to 6.
- valence electrons of oxygen = 6 (There are two oxygen atoms in the compound.)
Production of sulfur dioxide
Sulfur or iron pyrites are burnt in excess of air to produce SO2.
S + O2 (gas) —> SO2 (gas)
4FeS2 + 11O2—-> 2Fe2O3 (solid) + 8SO2 (gas)
Similarities between Sulfur and Oxygen atoms
- Both O and S have the same outer electric configuration of ns2 and np4.
- O and S are usually divalent.
- Both exhibit an allopatric form.
- O and S are non-metals.
- In reaction with metals, they both react with the oxidation state of-2.
- While reacting with nonmetals, both form covalent compounds, for instance, H2O, H2S, CO2, and CS2.
Dissimilarities between oxygen and sulfur
| Oxygen | Sulfur |
| Two allotropic forms | 3 allotropic forms |
| Gas at ordinary temperature | Solid at ordinary temperature |
| Sparingly soluble in water | Not soluble in water |
| Helps in combustion | Combustible itself |
| Paramagnetic in nature | diamagnetic in nature |
| Does not react with water | When steam is passed through boiling sulfur, a little hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide is formed. |
| Does not react with acids | It is readily oxidized by concentrated sulfuric acid or nitric acid. |
SO2 Is Polar or Nonpolar?
Sulfur dioxide is polar in nature.
The difference in electronegativity between sulfur and oxygen atoms creates polarity in the molecule.
Oxygen has a greater electronegative potential than sulfur.
Therefore, oxygen exerts more pull on the covalent bonds in sulfur dioxide.
The portion of the molecule that has both oxygen atoms on it is slightly negatively charged.
whereas the portion that has the sulfur atom has a slightly positive charge.
This makes SO2 a polar molecule like H2S.
In addition, the unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen create repulsion between atoms.
This is another cause of the polarity of the sulfur dioxide molecule.
Check the full article “SO2 is polar or nonpolar?”.
Related Links
SiO2 Lewis Structure
Laughing Gas
HCN Lewis Structure
Sulfur Dioxide Effects on Humans
Sulfur dioxide is a toxic gas and is directly harmful to human health.
It can irritate the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs.
Its high concentrations can cause inflammation and irritation of the respiratory system.
High emissions of sulfur dioxide in the air can lead to the formation of other sulfur oxides (SOx).
SOx can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles.
These small particles may penetrate deeply into the lungs, and their sufficient quantity can contribute to health problems.
CO2 Lewis Structure
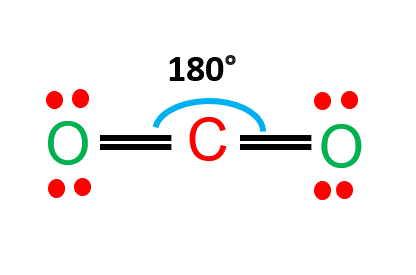
Another similar Lewis structure is the CO2 Lewis structure.
In this structure, there are two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom.
Two oxygen atoms are located on either side of the carbon atom.
Both oxygen atoms share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom.
The carbon atom is in the central position as it is the least electronegative atom in the molecule.
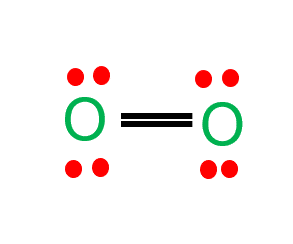
O2 Lewis Structure
O2 Lewis structure comprises two oxygen atoms connected in a pair.
The molecular geometry of O2 is linear with bond angles of 180 degrees.
Valence electrons in the O2 molecule are 12.
Each oxygen atom contains one lone pair of electrons.
Summary
- The SO2 Lewis structure would consist of two oxygen (O) atoms and one sulfur atom. Both the sulfur and oxygen atoms have six valence electrons.
- The molecular geometry of sulfur dioxide is a bent shape.
- The sulfur to oxygen ratio in sulfur dioxide is 1:2.
- The sulfur dioxide molecule has two double bonds between the Sulfur atom and Oxygen atoms.
- There are 5 lone pairs of electrons in the molecule of SO2.
- SO2 gives a weak acid solution when dissolved in water.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below. If you have any questions, feel free to comment or send an email to [email protected]
1. How many lone pairs of electrons are present in the SO2 Lewis structure?
In the sulfur dioxide molecular geometry, there are two double bonds between the sulfur atom and oxygen atoms. The sulfur atom has one lone pair and each oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
2. What is the biggest source of SO2?
Burning fossil fuels is the largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere.
3. What is sulfur electronic configuration?
Sulfur electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
4. What is sulfur hexafluoride?
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a non-toxic gas that is used in a variety of applications due to its inert properties. While SF6 is non-toxic when used properly, toxic byproducts can be produced during electrical discharges within SF6-filled equipment, posing a threat to the health of workers who come into contact with them.
5. What is sulfur trioxide?
SO3 (sulfur trioxide) is a chemical compound. It is available in three forms: gaseous monomer, crystalline trimer, and solid polymer. It is solid at just below room temperature and has a relatively narrow liquid range. Gaseous SO3 is the primary precursor to acid rain.
More on Lewis Structures
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Master’s degree in Materials Science.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023