In the SiO2 Lewis structure, there is one atom of silicon (Si) atom and two atoms of Oxygen (O). The number of valence electrons in Si is 4 and the number of valence electrons in O is 6. The total number of valence electrons is 16.
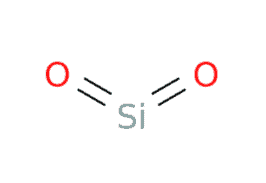
Table of Contents
SiO2 Lewis Structure (Step by Step Construction)
In the SiO2 lewis Structure, the overall ratio of silicon to the oxygen atom is 1:2. The silicon oxygen bonds are strong and keep the atoms firmly in place. The following are the steps to construct the SiO2 Lewis Structure.
Step-1: Count the valence electrons of atoms
For the SiO2 Lewis structure, we need to figure out the number of valence electrons in individual atoms as shown in the table.
| Atom | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons (VEs) |
| 8O | 1S2 2S2 2P4 | 6 |
| 14Si | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 | 4 |
VEs in SiO2 = VEs in 1 Silicon atom + VEs in 2 Oxygen atoms
Valence electrons in SiO2 = 1(4)+2(6) =10
Step-2: Determine the central atom
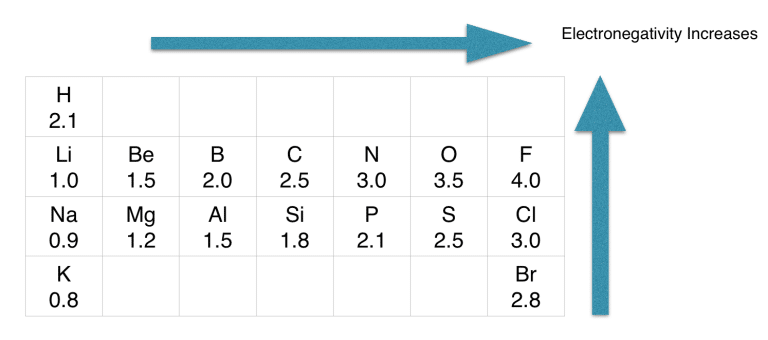
As per rule, Si is placed in the middle because it’s the least electronegative.
If we check the proper arrangement of Si and oxygen in the periodic table, we will find that Si is less electronegative than an oxygen atom.
Put Si in the center and then the oxygen on either side.
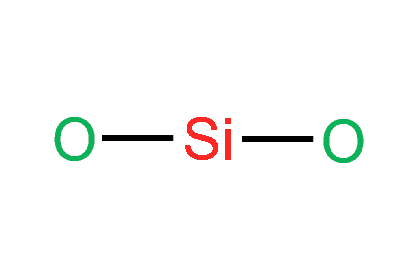
Step-3: Place electron pairs between the atoms
We need to distribute the 16 remaining valence electrons.
In the figure, one electron pair between two atoms is equivalent to one line. Out of 16 electrons, 4 will be used in pairs between atoms. Now we have 12 valence electrons to distribute.
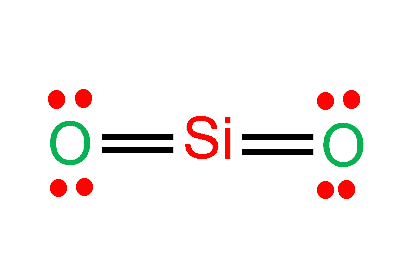
Step 4: Place remaining electrons around the other atoms
Both Oxygens have eight remaining valence electrons (four each), but the Si has four valence electrons.
So we need to move two electrons between Si and O to create a double bond.
Now Distribute the remaining 8 electrons so that each atom has an octet.
What is Silicon dioxide (SiO2)
Silicon dioxide (SiO2), also called silica, is the most common and most important silicon compound. In silica, every silicon atom is attached tetrahedrally to four oxygen atoms, and each oxygen atom has two close silicon neighbors. It is the main constituent of more than 95 percent of the known rocks. The mass of the Earth’s crust is 59 percent silica.
Silica has three main crystalline varieties: quartz (by far the most abundant), tridymite, and cristobalite. Other varieties include coesite, keatite, and lechatelierite
Properties of Silica
- Silica is transparent to light
- SiO2 is refractory, which means it does not soften below 1500 °C to 1600 °C.
- Silica has a very low thermal expansion.
- Silica is an excellent insulator
- It is hard, brittle, and elastic.
- insoluble in water and inert to many reagents.
- Low thermal expansion and an excellent insulator
- Hard, brittle, and elastic
- Density = 2.648 g/cm3
- Resistant towards all acids except HF
SiO2 Lewis structure (Key Points)
- The simplest formula for silica is SiO2.
- covalent compound and transparent to light.
- very refractory, does not soften below 1500 °C to 1600 °C
- insoluble in water, and inert to many reagents.
- SiO2 has two places of electron concentration and no lone pairs, so it is linear.
- The SiO2 molecule is non-polar. As either side of the Si are oxygen atoms, the dipole moments cancel (dipole moments are formed when there is a difference in electronegativity between the two atoms).
- In polymer form, SiO2 is tetrahedral.
Important Features of SiO2 Lewis Structure
- The overall ratio of sulfur to oxygen atoms is 1:2.
- The simple formula of silica is SiO2.
- In each of the various crystalline forms of silica, there is a special pattern that is repeated throughout the crystal in a regular definite crystal lattice.
- The regular tetrahedral arrangement of four oxygen atoms around each silicon persists in each crystalline form.
- The Si-O-Si bond angles and the rotation of each Si-O bond are different in the different polymorphic species.
- Crystalline silica melts at high temperature to give a viscous liquid having a random structure, presumably with the silicon atoms still close to four oxygen atoms and the oxygen atoms close to two silicon atoms.
- When liquid silica gets cool, it does not crystallize readily. Usually, it undercools tremendously and eventually becomes rigid without having undergone orientation into a regular crystal pattern.
Silicon Dioxide Formula
The silicon dioxide formula is SiO2, silica is its other name.
The compound is composed of linear triatomic molecules with a silicon atom covalently linked to two oxygen atoms.
Molar Mass of Silica (SiO2)
Molecular mass of Si = 28.08 g/mol.
O2 molar mass = 16.00 x 2 = 32.00 g/mol.
Molar mass of SiO2 = 60.08 g/mol

Uses of Silica (SiO2)
- Industrial Silica is used in industries like glass, foundries, construction, ceramics, and the chemical industry. Its finest form is also used as a functional filler for paints, plastics, and rubber.
- Silica sand is used in water filtration and agriculture.
- SiO2 is also used in buildings and roads in the form of portland cement, concrete, and mortar, as well as sandstone.
- Silica is also used in grinding and polishing glass and stone; in foundry molds.
- Silica gel is often used as a desiccant to remove moisture.
- SiO2 is used as a fining agent in juice, beer, and wine.
- Silica is used in pharmaceutical tablets.
Related Links
| CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry | HCN Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction |
| SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure | N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas |
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Is Chlorine a metal?
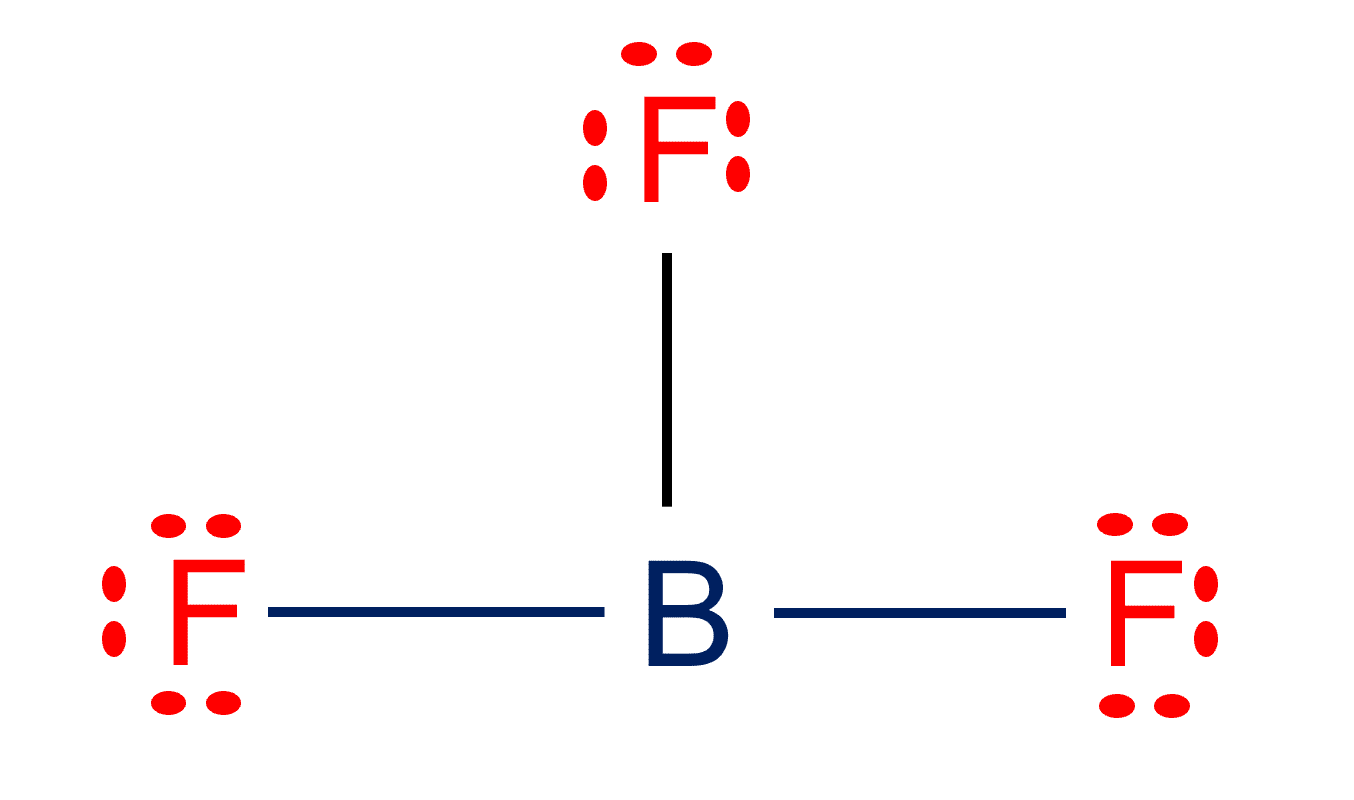
Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?| BF3 Molecular Geometry
BF3 Lewis structure| Molecular geometry, Hybridization
Frequently Asked Questions
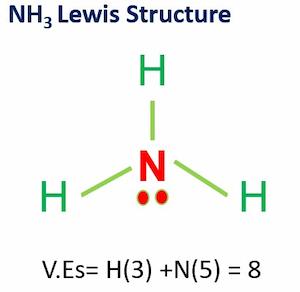
1. Does oxygen have 6 or 8 valence electrons?
Because oxygen is in Periodic Group VI, it possesses six valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and four in the 2p subshell. Check the full article for oxygen valence electrons.
2. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
Silica is a crystalline polymer with a tetrahedral structure. The silicon atom is attached to four oxygen atoms to form a single bond with each oxygen atom at tetrahedral angles.
SiO2 is an acidic oxide. It will react with strong bases to form silicate salts.
Silica is used in industries like glass, foundries, construction, ceramics, and the chemical industry. Its finest form is also used as a functional filler for paints, plastics, and rubber.
In SiO2 Lewis Dot Structure, the Silicon atom is a bigger atom and attaches with four oxygen atoms to form a single bond at tetrahedral angles.
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
More Interesting Topics
Sf4 Lewis Structure
O3 Lewis Structure | Step By Step Drawing
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
H2S Polar Or Nonpolar| Easy Explanation
BrF3 (Bromine trifluoride) Molecular Geometry, Bond Angles
Is Nh3 Polar?
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023