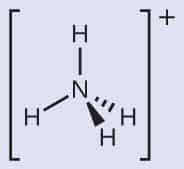
The ammonium ion (NH4+) is a positively charged ion (cation). It is formed as a result of the protonation of an ammonia molecule. This article describes whether or not ammonium ion is polar, as well as the properties of ammonium ion.
The ammonium ion (NH4+) is nonpolar in nature because of its tetrahedral structure. In the NH4+ molecular structure, all the four hydrogen atoms are symmetrically bonded to the nitrogen atom and cancel out the polarity of the N-H bonds, resulting in a nonpolar NH4+ molecule.
| Name of ion | Ammonium ion (NH4+) |
| Bond Angles | approximately 109.5 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of Ammonium ion | Tetrahedral |
| Is Ammonium Ion (NH4+) Polar or Nonpolar? | Non-Polar |
Table of Contents
The polarity of a Molecule
Polar molecules form when the electronegativity of the bound atoms differs. Nonpolar molecules are formed when electrons in a diatomic molecule are shared equally or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other out. Examples of polar molecules include water, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and ethanol. Examples of nonpolar molecules include helium, neon, krypton, and xenon.
Why is NH4+ nonpolar?
The ammonium ion displays a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry as well as a tetrahedral molecular structure.
There are four bonds from the nitrogen atom to the hydrogen atom in NH4+ and no lone pairs. The four high electron density regions arrange themselves so that they point to the corners of a tetrahedron, with the central nitrogen atom in the center. As a result, the electron pair geometry of NH4+ is tetrahedral, and the molecular structure is also tetrahedral.
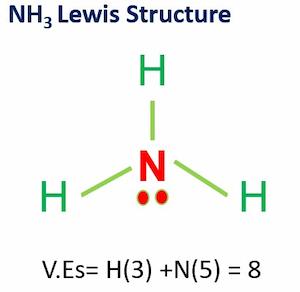
The polarity of Ammonia (NH3)
The electronegativity difference between N (3.04) and H (2.2) causes the polarity of the NH3 molecule.
This mismatch in electronegativity results in three dipole moments in one direction.
As a result, ammonia has a net dipole moment, making it a polar molecule.
In addition, the NH3 Lewis structure shows that there is a lone pair of electrons present in nitrogen.
This exerts an outward force on the bond due to which the shape of NH3 becomes unsymmetrical.
Check the full article “Is NH3 is polar?”.
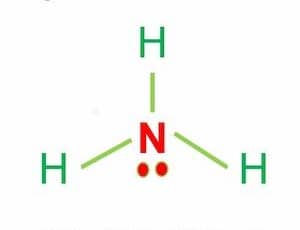
Polarity of H2S
H2S is a slightly polar molecule because of the minor difference in electronegativity values of hydrogen (2.2) and sulfur (2.58) atoms. Furthermore, the existence of two lone pairs on the opposite side of the two hydrogen atoms makes the molecule more polar and causes the H2S molecule to have a bent shape geometrical structure.
Summary
- The answer to the question “is ammonium ion is polar or nonpolar” is ammonium ion is nonpolar in nature
- Ammonium ion (NH4+) is nonpolar in nature because of the tetrahedral structure.
Recommended Video
Related Links
Is O2 Polar or Nonpolar?| Easy Explanation
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Sodium Phosphate – Formula, Structure, Types, and Uses
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Charge of Ammonia (NH3)| Simple Steps
Frequently Asked Question
1. HCL Polar or Nonpolar?
HCl (hydrochloric acid) is a polar molecule. Since chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, it pulls the bonded electron pair closer to it and obtains a partial negative charge, whereas hydrogen gains a partial positive charge. HCl has a dipole moment of 1.03 D.
2. CO2 Polar or Nonpolar?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is nonpolar because of its linear and symmetrical structure. The two oxygen atoms from either direction of the carbon atom pull the electrons equally from both sides. Due to unequal sharing of valence electrons, CO2 is nonpolar in nature.
3. SO2 Polar or Nonpolar?
The gas sulfur dioxide (SO2) has a polar character. It’s a polar molecule because of the electronegativity difference between the sulfur (2.58) and oxygen (3.44) atoms. SO2 has a bent form due to the existence of unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
4. What is the Polar covalent bond?
Polar molecules form when the electronegativity of the connected atoms changes. When electrons are evenly divided between atoms in a diatomic molecule or when polar molecules in a larger molecule cancel each other out, nonpolar molecules arise.
5. What is a hydrogen bond?
A hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a dipole-dipole interaction. It is not an actual chemical bond.
It develops when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a strongly electronegative atom.
(fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen ) exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons.
This type of bond is weaker than an ionic or covalent bond, but it is stronger than van der Waals forces.
6. What is the electronegativity difference?
Electronegativity refers to an atom’s tendency to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond.
The greater the difference between electronegativity values, the more polar the chemical bond formed between them.
7. CH4 polar or nonpolar?
Methane (CH4) is a nonpolar molecule.
8. Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?
SiCl4 (silicon tetrachloride) is a nonpolar molecule. Because the four chemical bonds between silicon and chlorine are uniformly distributed, SiCl4 is non-polar. A polar covalent bond is a type of covalent link that is intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Such bonds occur when the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7.
Check the full article here“Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?”.
9. What is the oxidation number of NH3?
Ammonia is made up of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms (NH3). The NH3 oxidation number is zero because the sum of the individual oxidation values of the atoms nitrogen (oxidation number =-3) and hydrogen (oxidation number =1) is zero.
10. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar compound. In BF3, the central boron atom has sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an unfilled p orbital on the Bron atom and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Because the boron-fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart, any net dipole in that plane is canceled out. Even if each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero because adding the bond vectors cancels everything out.
Check the full article here“Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”.
More Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
HCN Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
SiO2 Lewis Structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
Valence Electrons in Nitrogen
BrF3 (Bromine trifluoride) Molecular Geometry, Bond Angles
Disclaimer
Whatsinsight.org’s blog and everything published on it are provided solely as an information resource. The blog, its authors, and affiliates accept no responsibility for any accident, injury, or damage caused by following the information on this website, in part or in whole. We do not recommend using any chemical without first consulting the manufacturer’s Material Safety Data Sheet and following the safety advice and precautions on the product label.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023