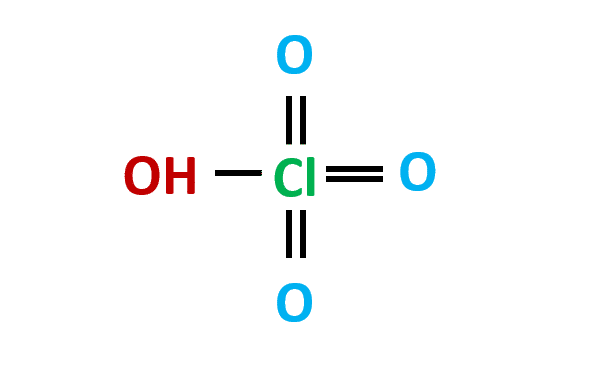
Perchloric acid (HClO4) is a corrosive inorganic liquid. It’s most commonly found as an aqueous solution. Since a cold 70 percent aqueous HClO4 solution is stronger than sulfuric (H2SO4) and nitric acids (HNO3), it is also known as super acid. Keep reading to know more about the properties and lewis structure of HCLO4.
| Name of molecule | Perchloric acid ( HClO4 ) |
| Boiling point | 230 °C |
| Melting point | −19 °C |
| Vapor Pressure | 6.8 mm Hg at 25 °C |
| The molar mass of HClO4 | 100.454 g/mol |
| Shape | Tetrahedral geometry |
| Bond angles | 109.5 degrees |
Table of Contents
Perchloric Acid (HClO4)
Perchloric acid (HCLO4) disassociates readily in water to yield the perchlorate anion.
Its toxicity comes from the toxicity of the perchlorate anion.
HCLO4 is a strong oxidant and reacts violently with combustible and reducing materials, organic materials, and strong bases, causing a fire and explosion hazard.

Step By Step Drawing of Lewis Structure
Four main steps to find lewis’s structure are listed below:
Step-1: Count the valence electrons of atoms
HCLO4 molecule consists of one hydrogen, four oxygen, and one chlorine atom. The electronic configuration of individual atoms is given in Table.
| Atom | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons |
| 1H | 1S1 | 1 |
| 8O | 1S2 2S2 2P4 | 6 |
| 17Cl | 1s22s22p63s23p5 | 7 |
HCLO4 = 1 H atom + 1 Cl atom + 4 O atoms
= 1(1)+1(7)+4(6)
Valence electrons in HCLO4 = 32
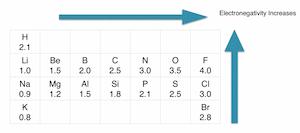
Step-2: Determine the central atom
If we check the proper arrangement of chlorine and oxygen in the periodic table, we will find that chlorine is the least electronegative of both. So chlorine will be the central atom.
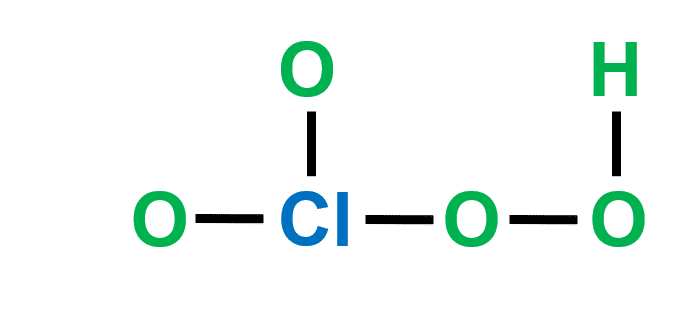
Step-3: Place electron pairs between the atoms
In the figure, one line is equivalent to one electron pair. Out of 32 electrons, 10 will be used in pairs between atoms.
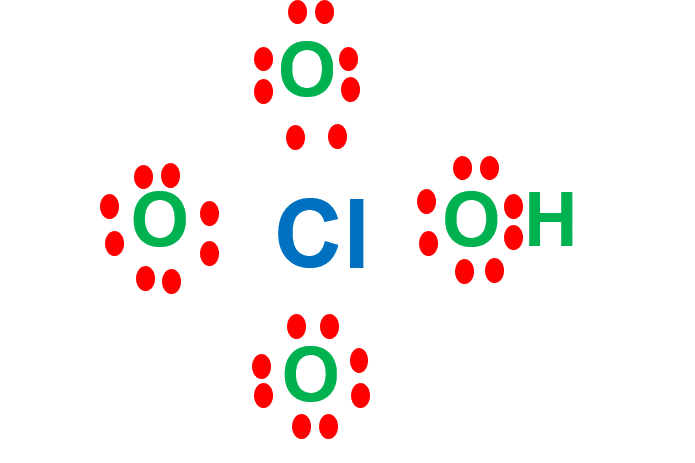
Step 4: Place remaining electrons around the other atoms
We need to distribute the 22 remaining valence electrons. Hydrogen can only contain a maximum of two electrons. Oxygen can contain 8 electrons, so we add more electrons to them to complete the octet (8 electrons).
Chlorine is below period 2 in the periodic table. That means it can have an expanded octet. It can hold more than eight electrons.
Key Points

- Corrosive inorganic liquid.
- Hot concentrated solutions of HCLO4 can be extremely dangerous (explosion hazard, fire hazard).
- HClO4 can react violently at room temperature with cellulose materials (e.g., wood, paper), and oxidizable organic materials (e.g., alcohols, ketones, and aldehydes).
- When heated, HCLO4 can decompose and generate toxic and corrosive fumes.
- It should be handled with extreme care due to its rapid reactivity with organic matrices.
- HCLO4 can be corrosive to the skin. Therefore, it should be handled with care.
Molar Mass of HCLO4
The molar mass of Oxygen =15.9994 g/mol
Hydrogen Atomic mass = 1.00794 g/mol
Atomic mass of Chlorine= 35.453 g/mol
Molar mass of HCLO4 = 1(1.00794)+ 35.453 +4(15.9994)
=100.454 g/mol
Uses Of HCLO4
- HCLO4 is used to separate potassium from sodium in many laboratory tests and industrial processes.
- It is an oxidizing agent, especially in the determination of chromium in steel, ferrochrome, chromite, leather
- It acts as a dehydrating agent, particularly in the determination of silica in iron and steel and in cement and other silicate materials
- Used as a solvent for sulfide ores to determine copper and other metals
Is Perchloric Acid a strong acid?
A cold 70% aqueous HCLO4 solution is considered to be a strong acid or superacid (sulfuric acid and nitric acid but is not necessarily a strong oxidizing agent. However, as the concentration and temperature increase, it behaves as an oxidizing agent.
Is HCLO4 Polar or Nonpolar?
HCLO4 is a polar molecule. The molecule consists of one hydrogen, four oxygen, and one chlorine atom.
All oxygen atoms have double bonds with central chlorine atoms. Therefore, the central Cl atom would have three double bonds with three oxygen atoms and one single bond with OH.
Since oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine atoms, this makes HCLO4 a polar molecule.
Related Links
N2O | Laughing Gas
HCN Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide)
SiO2 Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
Hydrogen Bond| Definition and Easy Explanation
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Oxygen (O2) Polar or Nonpolar?
The oxygen (O2) molecule is nonpolar because it is diatomic and both atoms have similar electronegativity. Both oxygen atoms have equal charges, and there are no partial charges on either atom. As a result, O2 is a nonpolar molecule with a zero dipole moment.
2. Is carbon dioxide Polar or Nonpolar?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is nonpolar due to its linear, symmetrical structure. The two oxygen atoms from either side of the carbon atom pull the electron density equally from both sides. CO2 is nonpolar in nature because there is no uneven sharing of valence electrons.
3. Is Methane (CH4) polar?
Methane (CH4) is a nonpolar molecule. Please check the full article “Is CH4 polar?”.
4. What is the magnesium element?
Magnesium (Mg) is a chemical element with an atomic weight of 24,312 and an atomic number of 12. It belongs to Periodic Table Group IIa. Magnesium is a metallic element with a silvery-white color. It has a relative density of 1740 kg/m3 (0.063 pounds per inch3 or 108.6 pounds per square foot). Because of its low weight and ability to make mechanically robust alloys, it has long been recognized as the lightest structural metal in the industry.
5. What are the characteristics of sulfur trioxide?
SO3 (sulfur trioxide) is a chemical substance. It is available in three forms: gaseous monomer, crystalline trimer, and solid polymer. It is solid at a little below room temperature and has a somewhat narrow liquid range. Gaseous SO3 is the major precursor to acid rain.
6. What is nitric acid?
Nitric acid (HNO3) is a colorless, fuming, and very corrosive liquid that is employed as a laboratory reagent as well as an important industrial chemical in the manufacture of fertilizers and explosives. It is toxic and can result in severe burns.
7. specific heat of air?
The specific heat of air at constant pressure is 1.005 kJ/kg K and the specific heat of air at constant volume is 0.718 kJ/kg K.
The specific heat (C), also called heat capacity, of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise its temperature by one degree.
8. hydrogen ion?
A hydrogen ion is the nucleus of a hydrogen atom that has been detached from its electron. The hydrogen nucleus is made up of a proton, which is a particle with a unit positive electric charge. As a result, the solitary hydrogen ion, indicated by the symbol H+, is widely employed to represent a proton.
9. What is the process of Sublimation?
Sublimation is the process by which a solid turns straight into a gaseous state without first going through the liquid stage. Dry ice is one of several sublimation instances (frozen carbon dioxide). When dry ice is exposed to air, it immediately changes its phase from solid to gaseous (fog).
Vapor deposition is the inverse of sublimation.
10. Briefly define the process of Distillation?
Distillation is the separation of a mixture of liquids based on variations in their boiling points (or volatility). Water may be extracted from a salt solution using this method.
Yes, it is dangerous. It can cause digestive and respiratory tract burns if swallowed.
It can also cause eye and skin burns if exposed to the body. Due to its unstable nature, it can explode easily.
It is a highly corrosive substance and it behaves like other strong mineral acids up to a concentration of 72%. It can cause severe burns on contact with the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes.
More Links
Is Carbon Dioxide a Pure Substance?
Is Chlorine a metal?
Electron Configuration for Calcium
Valence Electrons in Nitrogen
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Delocalized pi bond
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023