The vast majority of hydrogen atoms have no neutrons; these atoms are the lightest possible since they only have one electron and one proton. Rare hydrogen isotopes such as deuterium and tritium, on the other hand, do have neutrons. Tritium, which is unstable and not found in nature, has two neutrons. Keep reading to know the answer “How many neutrons does hydrogen have?”
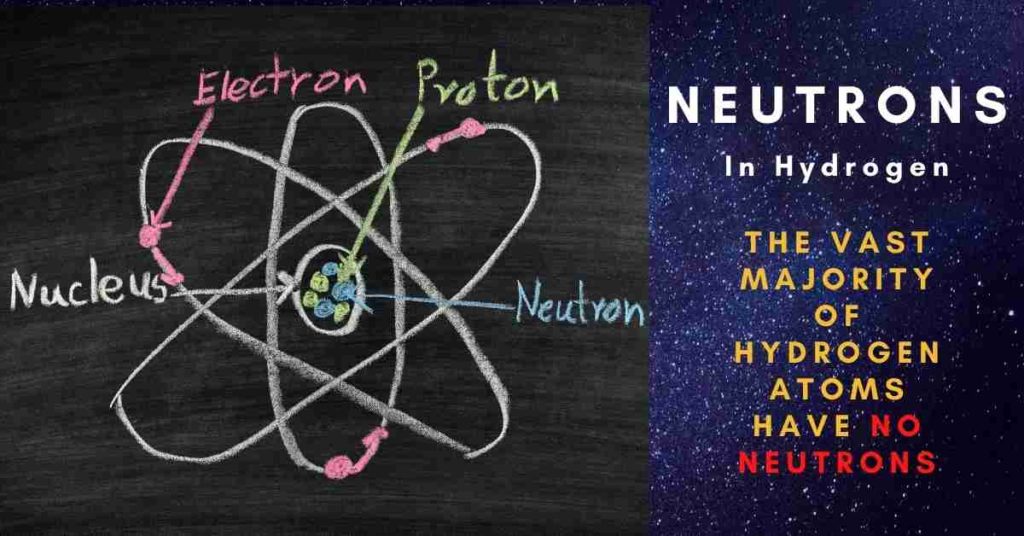
Table of Contents
Hydrogen atom-Key Points
- Most abundant element in the universe.
- Much more often it is combined with oxygen, carbon, and other elements in chemical compounds.
- Water, for example, is hydrogen joined with oxygen.
- Hydrogen plays an important role in hydrocarbons, such as oils, sugars, alcohols, and other organic substances.
- Hydrogen also serves as a “green” energy source; when burned in the air; it gives off heat and pure water without producing CO2 or other harmful emissions (Read more about greenhouse gases).
Protium Deuterium & Tritium
Protium
Protium is the name given to the most basic hydrogen atom, which consists of a single proton surrounded by a single electron.
An atom with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons is called an isotope of that element. The letter H stands for protium, which is the normal form of hydrogen. Protium is a one-proton element with no neutrons.
Deuterium
Deuterium, commonly known as “heavy hydrogen,” is found in nature but is rare, accounting for just one out of every 6,420 hydrogen atoms. It, like hydrogen, reacts with oxygen to form “heavy water,” a material that resembles regular water in appearance and behavior but is somewhat heavier and has a higher freezing point of 3.8 degrees Celsius (38.4 degrees Fahrenheit). It contains one neutron.
Tritium
Tritium is radioactive due to the extra two neutrons it contains, having a half-life of 12.28 years. Tritium must be produced in nuclear reactors since there is no natural source. Tritium can be useful in tiny doses and with proper handling and storage, despite its radiation being relatively dangerous (Check Arrhenius equation to know more about chemical reactions and the effect of temperature)
Properties of H
Hydrogen is a nontoxic, nonmetallic, odorless, tasteless, colorless, and highly flammable diatomic gas having the molecular formula H2 at normal temperature and pressure. Hydrogen may also be found in chemical substances like hydrocarbons and water on Earth.
Neutral hydrogen atom
A typical hydrogen atom with one proton and one electron is known as neutral hydrogen. It’s known as HI (pronounced H-one) and may be found in HI clouds across galaxies or as part of the intercloud gas outside of galaxies (Read more about hydrogen bond).
H2 lewis Structure
The simplest example of a covalent bond is the diatomic hydrogen molecule (H2), represented in Lewis structures: The shared pair of electrons gives each hydrogen atom with two electrons in its valence shell (1s) orbital. It possesses the electron configuration of the noble gas helium in several ways.
Hydrogen Oxide
The diatomic anion hydrogen oxide (Hydroxide) has the chemical formula OH. It is composed of oxygen and hydrogen atoms joined by a single covalent bond and have a negative electric charge. It is a significant but in most cases minor component of water.
Summary
- The answer to the question “How many neutrons does hydrogen have” is zero
- Natural hydrogen is a simple atom with one proton, one electron, and no neutron.
- Deuterium or heavy hydrogen contains one neutron
- Tritium contains two neutrons
- Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the nature
Related Topics
How many electrons does Helium have?
What is the Molar Mass of Nitrogen?
Polar Versus Nonpolar Molecules
Hydrogen Ion | Definition, Charge & Formula
Is Hydrogen a Metal?
Sodium Hydrogen Sulfate
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Charge of an electron?
The fundamental scientific constant representing the naturally occurring unit of electric charge, the electron charge (symbol e), is equal to 1.602176634 x 10-19 coulomb. (Check the electric field topic to know more about electric charge)
2. Mass of an electron?
The electron has a rest mass of 9.1093837015 x 10-31 kg, which is only 1/1,836 that of a proton.
3. What is the atomic number?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. For instance, a hydrogen atom has one proton and an atomic number of one. Carbon atoms, on the other hand, have six protons and an atomic number of 6.
4. Isotope definition?
Isotope: one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table, but different atomic weights and physical characteristics. There are one or more isotopes for every chemical element.
5. how many neutrons does aluminum have?
There are 14 neutrons in aluminum. Aluminum has an atomic number of 13 and is a metal.
6. how many neutrons does chlorine have?
Chlorine is usually an element with 17 protons. The mass numbers of an element, on the other hand, can change, implying that it can contain varying amounts of neutrons. So, while chlorine has a mass number of 35, indicating 18 neutrons, it may also have a mass number of 37, indicating 20 neutrons.
7. Magnesium protons neutrons electrons?
There are 12 protons, 12 neutrons, and 12 electrons in the most frequent and stable form of magnesium atom found in nature (which have a negative charge). Read another interesting topic Is MgCl2 Ionic or Covalent?
8. Which subatomic particle has the least mass?
The electron has the lowest mass of the three subatomic particles. An electron has a mass of 1/1840 of an atomic mass unit (amu).
9. Mass of hydrogen atom in grams?
The weight of 1 atom of hydrogen is calculated as 1.66058 × 10-24 grams.
10. What is heavy water?
Heavy water (D2O), also known as deuterium oxide, is water made up of deuterium, a hydrogen isotope with twice the mass of ordinary hydrogen, and oxygen. Heavy water is used in nuclear power plants as a neutron moderator.
More Interesting Topics
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
Perchloric Acid| Is It Super Acid?
Sulfurous Acid Formula & Lewis Structure
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Electric Field Units & Definition
Mass Vs Weight| 5 Easy Examples
Hydrogen Phosphate Formula
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023