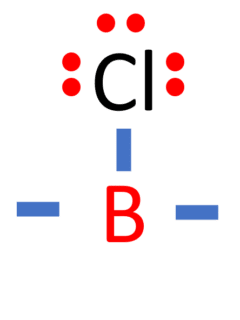
Boron trichloride, commonly abbreviated as BCl3 or BCl₃, is a chemical compound composed of boron (B) and three chlorine (Cl) atoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the Lewis structure of BCl3 and delve into its molecular shape, bond characteristics, electronegativity, bond angles, and other key properties. Name of Molecule Boron trichloride (BCl₃) Bond …
Lewis Structure
Delve into our in-depth exploration of Lewis structures, which elucidate the spatial arrangement of atoms and the distribution of valence electrons in molecules and compounds. Tailored for the discerning science enthusiast, our articles provide nuanced insights into electron configurations, covalent bonding, and resonance structures. Engage with advanced perspectives on the pivotal role of Lewis structures in molecular chemistry.
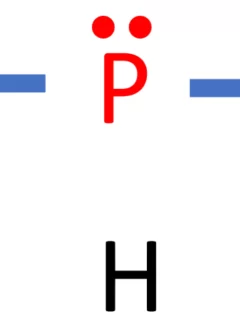
Phosphine, represented as PH3 or PH₃, is a chemical compound composed of one phosphorus (P) atom bonded to three hydrogen (H) atoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the Lewis structure of PH3 and delve into its molecular shape, bond characteristics, properties, and its significance in the field of chemistry. Name of Molecule PH₃ …
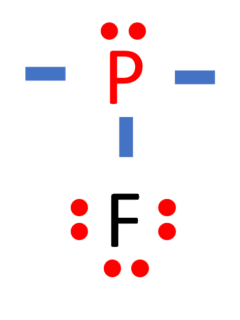
Phosphorus trifluoride, often abbreviated as PF3 or PF₃, is a chemical compound composed of phosphorus (P) and three fluorine (F) atoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the Lewis structure of PF3 and delve into its molecular shape, bond characteristics, electronegativity, bond angles, and other key properties. Name of Molecule Phosphorus Trifluoride (PF₃) Bond …
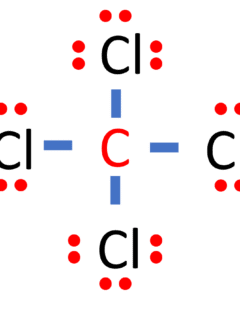
Carbon tetrachloride, often abbreviated as CCl4 or CCl₄, is a chemical compound composed of one carbon (C) atom bonded to four chlorine (Cl) atoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the Lewis structure of CCl4 and delve into its molecular shape, bond characteristics, properties, historical uses, and environmental considerations. Name of Molecule Carbon Tetrachloride …
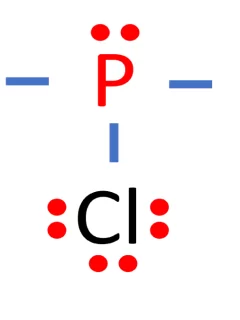
Phosphorus trichloride, often abbreviated as PCl3 or PCl₃, is a chemical compound composed of phosphorus (P) and chlorine (Cl) atoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the Lewis structure of PCl3 and delve into its molecular shape, bond characteristics, polarity, and hybridization. Name of Molecule Phosphorus Trichloride (PCl3) Bond Angles approx. 109.5 degrees Molecular …
Carbon disulfide, often denoted as CS2 or CS₂, is a chemical compound consisting of carbon (C) and sulfur (S) atoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the Lewis structure of CS2 in four simple steps and delve into its molecular shape, bond characteristics, polarity, and hybridization. Name of Molecule Carbon Disulfide Bond Angles 180 …
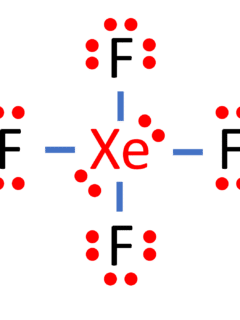
Xenon Tetrafluoride, represented as XeF4, is a fascinating chemical compound that has garnered significant attention in the world of chemistry due to its intriguing molecular structure and unique properties. In this article, we will embark on an in-depth exploration of the Lewis structure of XeF4, discussing its valence electrons, molecular geometry, hybridization, and polarity. Formula …
Lewis structures, also known as Lewis-dot diagrams, show the bonding interactions between atoms in a molecule and lone pairs of electrons in the molecule. Lewis structures can also be used to predict molecular geometry when combined with hybrid orbitals.This article explains the Lewis structure of hydrogen (H2) and the Lewis structure of water (H2O). Lewis …
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is a poisonous, odorless, and colorless gas. When exposed to moist air, it emits a strong odor and produces white vapors. When breathed, boron trifluoride is extremely poisonous. BF3 Lewis structure comprises two different atoms: Boron, and Fluorine and is a nonpolar molecule with bond angles of 120 degrees. Boron trifluoride is …
Sulfur difluoride (SF2) is a highly unstable inorganic compound. SF2 lewis structure comprises one Sulfur Atom and two Fluoride atoms. It is a polar molecule with bond angles of 98 degrees. Name of molecule Sulfur difluoride (SF2) Other names sulfur difluoride, sulphur(II) fluoridesulfur difluoride, sulfur fluoridesulfur(II) fluoride, sulfur fluoride Bond Angles 98 degrees Molecular Geometry …
Chlorine trifluoride (ClF3) is a colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas. ClF3 is a polar molecule due to its asymmetrical structure and the existence of two lone pair electrons, which results in an uneven distribution of charge, making it polar in nature. Keep reading to learn more about clF3 polarity, bond angle, and molecular shape. …
Ozone (O3) is a gas that is naturally present in our atmosphere and is a highly reactive gas. Ozone is a very strong oxidizing agent and is highly unstable at higher concentrations. At high concentrations, ozone is decayed into diatomic oxygen. O3 Lewis structure shows that the ozone molecule contains three oxygen atoms bound together …
Sulfur Tetrafluoride (SF4) is a colourless corrosive gas used to synthesize several organofluorine compounds. SF4 lewis structure comprises one sulfur and four fluorine atoms. The central sulfur atom is linked to four fluorine atoms and contains one lone pair.SF4 is a dangerous substance that is frequently utilized in chemical and pharmaceutical businesses. It has trigonal …
Methane (CH4) is a colorless, odorless, and highly combustible gas that is utilized to generate energy and heat houses all over the world. The CH4 Lewis structure comprises two different atoms: carbon and hydrogen. It is a nonpolar molecule with a bond angle of 109.5°. CH4 is utilized in chemical processes to create other essential …
Nitrogen (N2) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas and is the most abundant element in Earth’s atmosphere. The N2 Lewis structure would comprise two nitrogen (N) atoms bonded together by a triple bond. Each nitrogen atom is surrounded by a lone pair of electrons. Name of molecule Nitrogen Bond Angles 180 degrees Molecular Geometry of …