Ionic compounds are made up of ions, which are charged particles formed when an atom (or group of atoms) acquires or loses electrons. (A cation is a positively charged ion, while an anion is a negatively charged ion.) Covalent or molecular compounds, on the other hand, form when elements share electrons in a covalent bond to form molecules.
Table salt (sodium chloride) with the formula NaCl is an example of an ionic compound. The sodium atom in this compound loses an electron to become Na+(cation), while the chlorine atom gains an electron to become Cl– (anion).
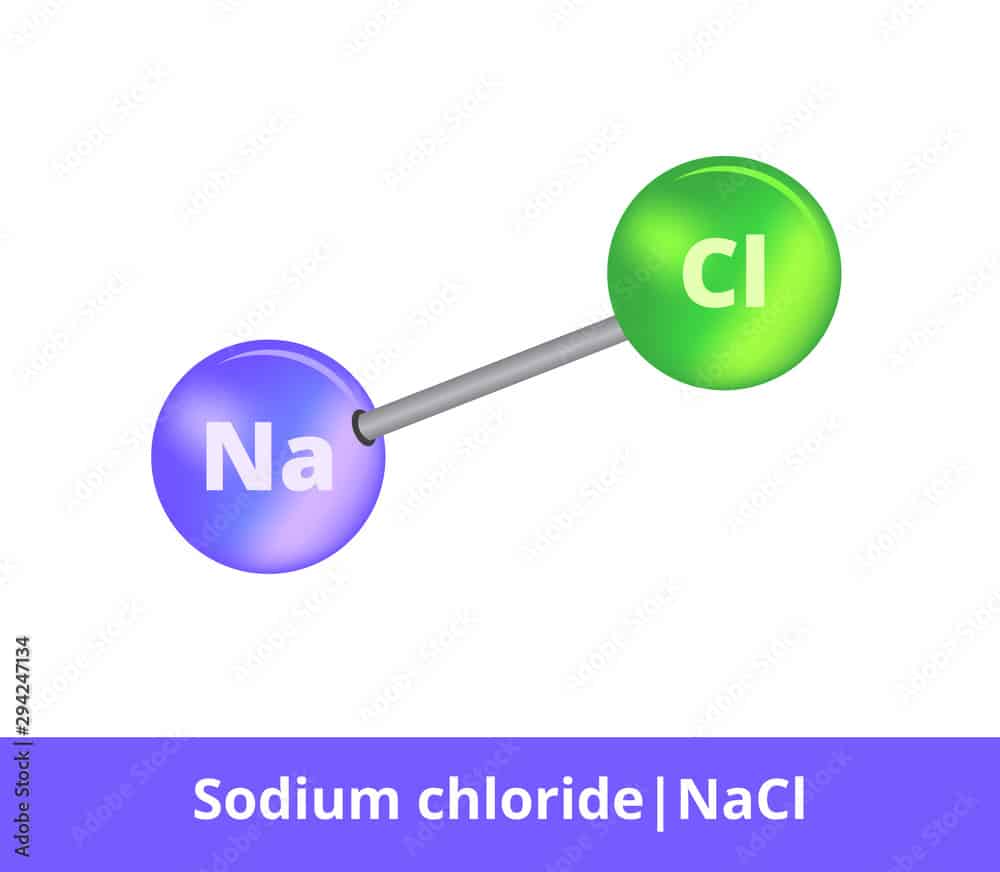
Table of Contents
Ionic Compounds Formation
Ionic compounds are formed by a process known as electron transfer, in which one atom transfers electrons to another. An atom of one element loses one or more electrons during electron transfer, and an atom of another element gains those electrons. Both atoms are involved in the electron transfer from ions. The atom that gains electrons changes into a negatively charged anion, while the atom that loses electrons changes into a positively charged cation. An ionic bond is a bond between such oppositely charged ions which attract and cancel each other’s charges to form neutral compounds.
NaCl Bond Formation
In Sodium chloride (NaCl) bond formation, an electron is transferred from a sodium atom to a chlorine atom. Sodium loses one electron during this process to become a positive Na+ cation, while chlorine gains an electron to become a Cl– anion. Electrostatic forces then bond the Na+ ion to the Cl– ion. The sodium’s 1+ charge is balanced by the chlorine’s 1– charge. The sodium chloride (NaCl) compound formed as a result is neutrally charged.
MgCl2 Bond Formation
In Magnesium chloride (MgCl2), each magnesium atom can lose two electrons and each chlorine atom can only gain one, magnesium must transfer its two electrons to two chlorine atoms in Magnesium chloride (MgCl2). Following that, two chloride anions bond with the magnesium cation (Mg2+) (Cl–).
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds are solids that are difficult to break apart due to the strong attraction between the positive and negative ions. However, when pressed, ionic compounds break into pieces. As a result, they are brittle.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points as a large amount of energy is required to break the ionic bonds between the atoms.
- Ionic compounds are generally soluble in polar solvents like water, but their solubility decreases in nonpolar solvents like petrol, gasoline, and so on.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state because ion movement is not possible. In a molten state, however, they are good conductors because electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions are overcome by the heat released.
| Ionic Compounds | Covalent Compounds |
| crystalline solids | usually liquids or gases. |
| high melting points and boiling points. | usually low melting points and boiling points. |
| conduct electricity when dissolved n water or melted. | do not conduct electricity |
| usually soluble in water | usually insoluble in water (except, glucose, sugar, urea, etc.) |
| insoluble in organic solvents (like alcohol, ether, acetone, etc.). | soluble in organic solvents |
Summary
Ionic compounds are made up of ions, which are charged particles that form when an atom (or group of atoms) acquires or loses electrons. (A cation is a positively charged ion, whereas an anion is a negatively charged ion.)
Related Links
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
SiO2 Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
NH3 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Is HCl Polar or Nonpolar?
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a sigma bond?
In chemistry, sigma bonds (bonds) are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond. Atomic orbitals colliding head-on produce them. The symbol for a sigma bond is σ
Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds because the relevant orbitals are directly overlapping. Electrons are the electrons that are involved in forming a connection.
Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds because the relevant orbitals are directly overlapping. The electrons that are involved in a bond are known as electrons.
2. What is Sodium Sulfate?
The sodium salt of sulfuric acid is sodium sulfate. It has the formula Na2SO4 and is an inorganic chemical.
It is mostly utilized in the production of detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping. It exists in all forms as white solids that are very water-soluble. With an annual output of 6 million tonnes, decahydrate is an important commodity chemical product.
3. What is sulfur electronic configuration?
Sulfur electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
4. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
5. What is Sulfur hexafluoride?
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a non-toxic gas that is used in a variety of applications due to its inert properties. While SF6 is non-toxic when used properly, toxic byproducts can be produced during electrical discharges within SF6-filled equipment, posing a threat to the health of workers who come into contact with them.
6. What is Sulfur trioxide?
SO3 (sulfur trioxide) is a chemical compound. It is available in three forms: gaseous monomer, crystalline trimer, and solid polymer. It is solid at just below room temperature and has a relatively narrow liquid range. Gaseous SO3 is the primary precursor to acid rain.
7. What are ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds are formed by a process known as electron transfer, in which one atom transfers electrons to another. An atom of one element loses one or more electrons during electron transfer, and an atom of another element gains those electrons. Both atoms are involved in the electron transfer from ions.
8. What is convection in the atmosphere?
Convection in the atmosphere is frequently seen in our weather system. As the sun heats the Earth’s surface, the air above it warms and rises. If the conditions are favorable, this air can continue to rise, cooling and producing Cumulus clouds.
9. What is the process of distillation?
Distillation is the separation of a mixture of liquids based on variations in their boiling points (or volatility). Water may be extracted from a salt solution using this method.
10. What is the combustion process?
Combustion is a chemical process in which heat and light are produced. The most common sort of combustion is fire.
11. What is Xenon Tetrafluoride (XeF4)?
Xenon tetrafluoride (XeF4) is a colorless/white crystalline chemical. It’s made up of xenon (a noble gas) and fluoride (a naturally occurring mineral). Trace metals that contaminate silicone rubber can be detected and analyzed using XeF4.
12. What is titanium and what is its electronic configuration?
Titanium is an atomic element with the symbol Ti and the atomic number 22. Titanium metal is a particularly durable metal for engineering applications due to its corrosion resistance, as well as its exceptional strength and low weight. It is 40% lighter than steel while maintaining the same strength as high-strength steel. The electron configuration of titanium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2. Check another article “is titanium magnetic?”.
13. is aluminum conductive?
Aluminum is a metal with high electrical conductivity. Despite having just 60% the conductivity of copper by volume, one pound of aluminum has the electrical current-carrying capability of two pounds of copper by weight. Aluminum is a common material used to make satellite dishes. For details, please check the full article “is aluminum conductive?”.
14. What is the oxygen gas formula?
The oxygen formula is O2. Oxygen is a diatomic, colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with 180-degree bond angles. The Oxygen formula comprises two oxygen atoms connected in a pair.
15. Oxalic acid formula?
Oxalic acid is classified as a bi-carboxylic acid (IUPAC name: ethanedioic acid, formula H2C2O4). Because of the combination of two carboxyl groups, it is one of the most powerful organic acids. Oxalates are oxalic acid anions, as well as their salts and esters.
16. What is Aluminium chloride?
Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) is a crystalline chemical compound that is white or yellow in color.
Aluminum oxide and hydrochloric acid are combined to create it. Its anhydrous form can also be produced by reacting with aluminum and chlorine.
17. Is Neon a noble gas?
Neon is a noble gas at normal temperature. Under normal conditions, it has roughly two-thirds the density of air and is colorless, odorless, inert, and monatomic gas.
More Links
Cathode| Component of Cells and Batteries
Wavelength| Simple Definition and Examples
Physical Weathering| Short Overview
Is Ammonium Ion (NH4+) Polar or Nonpolar?
SO2 Ionic or Covalent?| Simple Explanation
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023