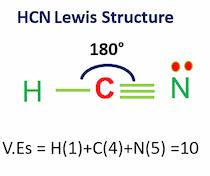
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) is a polar molecule due to a large electronegativity difference between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms across the linear molecule. The molecule is made up of two polar bonds with opposite polarities. As a result, one end of the molecule has a partial positive charge and the other end has a partial negative charge. Keep reading to find out more about the question “Is HCN a polar or nonpolar molecule?”.
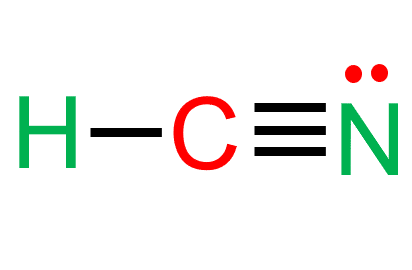
| Name of molecule | Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) |
| Bond Angles | 180 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry | Linear |
| Hybridization | sp hybridization |
| No Valence Electrons in the molecule | 10 |
| Polarity of HCN | Polar molecule |
| Properties | colorless, flammable, and poisonous liquid |
Table of Contents
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar?
HCN is a polar molecule.
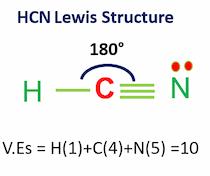
As can be seen from the HCN Lewis structure, the electronegativity difference between nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) makes it a polar molecule.
The difference in electronegativity between atoms is directly proportional to the polarity of the molecule.
Carbon is in the center, surrounded by nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
Carbon and hydrogen share electrons to form a covalent bond.
Whereas carbon and nitrogen form a triple bond to share three electrons.
This results in unequal charge sharing in the linear-shaped HCN molecule and a non-zero dipole moment.
The nitrogen gains a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen gains a partial positive charge.
As a result, positive and negative poles are formed across the molecule, and HCN becomes a polar molecule.
Properties of Hydrogen Cyanide
- colorless and extremely flammable.
- It is very poisonous in gaseous form.
- density = 2.648 g/cm3
- The molar mass is 27.03 g/mol.
- In the HCN Lewis structure, there is a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen and a single bond between C and H.
What is Polarity?
Polarity is caused by the distribution of electrical charge across the atoms connected by the bond.
It has been discovered, for example, that bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent. For example, if we analyze Hydrogen chloride (HCL) intermolecular forces, the hydrogen atom is slightly positively charged, whereas the chlorine atom is slightly negatively charged. Check the full article here: “Is HCL polar or nonpolar?”. The presence of minor electrical charges on dissimilar atoms is referred to as “partial charges,” and the presence of partial charges indicates the presence of a polar bond.
Examples of polar molecules
Some examples of polar molecules are Water (H2O), Ethanol, Ammonia, and SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide).
The polarity of water molecules
Water is another example of a polar molecule.
The molecule consists of two H atoms and one oxygen atom.
The difference in electronegativity is 1.2 for each of the H-O bonds.
Since oxygen is the more electronegative atom, it exerts a greater pull on the shared electrons.
Oxygen also has two lone pairs of electrons. This develops a dipole moment in the water molecules.
Please refer to the full article, “Why water is a polar molecule?”.
Polarity of CO2
Carbon dioxide is a nonpolar molecule that contains polar bonds.
CO2 is a linear molecule and the C=O bonds are polar bonds.
The central carbon has a net positive charge, whereas the outer two oxygens have a net negative charge.
Due to the linearity of the carbon dioxide molecule, these two bond dipoles cancel each other out.
As a result, the molecule as a whole lacks a dipole.
Check the full article here“is CO2 polar or nonpolar?”.
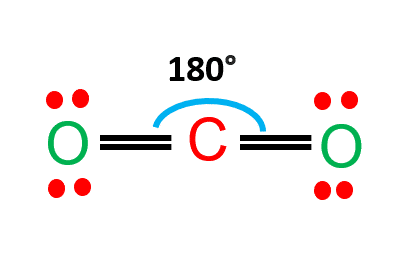
CO2 lewis’s structure shows CO2 is made up of two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom that are covalently bonded together. Two oxygen atoms are found on the sides of a carbon atom, where they share electrons and form bonds. Because it is the least electronegative atom in the molecule, the carbon atom is in the center.
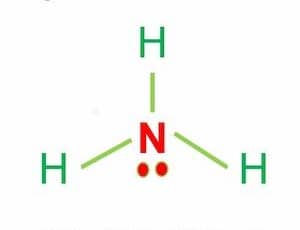
The polarity of Ammonia (NH3)
The polarity of the NH3 molecule is due to the electronegativity difference between N (3.04) and H (2.2).
This electronegativity difference causes three dipole moments in one direction.
This results in a net dipole moment that makes ammonia a polar molecule.
In addition, the NH3 Lewis structure shows that there is a lone pair of electrons present in nitrogen.
This exerts an outward force on the bond due to which the shape of NH3 becomes unsymmetrical.
Check the full article here“Is NH3 polar or nonpolar?”.
Uses of HCN
- Hydrogen cyanide is used in the preparation of acrylonitrile, which is used in the production of acrylic fibers, synthetic rubber, and plastics.
- Hydrogen cyanide and its compounds are used for many chemical processes, including fumigation, the case hardening of iron and steel, electroplating, and the concentration of ores.
- Hydrogen cyanide is an excellent solvent for many salts, but it is not widely used as a solvent because of its toxicity.
Molar Mass of HCN
Molar mass of Hydrogen = 1.00794 g/mol
Carbon molar mass = 12.011 g/mol
Molar mass of nitrogen = 14.0067 g/mol
The HCN molar mass is 27.026 g/mol.
Hydrogen Cyanide Effects
HCN can have a particularly negative impact on organ systems that are most sensitive to low oxygen level, such as the central nervous system (brain), the cardiovascular system (heart and blood vessels), and the pulmonary system (lungs).
HCN Molecular Geometry
Hydrogen cyanide has a linear molecular geometry with 180-degree bond angles.
Because hydrogen and nitrogen are usually far apart, HCN takes on a linear shape.
Because of its electronegative value, nitrogen tries to pull electrons to itself, making it slightly polar.
As a result of these differences, as the vector moves from hydrogen to nitrogen, hydrogen will have slightly positive charges and nitrogen will have slightly negative charges.
As a result, the nitrogen atom becomes a negative pole and the hydrogen atom becomes a positive pole, resulting in a polar molecular structure.
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In the HCN lewis structure, carbon forms one single bond with the hydrogen atom and a triple bond with the nitrogen atom.
- HCN is a polar molecule with linear geometry.
- The bond angle is 180 degrees and there are 10 valence electrons.
- Exposure to Hydrogen cyanide can be dangerous.
Related Links
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
SiO2 Lewis Structure
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
Is HCl Polar or Nonpolar?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below
1. Why Hydrogen Cyanide is polar?
In hydrogen cyanide, carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, hydrogen’s electronegativity is 2.1, and nitrogen has an electronegativity of 3. Any molecule that has a difference in electronegativities of any dipole moment is considered polar. Therefore, HCN is a polar molecule.
2. What is hydrocyanic acid?
A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water is called hydrocyanic acid.
3. How to draw Lewis’s structure of oxygen?
In the O2 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between two oxygen atoms.
Oxygen is a diatomic nonpolar molecule with a bond angle of 180 degrees.
In its molecule, both oxygen atoms have the same electronegativity value, both atoms share equal ratios of bonded shared electrons, and the overall O2 molecule turns out to be nonpolar.
4. What is the dot structure of hydrogen sulfide?
On both sides of the central sulfur atom in the H2S Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms.
The molecule bends due to the existence of two unbonded pairs of electrons.
The molecule is slightly polar because sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen.
In the case of H2S, the vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments results in a non-zero total dipole moment. As a result, dipole-dipole interactions are observed in hydrogen sulfide.
5. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
6. Is HCN an ionic compound?
HCN is not an ionic compound, in fact, it is covalent in nature.
HCN has a triple covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen, consisting of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
7. Is hydrogen cyanide a product of combustion?
Various quantities of hydrogen cyanide can be found in the combustion of carbon and nitrogen-based compounds. When commercial items composed of materials like wool, paper, cotton, silk, and plastics are burned, they can release HCN.
8. What is hydrogen phosphate used for?
In the form of salts, sodium hydrogen phosphate is used as a food additive and an acid regulator in the food industry.
9. What is liquid nitrogen used for?
Liquid nitrogen is used in applications where a substance needs to be protected from oxidation or combustion by atmospheric air, or contamination by moisture.
More Links
Viscosity| Definition, Types, Formula, Examples
Cathode| Component of Cells and Batteries
Is O2 Polar or Nonpolar?| Easy Explanation
What is the Specific Heat of Air?
Density of Oxygen
BF3 Lewis structure| Molecular geometry, Hybridization
Is NH3 Polar or Nonpolar?| Simple Answer
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023