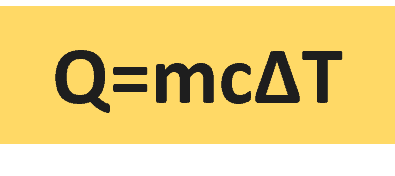The specific heat of air at constant pressure is 1.005 kJ/kg K and the specific heat of air at constant volume is 0.718 kJ/kg K.
The specific heat (C), also called heat capacity, of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise its temperature by one degree. In a constant pressure (ΔP = 0) system, isobaric-specific heat (cp) is applied to air. In a constant volume system (ΔV = 0), isochoric specific heat (cv) is used for air.

The specific heat of a gas is the amount of energy required to raise its temperature by one degree. Due to the fact that the amount varies according to the process used to raise the temperature, there is a specific heat (cv) coefficient for a constant volume process and a different coefficient for a constant pressure process (cp). The ratio of these coefficients is denoted by the Greek letter gamma and can be found in a large number of thermodynamic equations.
| Specific heat definition | The amount of heat required to increase the temperature of the one-kilogram mass of a substance by one Kelvin temperature is referred to as specific heat (cp). |
| Specific heat of air constant pressure | 1.005 kJ kg-1 K-1 |
| Specific heat of air constant volume | 0.718 kJ kg-1 K-1 |
| Specific heat of water | 4.179 kJ kg-1 K-1 |
Table of Contents
Specific Heat Formula and Units
Consider the temperature of a body of mass “m” changing by ΔT. The amount of heat (Q) absorbed or released by a body is proportional to its mass and change in temperature.
Q ∝ mass of the body (m).. (1)
Q ∝ change in temperature (T)………. (2)
Combining equation 1 and equation 2
Q ∝ mΔT ⇒ Q = c.m.ΔT
c = Q/m.ΔT ( c is specific heat or heat capacity with units of kJ/kg K)
Where c is the constant of proportionality, it depends on the nature of the substance.
The specific heat of a gas is the amount of energy required to raise its temperature by one degree. Due to the fact that the amount varies according to the process used to raise the temperature, there is a specific heat (cv) coefficient for a constant volume process and a different coefficient for a constant pressure process (cp). The ratio of these coefficients is denoted by the Greek letter gamma and can be found in a large number of thermodynamic equations.
Important Points
- The pressure (p) of a gas equals the perpendicular (normal) force exerted by the gas divided by the surface area on which the force is exerted.
- The temperature (T) of a gas is a measure of the kinetic energy of the gas.
- The sum of the masses of all the molecules is equal to the mass of the gas.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Specific heat of the air in Btu?
The specific heat for dry air (at sea level) is 0.2402 Btu/lbF at -100F and 0.242 Btu/lbF at 250F [reference].
2. Specific heat of air at constant volume?
The specific heat of air at constant volume is 0.718 kJ/kg K
3. What is specific heat formula?
Specific heat (cp) or specific heat capacity refers to the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram mass of a substance by one Kelvin temperature.
The Specific heat formula is Q/m ΔT = cp where Q refers to the amount of heat supplied to the specimen and ΔT is the rise in temperature.
The value of cp depends on the nature of the substance.
4. What is a PV diagram?
The pressure-volume diagram (abbreviated as the PV diagram) is a graphical depiction of pressure variations with respect to volume in a closed system. P-V diagrams can be used to determine a system’s efficiency and the work done by a system or on a system.
5. Solar thermal power plant?
A solar thermal power plant absorbs and concentrates sunlight to generate the high-temperature heat necessary to generate electricity. In a traditional solar thermal power plant, reflectors (mirrors) capture and focus sunlight onto a receiver.
6. Ideal gas law?
Ideal gas law states that the pressure of gas times its volume equals the number of moles of the gas times a constant (R) times the temperature of the gas. The ideal gas law is quite an important statement of the gas laws since it relates the quantity of gas (moles) to its pressure, volume, and temperature.
7. alternate fuel vehicles?
An alternative fuel vehicle (AFV) is a vehicle that operates on fuels other than gasoline and diesel. Alternative fuels are obtained from non-petroleum sources.
8. Conduction in physics?
Conduction in physics refers to the transfer of energy that occurs via the movement of particles in contact with one another.
9. Carbon footprint?
A carbon footprint, also known as a CO2 footprint, is the total quantity of greenhouse gases (including carbon dioxide and methane) emissions created as a result of an individual’s actions over a specific time period, usually a year.
10. Definition of metal?
Metals are substances with characteristics such as malleability, ductility, conductivity, brilliance, – and solidity.
More Links
Combustion Reactions
Sublimation Examples| Process & Case Study
Distillation| Principles, and Processes
Hydrogen Molar Mass
Hydrogen Ion | Definition, Charge & Formula
Is Hydrogen a Metal?
Gauge Pressure Formula
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023