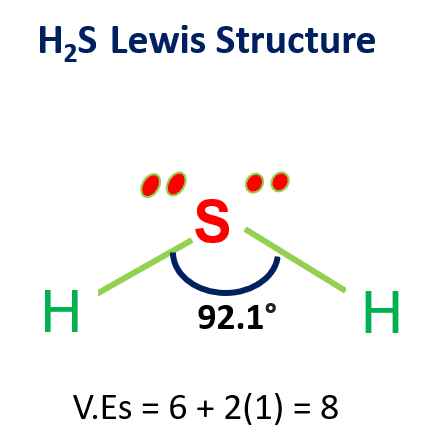
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a colorless toxic gas. In its Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms on both sides of the central sulfur atom. Around the sulfur atom, there are also two lone pairs. H2S forms hydro-sulfuric acid when dissolved in water.
| Name of molecule | Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) |
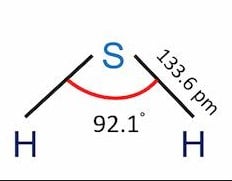
| Bond Angles | 92.1° |
| Molecular Geometry of Hydrogen sulfide | Bent shape |
| Molar mass | 34.1 g/mol |
| Valence electrons | 8 |
Table of Contents
Step by Step Construction of H2s Lewis Structure
The following are the steps to constructing the Lewis Structure:
Step-1: Count the valence electrons of atoms.
To draw the Lewis structure, we need to figure out the number of valence electrons in individual atoms as shown in the table below.
| Atom | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons (VEs) |
| 16S | 1s22s22p63s23p4 | 6 |
| 1H | 1s1 | 1 |
Valence electrons in H2S= VEs in hydrogen + VEs in sulfur
VEs = 2(1)+6
H2S valence electrons = 8 electrons
Step-2: Determine the central atom
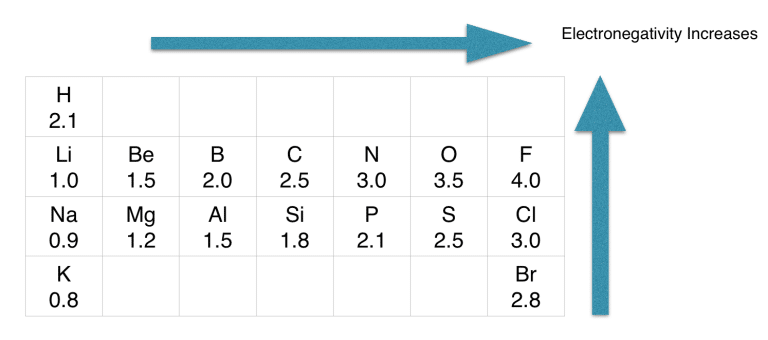
If we compare the electronegativity values of H and S in the periodic table, we will find that the electronegativity value of hydrogen is the least.
As per the rule, hydrogen should be at the center of the structure, but H cannot serve as a central atom in a Lewis structure.
Hydrogen (1s1) only needs one electron to complete its valence shells. Thus, it can only bond to one other atom, and it does not have d orbitals available to expand its valence shells.
Therefore, in the H2S Lewis structure, sulfur comes in the middle and arranges valence electrons around it.
Next, place two hydrogen atoms on both sides of the central sulfur atom.
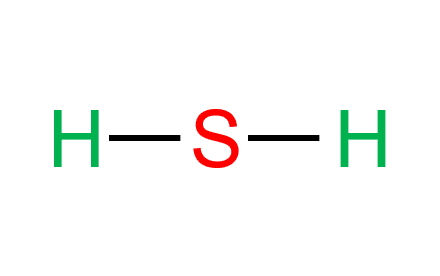
Step-3: Place electron pairs between the atoms
Sulfur donates electrons to both the neighboring hydrogen atoms to make hydrogen stable. Two out of six valence electrons participate in bond formation. Each line in the figure shows a single bond.
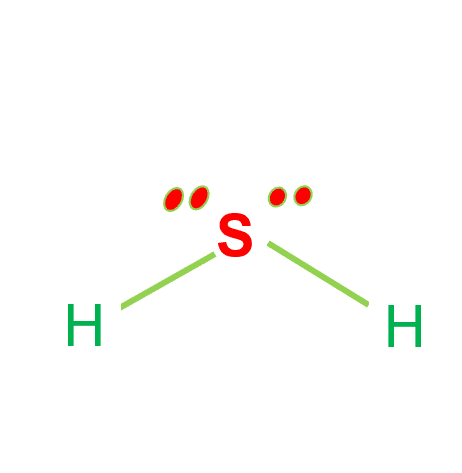
Step-4: Place remaining electrons around the other atoms
The remaining four electrons are lone pairs of electrons and are hence displayed as dots near the sulfur atom. In total, there are two non-bonding electrons in this compound, and hydrogen atoms have a complete valence shell.
H2S Molecular Geometry
The hybridization of the H2S molecule is sp3; the sulfur atom is in the center bonded with two hydrogen atoms, forming a bond angle of fewer than 180 degrees.
The presence of two unbonded pairs of electrons makes the molecule bend.
Since sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen, this makes the molecule slightly polar.
The vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments in H2S produces a non-zero total dipole moment.
As a result, Hydrogen sulfide shows dipole-dipole interactions.
H2S Lewis Structure- Key Points
- Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless toxic gas.
- It emanates from sewers and is a by-product of industrial processes.
- In low concentrations, it smells like rotten eggs.
- soluble in water and many other liquids.
- It is highly explosive and only requires a concentration of 4% for a flash fire when exposed to a relatively cool heat source of 232 degrees Celsius.
- It is heavier and 1.136 times denser than air. This means it is likely to be found in low-lying areas with little to no ventilation.
- H2S is a polar molecule
Molar Mass of H2S
Molar mass of H = 1.00794 g/mol
Sulfur molar mass = 32.06 g/mol
The molar mass of H2S is 34.1 g/mol.

Uses of Hydrogen Sulfide
- It is the main precursor of elemental sulfur.
- It plays a vital role in signaling pathways in the human body.
- H2S is used primarily to produce sulfuric acid and sulfur.
- Farmers use hydrogen sulfide as an agricultural disinfectant and it is found in some cutting oils, which are coolants and lubricants designed specifically for metalworking and machining processes.
h2s polar or nonpolar?
H2S is a slightly polar molecule because of the small difference in electronegativity values of hydrogen (2.2) atoms and sulfur (2.58) atoms.
The molecular geometry of hydrogen sulfide is polar but the bonds are not polar.
Polarity is determined by electronegativity. A molecule is polar if the structure of that molecule is not symmetrical.
In the case of a symmetric structure, the dipole vectors on each molecule cancel each other, resulting in the nonpolar nature of the molecule.
In addition, the presence of two lone pairs that are on the opposite side of the two hydrogen atoms also makes the molecule more polar and causes the bent shape of the geometrical structure of H2S.
A detailed explanation can be found at the link “h2s polar or nonpolar“.
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In the H2S Lewis structure, two hydrogens form a single covalent bond with the sulfur atom.
- The bond angle is 92.1 degrees, and there are 8 valence electrons.
- H2S is a polar molecule with a bent geometry.
- Exposure to hydrogen sulfide can be dangerous.
More Interesting Topics
Molar Mass of Acetic Acid| Easy-Explanation
Concentration Gradient Definition
Sodium Phosphate – Formula, Structure, Types, and Uses
Sulfurous Acid| Formula & Lewis Structure
Valence Electrons in Nitrogen
Is Nh3 Polar?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below
1. What is Polarity?
The distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond causes polarity.
Specifically, it is found that bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent.
For instance, in hydrogen chloride, the H atom is slightly positively charged whereas the Cl atom is slightly negatively charged.
The slight electrical charges on dissimilar atoms are called partial charges, and the presence of partial charges signifies the occurrence of a polar bond.
Some examples of polar molecules are water (H2O), Ethanol, Ammonia, and SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide).
2. Explain Hydrogen sulfide Lewis Structure in simple words
Hydrogen sulfide is a polar molecule with a single bond between two hydrogen and sulfur atoms.
The structure is a bent structure with bond angles of 92.1 degrees.
3. H2S is acid or base?
In its gaseous form, H2S is neither acidic nor basic, i.e. it is neutral, but when it is made into an aqueous solution, it releases the hydronium ions H+ and S2- ions.
4. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and a trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
5. What is the hydrosulfuric acid formula?
The formula for hydrosulfuric acid, also known as hydrogen sulfide, is H2S. In the H2S molecular structure, the sulfur atom is in the center, connecting with two hydrogen atoms, producing a bond angle smaller than 180 degrees.
6. What is h2s acid’s name?
H2S (hydrogen sulfide) is a colorless, very deadly gas with a foul stench similar to rotten eggs. It is soluble in carbon disulfide and mildly soluble in water. When it dissolves in water, it generates a very weak dibasic acid known as hydro sulfuric acid.
Check the full article “Hydrogen sulfide acid”.
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
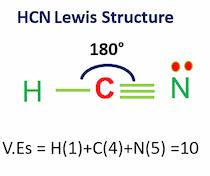
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
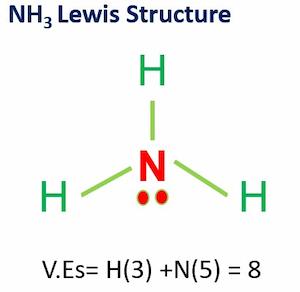
NH3 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023