A Lewis Structure of a Molecule is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons.
It shows how the electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule.
Electrons are represented as “dots” or “bonding electrons” as a line between the two atoms.
The objective of drawing the Lewis structure is to obtain the “best” electron configuration, i.e. the octet rule and formal charges need to be satisfied.
Table of Contents
Lewis structure definition
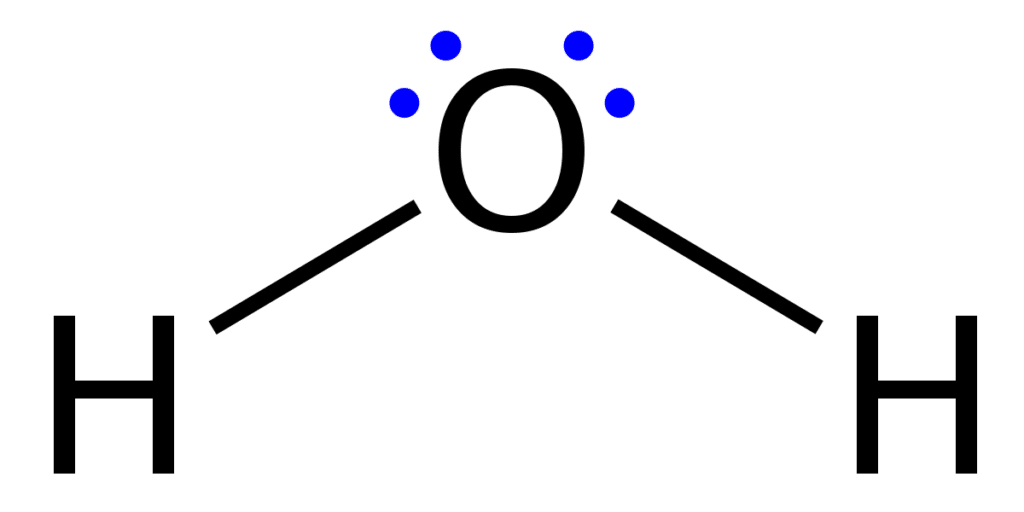
A Lewis structure is a structural representation of a molecule where dots are used to show electron positions around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms. They are also known as Lewis dot diagrams, electron dot diagrams, Lewis dot formulas, or electron dot formulas.
Rules to Draw Lewis Structure
The following are the rules to draw Lewis structure:
Count the Valence Electrons of Atoms.
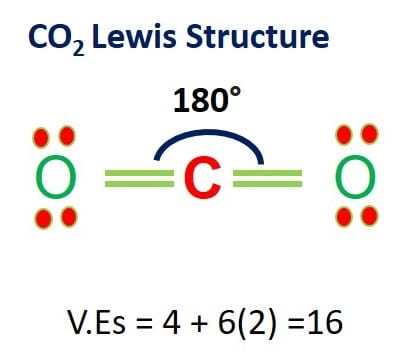
Determine the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule. For instance, in carbon dioxide, each carbon has four valence electrons. Oxygen has six valence electrons.
Determine the Central Atom
If a molecule has more than one type of atom, the least electronegative atom goes in the center.
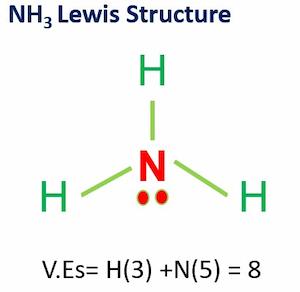
For instance, in the Ammonia lewis structure, Nitrogen is placed in the middle because it has the maximum number of valence electrons which is five. Hydrogen’s only one valence electron.
Place Electron Pairs Between the Atoms
In this step, we arrange electrons so each atom contributes one electron to form a single bond between each atom. Count the number of electrons around each atom. If each atom has eight electrons or an octet, then the octet is complete. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
Complete octet of the molecule
Give multiple bonds if required for fulfilling the octet of the atoms. Make sure all the atoms are having their lowest possible formal charge.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
Lewis structure examples
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SiO2 Lewis Structure
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
N2 Lewis Structure| Hybridization & Molecular Geometry
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
BF3 Lewis structure| Molecular geometry, Hybridization
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023