Calcium is a silvery-white, soft metal that tarnishes rapidly in the air and reacts with water. It is the fifth most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust (4.1%) and is not found uncombined in nature but occurs abundantly as limestone (calcium carbonate), gypsum (calcium sulfate), fluorite (calcium fluoride), and apatite (calcium chloro- or fluoro-phosphate).
Furthermore, Hard water contains dissolved calcium bicarbonate. When this filters through the ground and reaches a cave, it precipitates out to form stalactites and stalagmites.
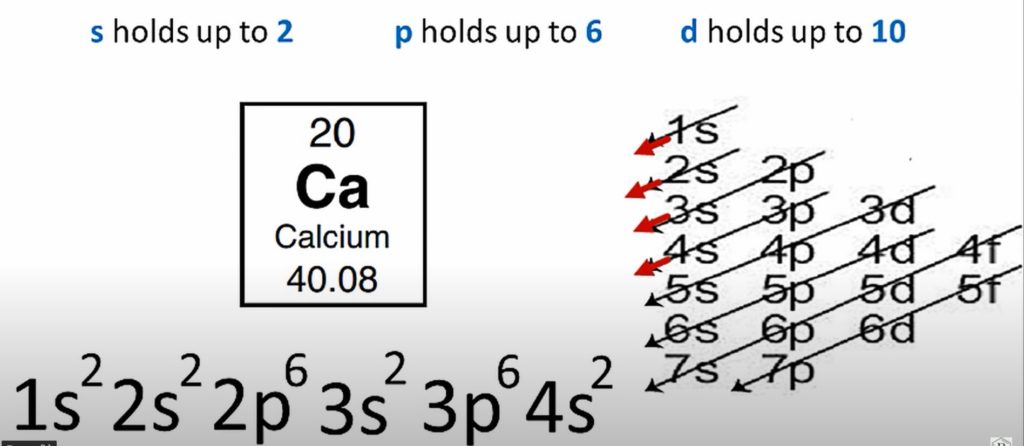
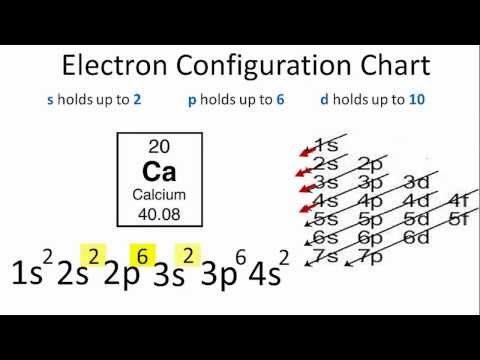
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and the atomic number 20. The first two electrons in the electron configuration for Calcium will be in the 1s orbital. Because the 1s orbital can only hold two electrons, Calcium’s next two electrons are placed in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will be assigned to the 2p orbital. As a result, the calcium electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 and is seen in the image below.
Table of Contents
Calcium- Key Points
- Atomic number: 20
- Atomic weight: 40.08 g/mol
- Melting point: 842°C, 1548°F, 1115 K
- Boiling point: 1484°C, 2703°F, 1757 K
- Density: 1.54 g/cm3
- Calcium isotopes are 40Ca, 42Ca, 43Ca, 44Ca, and 46Ca.
Element Calcium
Calcium (Ca) is the fifth element and the third most abundant metal in the earth’s crust, with an atomic number of 20. It’s a trimorphic metal that’s harder than sodium but softer than aluminum. It has the same properties as beryllium and aluminum, but unlike alkaline metals, it does not cause skin burns. It has lower chemical reactivity than alkaline metals and alkaline-earth metals.
| Name of element | Calcium (Ca) |
| Atomic number | 20 |
| Atomic mass | 40.08 g.mol -1 |
| calcium electron configuration | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 |
| Density | 1.54 g/cm3 |
Is Calcium a metal?
Calcium is metal because it is in group 2 which makes it an alkaline earth metal and a powerful reducing agent that loves to react with nonmetals, especially powerful oxidizing agents like fluorine and chlorine.
Calcium Isotopes
Ca has six naturally occurring isotopes (40Ca, 42Ca, 43Ca, 44Ca, 46Ca, and 48Ca), the most abundant of which is 40Ca, which is produced by the radioactive decay of potassium 40K and has a half-life of 1.277 billion years. Ca is a valuable tracer for earth system processes and biogeochemical pathways due to its numerous isotopes and high mobility in near-surface environments. Ca isotope studies are thus important for gaining a better understanding of global elemental cycles and mutual interactions between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Summary
- The electron configuration of calcium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2
- Calcium is metal because it is in group 2 which makes it an alkaline earth metal and a powerful reducing agent.
- Calcium isotopes are 40Ca, 42Ca, 43Ca, 44Ca, 46Ca, and 48Ca.
Related Topics
Neon Element| Properties & Uses
Sulfur trioxide (SO3)
Sulfur hexafluoride| Formula and Molecular Geometry
Hydrogen Bond| Definition & Easy Explanation
Hydrogen Cyanide-A Simple Overview
Recommended Video
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the sulfur electronic configuration?
Sulfur electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
2. How many electrons does oxygen have?
A single oxygen atom has eight protons, eight electrons, and eight neutrons.
Oxygen is a stable isotope of oxygen with a nucleus of 8 neutrons and 8 protons. Its mass is 15.99491461956 u. Check the full topic “How many electrons does oxygen have?”.
3. What is calcium’s electronic configuration?
Calcium electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2
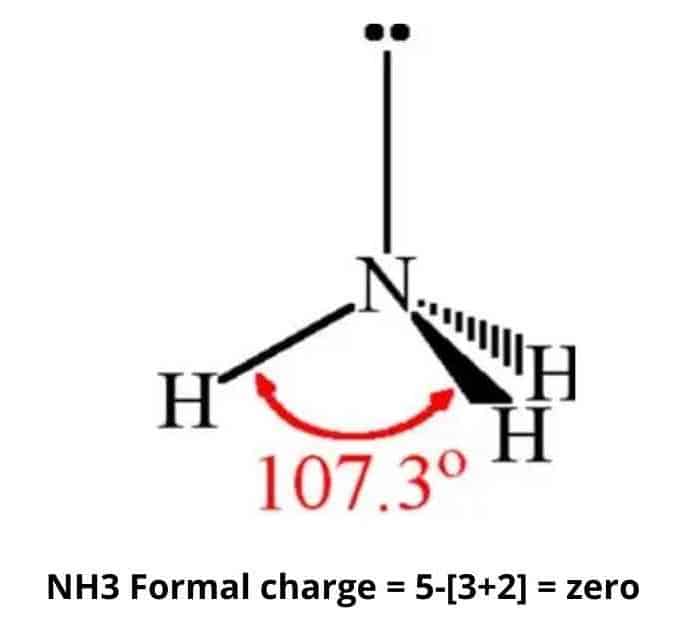
4. Is NH3 a polar molecule?
NH3 is polar because it has three N-H bond dipoles that do not cancel out. Nitrogen has a higher electronegative charge than hydrogen in every bond. The polarity of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms is due to the unequal distribution of charges.
5. How many electrons does helium have?
A single helium atom has two protons, two electrons, and two neutrons. The second element in the periodic table is helium. Because s subshells may store up to two electrons, both electrons fit into the 1s subshell, resulting in the electron configuration for helium atoms being 1s2.
More Interesting Links
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Nh3 Molecular Geometry| Trigonal Pyramidal
H2S Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
SO2 Polar or Nonpolar
Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023