Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a colorless or pale blue liquid or gas with an odor similar to that of an almond. Hydrocyanic acid, or prussic acid, is a solution of hydrogen cyanide in water. Hydrogen cyanide and its compounds are used in a wide variety of chemical processes, including fumigation, case hardening, electroplating, and ore concentration. Additionally, it is used to make acrylonitrile, which is used to make acrylic fibres, synthetic rubber, and plastics.
| Name of molecule | Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) |
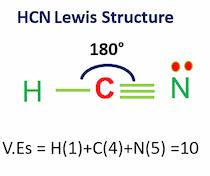
| Bond Angles | 180 degrees |
| HCN molecular geometry | Linear |
| Hybridization of Hydrogen cyanide | sp hybridization |
| HCN valence electrons | 10 |
| is HCN polar or nonpolar | HCN is a polar molecule |
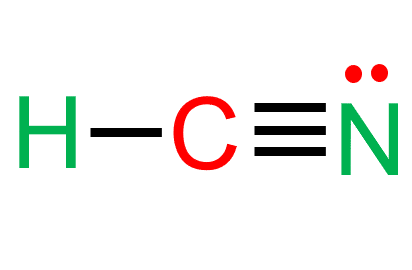
Table of Contents
HCN Molecular Geometry
Hydrogen Cyanide has geometry resembling AX2 molecule, where A is the central atom and X is the number of atoms bonded with the central atom.
Since Carbon is bonded to two atoms, Nitrogen, and oxygen. Therefore, HCN follows the molecular geometry of AX2. And as per VSEPR theory, molecules covered under AX2 have a linear molecular geometry with bond angles of 180 degrees. In addition, hydrogen cyanide is a slightly polar molecule as nitrogen tries to pull the electrons to itself due to its higher electronegative value.
Therefore, hydrogen will have slightly positive charges, and nitrogen will have slightly negative charges as the vector goes from hydrogen to nitrogen.
Hydrogen Cyanide- Key Points

- Hydrogen cyanide is a poisonous gas produced on an industrial scale
- It is flammable in nature
- Its solution with water is called prussic acid
- Poisonous by any means (absorption through skin of liquid, inhalation of vapors, etc).
- Molar mass f HCN is 27.0253 g/mol.
- In the HCN lewis structure, there is a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen and a single bond between C and H.
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar?
HCN is a polar molecule.
The electronegativity difference between Nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) makes HCN a polar molecule.
In the HCN molecule, carbon is in the middle, surrounded by nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
Carbon and hydrogen form a covalent bond by exchanging electrons.
Carbon and nitrogen, on the other hand, form a triple bond to share three electrons.
This causes unequal charge sharing in the linear-shaped HCN molecule and a non-zero dipole moment.
The nitrogen obtains a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen acquires a partial positive charge.
As a result, positive and negative poles form across the molecule, transforming HCN into a polar molecule.
Related Links
Binary Compound
SiO2 Lewis Structure
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
Sulfur hexafluoride| Formula and Molecular Geometry
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In Hydrogen cyanide molecule, carbon forms one single bond with the hydrogen atom and a triple bond with the nitrogen atom.
- The bond angle is 180 degrees and there are 10 valence electrons.
- HCN is a polar molecule with linear geometry.
- Exposure to Hydrogen cyanide can be dangerous.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below
1. Why Hydrogen Cyanide is polar?
In Hydrogen cyanide carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, hydrogen’s electronegativity is 2.1, and nitrogen has an electronegativity of 3. Any molecule that has a difference of electronegativities of any dipole moment is considered polar. Therefore, Hydrogen cyanide is a polar molecule.
2. Why Lewis structures are important?
Lewis structure is a simplified representation of valence shell electrons.
It depicts the arrangement of electrons around individual atoms in a molecule.
Electrons are shown as “dots” or as a line between two atoms when they are bonded.
3. How to draw Lewis structure of oxygen?
In the O2 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between two oxygen atoms.
Oxygen is a diatomic nonpolar molecule with bond angles of 180 degrees.
In its molecule, both oxygen atoms have the same electronegativity value and both atoms share equal ratios of bonded shared electrons and the overall O2 molecule turns out to be nonpolar.
4. What is dot structure of Hydrogen Sulfide?
On both sides of the central sulfur atom in the H2S Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms.
Because sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen, the molecule is slightly polar.
The vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments in the case of H2S results in a non-zero total dipole moment.
5. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
More Links
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
N2 Lewis Structure| Hybridization & Molecular Geometry
Chemical Reactions| Examples in Daily Life
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023