Sulfur trioxide (SO3) is a chemical compound. It comes in three different forms: gaseous monomer, crystalline trimer, and solid polymer. At just below room temperature, it is solid with a relatively narrow liquid range. The primary precursor to acid rain is gaseous SO3.
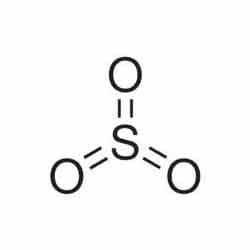
Sulfur trioxide is a colorless to white crystalline solid that emits fumes when exposed to air. frequently shipped with a polymerization inhibitor to prevent polymerization. With the release of heat, it reacts violently with water to form sulfuric acid. It corrodes metals and tissue. It causes skin and eye burns. Ingestion results in severe burns to the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. Inhaling the vapor is extremely hazardous. When it comes into contact with organic materials like wood, cotton, fiberboard, and so on, it causes a fire.
Table of Contents
Hybridization of SO3
From the lewis structure of SO3, we know that the SO3 molecule contains three sigma bonds and there are no lone pairs of electrons.
Number of hybrid orbitals = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs
So in a SO3 molecule, there are three hybrid orbitals.
Therefore, the hybridization of SO3 is sp2.
In sp2 hybridization, one s orbital and two p orbitals of the same shell within an atom overlap and mix to form three new hybrid orbitals of equal energy.
More Interesting Topics
Sulfur Electron Configuration
Sulfurous Acid Formula & Lewis Structure
SO2 Ionic or Covalent?
Sulfurous Acid| Formula & Lewis Structure
H2S Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
H2S Polar Or Nonpolar| Easy Explanation
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the molar mass of nitrogen?
The mass of an element in grams per mole of its atoms is known as its molar mass. It corresponds to the element’s atomic mass in AMU units (atomic mass units). The molar mass of Nitrogen is approximately 14.01 grams per mole of nitrogen atoms.
2. What is nitrogen trifluoride?
Nitrogen trifluoride is an odorless, colorless gas. It has a musty odor. It is used in the electronics industry and in high-power lasers because it is a source of fluorine. It is primarily used in the production of semiconductors and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panels, as well as some types of solar panels and chemical lasers, but not all of them. Unlike fluorinated carbons, nitrogen trifluoride is easily degraded due to the low bond energy in the N–F bond. This means it can be used as a fluorine source.
3. What is hydrogen iodide?
Hydrogen iodide (HI) is a diatomic molecule and a hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. It is used as a reducing agent and an analytical reagent. It is also used in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, disinfectants, and other chemicals. It is supplied as a compressed, liquefied gas.
4. How cold is liquid nitrogen?
Liquid nitrogen (LN) is an inert cryogenic fluid with a temperature of − 196 °C [− 320 °F]. Liquid nitrogen is much colder than dry ice, which makes it much more dangerous to handle. It can be between -346°F and -320.44°F. Because it’s a liquid and not a solid, it can be hard to work in many places and can be hard to keep under control.
5. how many valence electrons are in nitrogen?
Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. The last shell of nitrogen has five electrons. Therefore, the valence electrons of nitrogen are five.
6. h2S molecular geometry?
The molecular geometry of H2S is bent because the two lone pair electrons on the sulphur central atom repel each other and the electrons of the next two bonded pair electrons. As a result, these electron pairs (lone pair and bond pair) take the position where the repulsion is the least and they become stable (no further repulsion force exists in electron pairs).
7. Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) is polar or nonpolar?
HCN, or hydrogen cyanide, is a polar molecule because there is a large electronegative difference between the N and H across the linear molecule. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, hydrogen has a value of 2.1, and nitrogen has a value of 3. As a result of these differences, as the vector moves from hydrogen to nitrogen, hydrogen will have slightly positive charges and nitrogen will have slightly negative charges.
8. What is hydrogen molar mass?
The molar mass of hydrogen gas is 2.016 grams per mole.
A molar mass is the mass of 6.022 X 1023 atoms or molecules, depending on the basic unit being measured. This number produces a quantity of a substance in which the mass in grams is the same as the mass in atomic mass units of a single atom or molecule of the same substance.
Check another related topic “How many neutrons does hydrogen have?”.
9. What is Sulfur Hexafluoride?
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), also known as an inert gas, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is non-toxic and relatively unreactive. SF6 is a powerful greenhouse gas that has a high potential for global warming, and its concentration in the earth’s atmosphere is rapidly increasing. SF6 decomposes under electrical stress during its working cycle, producing toxic byproducts that endanger exposed workers’ health.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023