A hydrogen ion is the nucleus of a hydrogen atom that has been separated from its electron. The hydrogen nucleus is made up of a proton, which is a particle with a unit positive electric charge. As a result, the isolated hydrogen ion, denoted by the symbol H+, is commonly used to represent a proton. Because the bare nucleus easily combines with other particles (electrons, atoms, and molecules), the isolated hydrogen ion can exist only in a nearly particle-free space (high vacuum) and as a gas. The concentration of hydrogen ions in a water solution is used to determine a substance’s acidity; the greater the concentration of hydrogen ions, the more acidic the solution and the lower the pH.
Some other synonyms of hydrogen ion are hydron, hydrogen ion, hydrogen cation, proton, and hydrogen (1+).

Table of Contents
Isolated Hydrogen Ion
When a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron, a hydrogen ion is formed. Because a positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) easily combines with other particles, it is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particle-free space. The bare hydrogen ion cannot exist freely in solution due to its extremely high charge density, which is approximately 20 billion times that of a sodium ion, because it readily hydrates, i.e., bonds quickly.
Hydrogen Oxide
The diatomic anion hydrogen oxide (Hydroxide) has the chemical formula OH. It is composed of oxygen and hydrogen atoms joined by a single covalent bond and have a negative electric charge. It is a significant but in most cases minor component of water.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many neutrons does hydrogen have?
The majority of hydrogen atoms lack a neutron. Rare hydrogen isotopes, known as deuterium and tritium, have one and two neutrons, respectively. Check the full article “How many neutrons does hydrogen have?”.
2. The molar mass of methanol?
The molar mass of methanol is 32.04 g/mol. The methanol formula is CH3OH and it is also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, or wood spirit.
3. What is the weight of water?
The weight of water is roughly 224 grams, according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (half a pound). A liter of water weighs approximately 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds), according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS). A gallon of water weighs roughly 3.79 kg, according to the USGS (8.35 pounds).
4. What is hydrogen bonding?
The hydrogen bond (H-bond) interaction is a dipole-dipole interaction. It is not a chemical connection in the traditional sense. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom (fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen) and is in the proximity of another electronegative atom with a single electron.
This bond is weaker than ionic or covalent bonds, but stronger than van der Waals forces.
5. What is heavy water?
Heavy water (D2O), also known as deuterium oxide, is water made up of deuterium, a hydrogen isotope with twice the mass of ordinary hydrogen, and oxygen. Heavy water is used in nuclear power plants as a neutron moderator.
6. What is nitrogen fluoride?
Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is a colorless gas that has a moldy odor. It is extremely toxic when inhaled.
7. What is air?
Air is a homogeneous mixture of different gasses. The air in the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen, oxygen (which is required for animal and human life), carbon dioxide, water vapor, and trace amounts of other elements (argon, neon, etc.). At higher elevations, air contains ozone, helium, and hydrogen.
8. What is liquid oxygen?
Liquid oxygen is a liquified form of oxygen gas that is utilized as an oxidant for liquid fuels in defense systems. It is incredibly cold and has a boiling point of –297.3 degrees Fahrenheit (-182.9 degrees Celcius).
9. Density of oxygen?
Liquid oxygen is a liquified form of oxygen gas that is utilized as an oxidant for liquid fuels in missile and rocket propellant systems. It is incredibly cold and has a boiling point of –297.3 degrees Fahrenheit (-182.9 degrees Celcius).
Check the full article “Density of oxygen”.
10. Is helium a gas?
Helium (He) is an inert gas and chemical element in Periodic Group 18. (noble gases). Helium, the second lightest element (only hydrogen is lighter), is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that freezes at 268.9 degrees Celsius (452 degrees Fahrenheit).
11. At what temperature does water freeze?
Water’s normal freezing and melting points are 0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
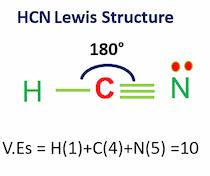
12. Hydrogen cyanide polar or nonpolar?
HCN is a polar molecule.
As can be seen from the HCN lewis structure, the electronegativity difference between nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) makes it a polar molecule.
More Interesting Links
Ideal Gas Law| Simple Overview
Cathode| Component of Cells and Batteries
Distillation| Principles, and Processes
Chemical Reactions| Examples in Daily Life
Hydrogen Molar Mass
Liquid Oxygen-Cryogenic Liquid
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Concentration Gradient Definition| Easy Examples
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023