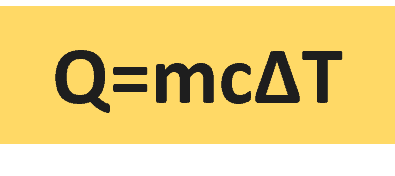The rate of thermal energy flow per unit surface area of a heat transfer surface, such as in a heat exchanger, is known as heat flux. W/m2 is the unit of measurement.

Heat flux is the most important factor to consider when estimating heat transfer. The heat flux vector is pointing in the direction of a lower temperature. The temperature differential between solid, liquid, or gaseous media involved in heat transfer determines convective heat flow. The proportionality factor is a heat transfer coefficient.
The heat flow vector is proportional to and generally parallel to the temperature gradient vector in heat conduction. The direction of the two vectors may not coincide in anisotropic substances, though. The effective heat flux in the event of simultaneous heat and mass transmission may be many orders of magnitude greater than the amount attributable to heat conduction alone.
Radiative heat flow is an electromagnetic radiation flux that, unlike convection and heat conduction, may proceed without the use of an intermediary medium, i.e., through a vacuum. Planck’s law describes the radiation heat flow for an idealized black substance. Only lower radiation flux values than this idealized value are possible.
Table of Contents
Flux Definition
Heat flux (Ф) can be defined as the rate of heat energy transfer through a given surface (W), and heat flux density (φ) is the heat flux per unit area (Wm²).
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a given material to conduct or transfer heat. It is generally denoted by the symbol ‘k’ but can also be denoted by ‘λ’ and ‘κ’. The reciprocal of this quantity is known as thermal resistivity. Materials with high thermal conductivity are used in heat sinks, whereas materials with low values of λ are used as thermal insulators.
Related Links
Condensation Reaction| Easy Explanation
Conductor And Insulator
Atmospheric Pressure| Definition & Examples
Boiling of Water| Phenomenon, and Factors Affecting
Thermal Conductivity of Water
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is heat flux?
The quantity of heat transferred per unit area per unit time to or from a surface is referred to as heat flux.
2. What are heat flux units?
A flow of energy per unit of area per unit of time is known as heat flux or thermal flux. It is also known as heat flux density, heat-flow density, or heat flow rate intensity. Watts per square meter (W/m2) are the SI units. It is a vector quantity since it has both a direction and a magnitude.
3. heat transfer coefficient?
The heat transfer coefficient is a numerical measure of convective heat transfer between a fluid medium (a fluid) and the surface (a wall) that the fluid passes through. In the Newton-Richmann relation, this feature appears as a proportionality factor.
4. what is heat?
Heat (thermal energy) is a type of energy that is exchanged between systems or things of various temperatures (flowing from the high-temperature system to the low-temperature system). also known as thermal energy or heat energy. Btu, calories, and joules are the most common units of heat measurement.
5. Specific Heat?
Specific heat (cp) or specific heat capacity refers to the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram mass of a substance by one Kelvin temperature.
Its formula is Q/m ΔT = cp where Q refers to the amount of heat supplied to the specimen and ΔT is the rise in temperature.
The value of cp depends on the nature of the substance.
6. What is thermite welding?
Thermite welding is a type of welding that involves reducing metal oxides with aluminum powder and releasing a large quantity of heat. A thermite reaction is used to repair railway rails or broken machine components.
7. What is the malleability of a material?
Malleability refers to a substance’s ability to distort under pressure. The material can be pounded or rolled into thin sheets if it is pliable. Metal malleability refers to the ability of a metal to deform under compression and take on a new shape.
More Interesting Links
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
Light Energy| Definition, and Properties
What is the Specific Heat of Air?
Mechanical Energy Formula & Examples
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023