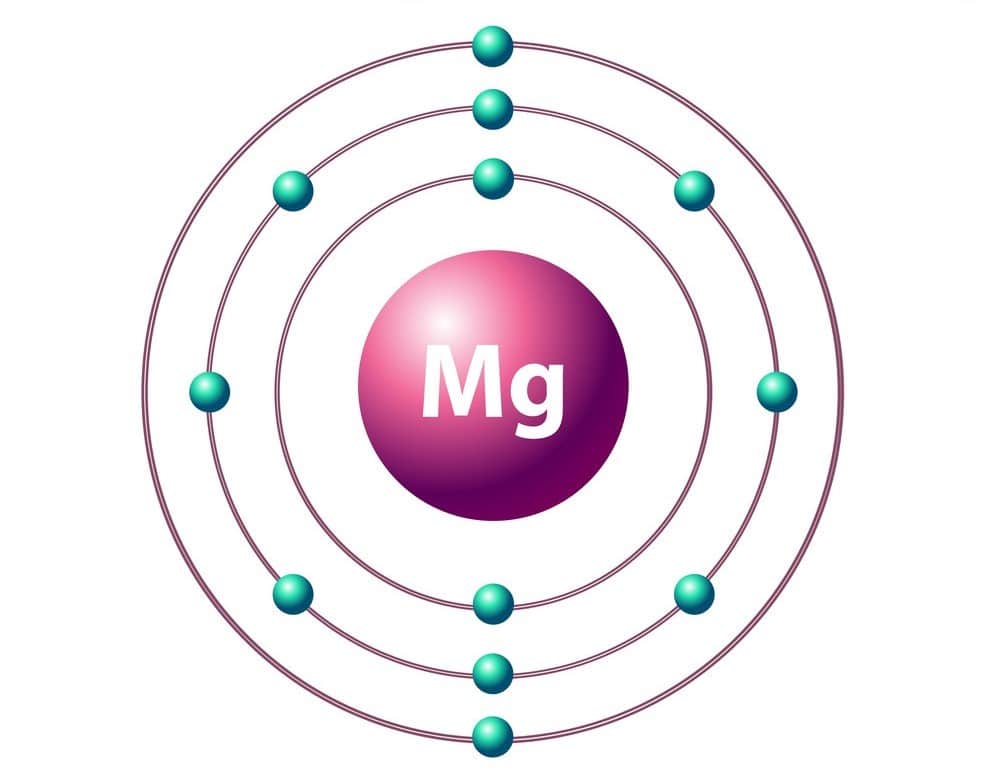
Magnesium (Mg) is a chemical element with an atomic number of 12 and an atomic weight of 24,312. It is found in Periodic Table Group IIa. Magnesium is a metallic element that is silvery-white in color. It has a relative density of 1740 kg/m3 (0.063 lb/in3 or 108.6 lb/ft3). It has long been known as the lighter structural metal in the industry due to its low weight and ability to form mechanically resistant alloys.
On Earth, magnesium is found both in the crust and in the mantle; it’s also the third-most abundant mineral dissolved in seawater, with a 0.13 percent concentration.
| Element | Magnesium (Mg) |
| Electronic shell | 1s22s22p63s2 |
| Density | 1.74 g.cm -3 at 20 °C |
| Atomic mass | 24.305 |
| Melting point | 650 °C (1,202 °F) |
| Oxidation state | +2 |
| Boiling point | 1,090 °C (1,994 °F) |
| Main Uses | The metal can be combined with other metals, particularly aluminum, to create car bodies, drink cans, and other lightweight and strong items. |
| Most common isotopes | Mg-24 (78.99 percent natural abundance), Mg-25 (10 percent natural abundance), Mg-26 (11 percent natural abundance) |
Magnesium is commercially produced through the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride (MgCl2), primarily from seawater, and through the direct reduction of its compounds with suitable reducing agents, such as the reaction of magnesium oxide or calcined dolomite with ferrosilicon (the Pidgeon process).
Table of Contents
Interesting Facts About Magnesium
- Silvery-white alkaline is solid at room temperature.
- Eighth-most abundant element.
- The second most abundant compound is found in the earth’s crust.
- For every cubic kilometer of seawater, there are about 1.3 billion kilograms of magnesium.
- Most lightweight out of all the metallic elements
- Used in products that benefit from being lightweight, such as car seats, luggage, laptops, cameras, and power tools.
- Ignites easily in the air and burns with a bright light, it’s used in flares, fireworks, and sparklers.
- Helps to maintain normal nerve and muscle function, supports a healthy immune system, keeps the heartbeat steady, and helps bones remain strong [reference].
Daily Life Uses of Magnesium
Magnesium is used in many everyday products and applications. Here are some examples of how magnesium is used in daily life:
- Construction and building materials in the form of lightweight and durable alloys that are used in construction materials, such as concrete, wallboard, and roofing materials.
- Automotive and aerospace industries use Magnesium parts to make parts that are lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant, such as engine blocks, wheels, and structural components.
- Magnesium is an essential nutrient for human health and is found in many foods, including nuts, seeds, whole grains, and green leafy vegetables. Magnesium supplements are also available to help meet daily recommended intake levels.
- A variety of medications, including antacids, laxatives, and supplements include magnesium to treat magnesium deficiency.
- Magnesium is used in fireworks to produce bright white light and is often used in combination with other metals to produce different colors.
- Magnesium is used in sports equipment, such as golf clubs, tennis rackets, and bike frames, because of its lightweight and strong properties.
- Certain types of batteries, such as magnesium-air batteries, which have high energy density and can be used in various applications.
These are just a few examples of how magnesium is used in everyday life. Magnesium’s properties make it a versatile material that can be used in a wide range of applications.
Magnesium As a Biocompatible Material
Magnesium can be used as a biocompatible material in certain biomedical applications. Magnesium is a lightweight metal that has excellent biocompatibility and bio-absorbability, which makes it attractive for use in a range of medical devices and implants.
One of the primary advantages of using magnesium is its ability to biodegrade over time. When magnesium is implanted in the body, it gradually dissolves and is absorbed by the surrounding tissue. This means that the need for surgical removal of the implant is eliminated, and the risk of long-term complications is reduced.
Magnesium has been used in a variety of biomedical applications, including orthopaedic implants, cardiovascular stents, and drug delivery systems. However, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed when using magnesium in medical devices, such as its rapid corrosion in physiological environments and its potential cytotoxicity at higher concentrations. Research is ongoing to optimize the use of magnesium and improve its biocompatibility for various medical applications.
Related Topics
Neon Element| Properties & Uses
Electron Configuration for Calcium
Liquid Oxygen-Cryogenic Liquid
Zinc Hydroxide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below. If you have any questions, feel free to comment or send an email to [email protected]
1. What is Milk of Magnesia?
Milk of magnesia is a creamy-like colloid form of magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. It is used as an antacid to neutralize excess stomach acid. Magnesium can also be used as a laxative and as a treatment for rashes in the form of Epsom salts.
2. Epsom salt?
Epsom salt is also known as magnesium sulfate. It is an inorganic salt with the chemical formula MgSO4(H2O)x where x varies from 0 to 7. It’s made up of magnesium, sulfur, and oxygen.
3. Is chlorine a metal?
Chlorine (Cl) is the second lightest member of the periodic table’s halogen elements, or Group 17 (Group VIIa). Because it lacks metal-like properties such as electrical conductivity, flexibility, and strength, chlorine is classified as a nonmetal.
Check the full article “Is chlorine a metal?”.
4. Is hydrogen a metal?
While hydrogen has the same ns1 electron configuration as alkali metals, it is not considered a metal because it forms cations (H+) more slowly than other alkali metals. As a result, the simple answer to the question “is hydrogen a metal?” is no.
5. Is magnesium magnetic?
A magnet will weakly attract paramagnetic metals such as magnesium, titanium, molybdenum, and tantalum are weakly attracted to a magnetic force.
6. What is sulfur electronic configuration?
Sulfur electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
7. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
CLF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
8. What is Sulfur hexafluoride?
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a non-toxic gas that is used in a variety of applications due to its inert properties. While SF6 is non-toxic when used properly, toxic byproducts can be produced during electrical discharges within SF6-filled equipment, posing a threat to the health of workers who come into contact with them.
9. What is Sulfur trioxide?
SO3 (sulfur trioxide) is a chemical compound. It is available in three forms: gaseous monomer, crystalline trimer, and solid polymer. It is solid at just below room temperature and has a relatively narrow liquid range. Gaseous SO3 is the primary precursor to acid rain.
10. What is the weight of water?
At 39.2°, the density of water is one kilogram per liter (kg/L). This means that one liter (L) of water weighs one kilogram (kg), while one milliliter (mL) of water weighs one gram (g). One gallon of water weighs 8.345 pounds in standard US measurements.
More Interesting Topics
Specific Heat of Water
How Much is a Liter of Water?
The Specific Gravity of Water
Density of Water in g/ml-Accurate Value
The Density of Water lbs/U.S gal
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023