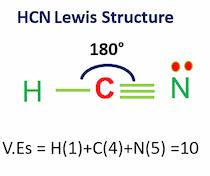
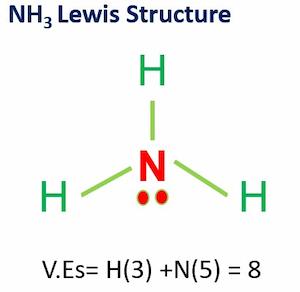
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) is a chemical compound having the formula HCN. It is also known as prussic acid and is a highly toxic liquid. Hydrogen cyanide is a colorless chemical that is utilized in the commercial manufacture of a variety of compounds.
Table of Contents
Hybridization of HCN
The atoms of hydrogen cyanide are hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. Carbon has one bond with a hydrogen atom and three bonds with a nitrogen atom.
The hydrogen atom only needs one valence electron to achieve a stable configuration. As a result of sharing one electron with a carbon atom, there is no hybridization for a hydrogen atom. The carbon atom shares the electron in its 1s orbital.
The carbon atom, which also serves as the center atom, requires hybridized orbitals to accommodate the shared electrons. We may determine the hybridization of an atom using simple and rapid methods such as the Steric Number and the number of sigma bonds.
There are two sigma bonds in HCN: C-H and C-N. The number of sigma bonds created equals the number of hybrid orbitals. As a result, the hybridization for the HCN molecule is an sp hybridization.
Molecular Geometry
The linear molecular geometry of hydrogen cyanide has bond angles of 180 degrees.
Because hydrogen and nitrogen tend to be far apart, HCN takes on a linear structure.
Because of its electronegative value, nitrogen seeks to attract electrons to itself, making it somewhat polar.
As a result of these changes, as the vector moves from hydrogen to nitrogen, hydrogen will have slightly positive charges and nitrogen will have slightly negative charges.
As a result, the nitrogen atom becomes a negative pole and the hydrogen atom becomes a positive pole, resulting in a polar molecular structure.
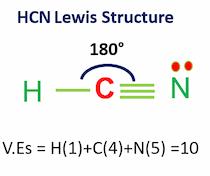
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar?
HCN is a polar molecule.
The difference in electronegativity between nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) makes it a polar molecule.
The difference in electronegativity between atoms is related to the polarity of the molecule.
Carbon is in the middle, surrounded by nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
Carbon and hydrogen create a covalent bond by exchanging electrons.
Carbon and nitrogen, on the other hand, form a triple bond to share three electrons.
This causes uneven charge sharing in the linear-shaped HCN molecule and a non-zero dipole moment.
The nitrogen receives a partial negative charge, whereas the hydrogen receives a partial positive charge.
As a result, positive and negative poles form across the molecule, transforming HCN into a polar molecule.
Important Links
Hydrogen Cyanide Effects
Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) poisoning can be fatal in a matter of minutes.
It can particularly affect those organ systems which are most sensitive to low oxygen levels, like the central nervous system (brain), the cardiovascular system (heart and blood vessels), and the pulmonary system (lungs).
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SiO2 Lewis Structure
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
N2 Lewis Structure| Hybridization & Molecular Geometry
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- The hybridization for the HCN molecule is an sp hybridization.
- The bond angle is 180 degrees, and there are 10 valence electrons.
- HCN is a polar molecule with linear geometry.
- Exposure to hydrogen cyanide can be dangerous.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below
1. Why Hydrogen Cyanide is polar?
Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5 in hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen has an electronegativity of 2.1, and nitrogen has an electronegativity of 3. Any molecule with a difference in electronegativities at any dipole moment is said to as polar. Hydrogen cyanide is thus a polar molecule.
2. Explain Hydrogen Cyanide Lewis Structure in simple words
Hydrogen cyanide is a polar molecule having a triple carbon-nitrogen link. The HCN lewis structure is composed of three distinct atoms: hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. It is a polar molecule with a 180-degree bond angle.
3. What is hydrocyanic acid?
A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water is called hydrocyanic acid.
4. What is cyanide poisoning?
Cyanide poisoning refers to the harmful effects of inhaling hydrogen cyanide or ingesting the salts of hydrogen cyanide, called cyanides.
6. How to draw Lewis structure of oxygen?
In the O2 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between two oxygen atoms.
Oxygen is a diatomic nonpolar molecule with a 180-degree bond angle.
Both oxygen atoms in their molecule have the same electronegativity value, and both atoms share identical ratios of bound shared electrons, resulting in a nonpolar O2 molecule.
7. What is the dot structure of Hydrogen Sulfide?
On both sides of the central sulfur atom in the H2S Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms.
Because of the presence of two unbonded pairs of electrons, the molecule bends.
Because sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen, the molecule is somewhat polar.
The vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments in the instance of H2S results in a non-zero total dipole moment. As a result, dipole-dipole interactions in hydrogen sulfide are detected.
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
More Link
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023