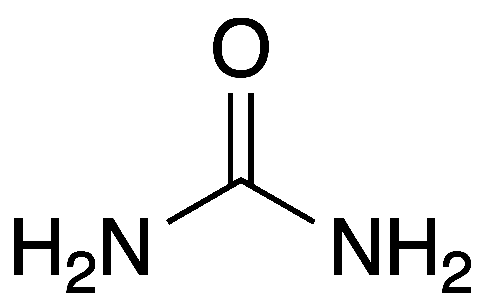
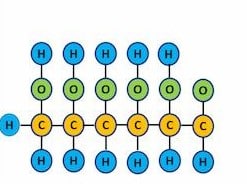
C6H12O6 (glucose) is a simple sugar with six carbon atoms and one aldehyde group.
It is also known as blood sugar.
It naturally occurs in both combined and free states.
In the free state, it is present in most sweet fruits and in honey.
In the combined state, it forms a major component of many disaccharides and polysaccharides.
It is a primary source of energy for living organisms.
Human blood and urine also contain small quantities of glucose.
| Compound Name | Glucose (C6H12O6) |
| Nature | Organic compound (Monosaccharide) |
| Properties | Odorless and sweet to taste |
| Other names | Aldohexose and Dextrose |
| Sources | Fruits, bread, dairy products, and vegetables |
| Major use | Body’s preferred sources of fuel in the form of carbohydrates |
Table of Contents
What is C6H12O6 made of?
C6H12O6 (Glucose) comprises 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms. Its other name is dextrose. It is synthesized naturally in the liver and kidneys of animals. In plants, it is found in fruits and in different parts of plants. D- glucose is the naturally occurring form of glucose
Key Points of Glucose
- Glucose is also known as aldohexose as well as dextrose
- Odorless and sweet to taste
- Its most abundant organic compound
- Density is 1.54 g/cm3
- The melting point is 146 °C
- Molar mass is 180.15 g/mol
- D- glucose is the naturally occurring form
- It occurs either in the solid or liquid form
- It water-soluble and is also soluble in acetic acid
- C6H12O6 is a monosaccharide that is the most basic unit of carbohydrate.
Glucose Molar Mass
Molar mass of Carbon =12.011 g/mol.
Oxygen molar mass = 16.00 g/mol.
The molar mass of Hydrogen =1.007 g/mol.
Molar mass of glucose = 6(12.011) + 12(1.007) + 6(16.00) = 180.15 g/mol
Sources of C6H12O6
Generally, glucose (C6H12O6) is obtained from bread, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Our body needs food to create the energy that helps keep us alive. Glucose is one of the body’s preferred sources of fuel in the form of carbohydrates. Although glucose is important, it’s best in moderation. Unhealthy glucose levels can have permanent and serious effects on our health.
How does the body process glucose?
- When we eat, our body immediately starts working to process glucose. Our blood sugar level normally rises after we eat.
- Enzymes start the breakdown process with help from the pancreas. The pancreas is a gland located behind the stomach and next to the small intestine. It helps the body with the absorption and digestion of food.
- The pancreas produces hormones such as insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin that regulate the nutrients and energy our body uses.
- When we eat, our body signals the pancreas to release insulin to deal with the rising blood sugar level.
What Is Diabetes?
- Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs due to the malfunctioning of the pancreas.
- Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas, that acts as a key to let glucose produce energy.
- All carbohydrate foods are broken down into glucose in the blood. Insulin helps glucose get into the cells.
- Not being able to produce insulin or use it effectively leads to raised glucose levels in the blood (known as hyperglycemia). Over the long term, high glucose levels are associated with damage to the body and failure of various organs and tissues.
- In type 1 diabetes our body produces very little or no insulin, which means that we need daily insulin injections to maintain blood glucose (C6H12O6) levels under control.
- In type 2 diabetes our body does not make good use of the insulin that it produces. Most people with type 2 diabetes require oral drugs and/or insulin to keep their blood glucose levels under control.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is C6H12O6 a compound or molecule?
Glucose is both a molecule and a covalent compound. It is made up of three elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Elements and compounds are pure substances. A pure substance like Glucose has a fixed composition.
2. Is glucose organic or inorganic?
The main difference between organic and inorganic compounds is the presence of carbon atoms; organic compounds contain a carbon atom (and often a hydrogen atom) to form hydrocarbons, while almost all inorganic compounds do not contain either of those two atoms. Therefore, C6H12O6 is an organic molecule.
3. Does the Keto diet contains glucose?
The main goal of the ketogenic diet is to use fat for energy instead of carbohydrates or glucose. On the keto diet, you use a diet with very little part coming from carbohydrates.
More Interesting Links
Avocado Oil| Health Benefits
Coconut Oil For Hair: Benefits, Uses, And Tips
Should I Drink Green Tea For Weight Loss?
Greenhouse Effect| Definition And 5 Key Factors
How Many Water Bottles Is A Gallon| Examples
How many cups in 128 ounces?
Is Water Vapour a Greenhouse Gas?
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023