Oxalic acid is a bi-carboxylic acid (IUPAC name: ethanedioic acid, formula H2C2O4). It is one of the most powerful organic acids due to the joining of two carboxyl groups. Oxalates are the anions of oxalic acid, as well as their salts and esters. Oxalic acid is present in many plants, including leafy greens, vegetables, fruits, chocolate, nuts, and seeds. Oxalic acid is also commonly used as an acid rinse in laundries, where it is useful in eliminating rust and ink stains because it transforms most insoluble iron complexes into soluble complex ions.
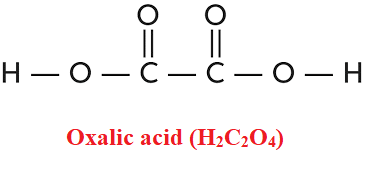
| Technical Name of compound | Oxalic acid (H2C2O4) |
| Occurrence | Very poisonous and occurs in certain plants such as sorrel and the leaf blades of rhubarb. |
| Other names | Ethanedioic acid |
| Appearance | White, crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 101.5°C (214.7°F). |
| Density | 1.90 g cm−3 |
| Uses | Oxalic acid is a powerful local irritant; when swallowed it produces a burning sensation in the mouth and throat, vomiting of blood, breathing difficulties, and circulatory collapse. |
Table of Contents
Oxalic Acid- Key Points
- The chemical formula of oxalic acid is C2H2O4. It is a dicarboxylic acid that is composed of two carboxyl functional groups.
- Oxalic acid crystallizes from water as colorless crystals that dihydrate twomolecules of water.
- Oxalic acid is an important household chemical that can be used mainly for cleaning or bleaching and the removal of rust.
- When heated above 200 °C, it decomposes to form carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, formic acid, and water.
Production of Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid can be made in the laboratory by oxidizing sugar or molasses with strong nitric acid in the presence of vanadium pentoxide as a chemical catalyst.
C12H22O11 + 18[O] → 6 (COOH)2 + 5H2O
Oxalic acid is prepared industrially by heating sodium formate rapidly to 360 °C.
2HCOONa → (COONa)2 + H2
By adding calcium hydroxide solution, free acid can be produced from its sodium salt. The calcium oxalate can then be treated with a determined amount of sulfuric acid to produce calcium sulfate and oxalic acid. Crystallization is achieved by removing calcium sulfate from the solution and evaporating the filtrate.
Molar Mass of Oxalic Acid (H2C2O4)
Molar mass of hydrogen = 1.00794 g/mol
Carbon molar mass = 12.0107 g/mol
The molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol.
The molar mass of oxalic acid is 90.03 g/mol.
Uses Of Oxalic Acid
- Oxalic acid can be used to bleach wood and stone. When wood or stone becomes grey, oxalic acid is used to restore its original color.
- Oxalic acid is quite good at removing stains created by ink and several types of food.
- Oxalic acid is used to clean or remove iron rust by forming water-soluble iron salt with oxalic acid.
Summary
- The chemical formula of oxalic acid is C2H2O4. It is a dicarboxylic acid that is composed of two carboxyl functional groups.
- Oxalic acid is an important household chemical that can be used mainly for cleaning or bleaching and removal of rust.
Related Links
Molar Mass of Acetic Acid| Easy-Explanation
Acetyl Group| 9 Key Points-Easy Explanation
Hydrogen Bond| Definition & Easy Explanation
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar| Simple Explanation
Liquid Oxygen-Cryogenic Liquid
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is flaring necessary?
Flaring is a method of disposing of flammable materials, mostly methane, as well as reducing odor irritants, health concerns, and negative environmental effects.
2. What is a volatile substance?
The term “volatile” refers to compounds with a high evaporation capability. They have fewer intermolecular interactions and, as a result, may be transferred to the vapor phase quickly. They also have higher vapor pressures and lower boiling temperatures.
3. What are ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds are formed by a process known as electron transfer, in which one atom transfers electrons to another. An atom of one element loses one or more electrons during electron transfer, and an atom of another element gains those electrons. Both atoms are involved in the electron transfer from ions.
4. What is convection in the atmosphere?
Convection in the atmosphere is frequently seen in our weather system. As the sun heats the Earth’s surface, the air above it warms and rises. If the conditions are favorable, this air can continue to rise, cooling and producing Cumulus clouds.
5. What is the process of distillation?
Distillation is the separation of a mixture of liquids based on variations in their boiling points (or volatility). Water may be extracted from a salt solution using this method.
6. What is the combustion process?
Combustion is a chemical process in which heat and light are produced. The most common sort of combustion is fire.
7. Is zinc a strong metal?
Zinc metal is a low-tensile-strength metal with less than half the tensile strength of mild carbon steel.
8. What are quarks?
In physics, quarks are the fundamental building units of matter. They’re most typically found within protons and neutrons, the fundamental components of the universe’s atoms. Based on present experimental findings, quarks appear to be really basic particles that cannot be further subdivided.
9. What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering and erosion are geological processes that contribute to the shaping of the Earth’s surface.
Weathering is the degradation of rocks, soils, and minerals due to direct contact with the Earth’s atmosphere. Erosion, on the other hand, is the movement of solids (soil, mud, rock, and other particles) downward or down-slope produced by current agents such as wind, water, or ice responding to gravity or by living organisms.
Please check the full article “Weathering vs erosion”.
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Material Science.
More Interesting Links
Flash| Vector-Graphic Animation Technology
What is Provisioning?
What is a Biochip?| A Short Overview
What is a Compiler?
Disclaimer
Whatsinsight.org‘s blog and everything published on it are provided solely as an information resource. The blog, its authors, and affiliates accept no responsibility for any accident, injury, or damage caused by following the information on this website, in part or in whole. We do not recommend using any chemical without first consulting the manufacturer’s Material Safety Data Sheet and following the safety advice and precautions on the product label.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023