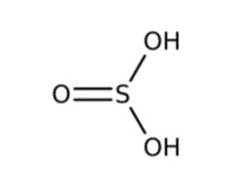
Sulfurous acid is a colorless weak dibasic acid, forms when sulfur dioxide is dissolved in water. It is the conjugate acid of hydrogensulfite. Like sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, it is an oxoacid since it is an acid with oxygen atoms in its chemical formula. The sulfurous acid formula is H2SO3.
Pure anhydrous H2SO3 has never been isolated or detected. Keep reading to know more about the Lewis structure, molar mass, and strength of H2SO3.
| Compound Name | Sulfurous acid |
| Sulfurous acid formula | H2SO3 |
| Molar mass | 82.07 g/mol |
| Density | 2.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Molecular Weight | 82.08 g/mol |
Table of Contents
H2SO3 d-Lewis Structure
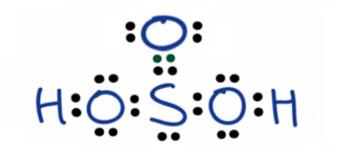
H2SO3 is also called sulfur dioxide solution or Dihydrogen tri-oxosulfate or Tri-oxosulfuric acid.
As per the rule, the Sulfur atom with the lowest electronegativity is at the center of the structure.
Three oxygen atoms surround a sulfur atom.
Two hydrogen atoms are attached to the polyatomic ion of SO-3. There are 16 electrons as lone pairs of electrons.
The Oxidation state of the sulfur atom in H2SO3 is +4.
H2SO3 has a trigonal Pyramidal structure.
Lewis Structure (Step by Step Construction)
Step-1: Count the valence electrons of atoms
H2SO3 molecule consists of two hydrogens, three oxygen, and one sulfur atom. The electronic configuration of individual atoms in H2SO3 is given in Table.
| Atom | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons |
| 1H | 1S1 | 1 |
| 8O | 1S2 2S2 2P4 | 6 |
| 16S | 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P4 | 6 |
H2SO3 = 2 Hydrogen atoms + 1 Sulfur atom + 3 Oxygen atoms
= 2(1)+1(6)+3(6)
Valence electrons in H2SO3 = 26
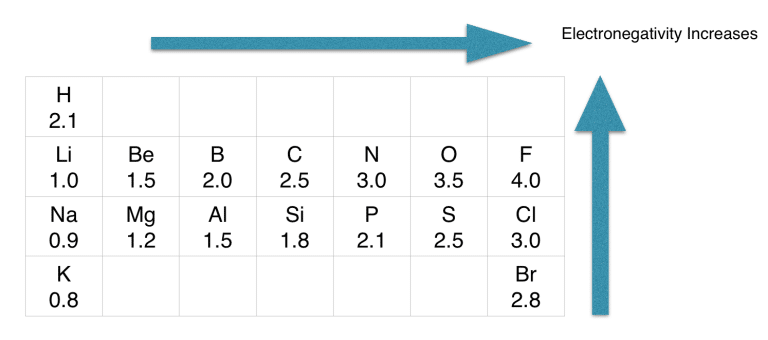
Step-2: Determine the central atom
As per the rule, sulfur is placed in the middle because it’s the least electronegative.
If we check the proper arrangement of hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen in the periodic table, we will find that sulfur is the least electronegative of all.
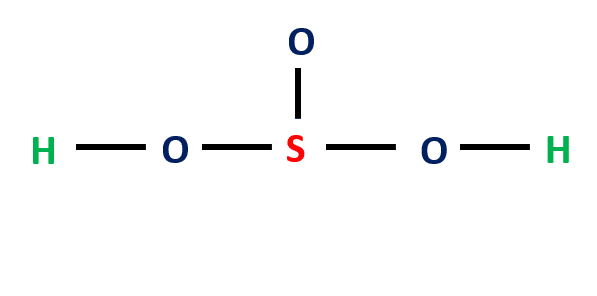
Step-3: Place electron pairs between the atoms
In the figure, one electron pair between two atoms is equivalent to one line (covalent bond). Out of 26 electrons, 10 will be used in pairs between atoms.
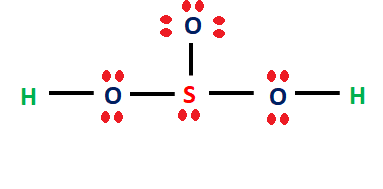
Step 4: Place remaining electrons around the other atoms
We need to distribute the 16 remaining valence electrons. Hydrogen can only contain a maximum of two electrons. Sulfur and oxygen can contain 8 electrons, so we add more electrons to them to complete the octet (8 electrons).
Key Points
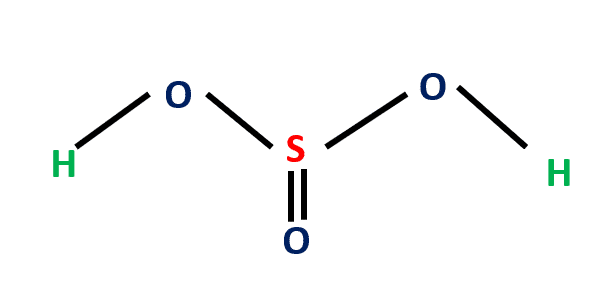
- Weak inorganic acid is considered an aqueous solution of SO2 in water.
- Its pure form is not available.
- Its solution gives the smell of SO2.
- It has a trigonal Pyramidal structure.
- Pungent burning sulfur odor.
- It exists in solution form.
- Upon heating at 150 degrees Celsius, H2SO3 can be decomposed into Sulfuric acid, water, and sulfur.
- It can also be obtained by reacting SOCl2 with Water.
- It is a diprotic acid, that contains two donatable ions.
- Molar mass of H2SO3 is 82.07 g/mol.
- The boiling point of H2SO3 is -60 degrees Celsius.
- It is corrosive to tissue and metals.
- It’s a major component of acid rain.
- the conjugate acid of hydrogen sulfide.
Molar Mass of H2SO3
The molar mass of Oxygen =15.9994 g/mol.
Hydrogen molar mass = 1.00794 g/mol.
The atomic mass of Sulfur = 32.065 g/mol.
Molar mass of H2SO3 = 2(1.00794)+32.065+3(15.9994)
=82.06288 g/mol.

Uses of H2SO3
- It can be oxidized to sulfuric acid or sulfate by accepting another oxygen atom.[Ref]
- Powerful reducing agent. Reduces chlorine to sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid.
- Good disinfecting agent.
- It is used to bleach paper products and straw products, like bags and hats.
Is Sulfurous acid is a strong acid?
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) is a weak acid; aqueous H2SO3 does not dissociate entirely into H+ (H3O+) and bisulfite ions, meaning that the bisulfite ion is comparatively stronger in maintaining a proton when there is a base, such as water.

Important Links
- Strength of H2SO3.
- Characterization of H2SO3.
- Sodium Sulphate-Properties
Related Links
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Sulfurous acid strong or weak?
Weak acids dissociate partially in the water, resulting in an equilibrium state containing the weak acid and its ions. Aqueous sulfurous acid will not fully dissociate into H+ (H3O+) and the bisulfite ion, implying that the bisulfite ion is comparatively stronger in retaining a proton when a base, such as water, is present (water is not solely basic; it is amphiprotic).
2. ka for H2SO3
The ability of an acid or basic to dissociate is measured using dissociation constants. These values are denoted as Ka for acids and Kb for bases. There are no units for these constants.
ka of H2SO3 is 1.3 * 10-2
Both Sulfuric acid and Sulfurous acid are diprotic acids, meaning they yield two protons on dissociation. However, sulfuric acid is a strong acid because dissociation of the first proton is most favored in it as compared to H2SO3.
H2SO3 is a Corrosive chemical. Any direct contact with it can severely irritate and burn the skin and eyes with possible eye damage. Breathing H2SO3 can irritate the nose and throat. Breathing H2SO3 can irritate the lungs causing coughing and/or shortness of breath.
It is a colorless gas that has a high solubility in water. In solution, it hydrates to sulphuric acid (H2SO3), which in turn dissociates to form ions of bisulfite (and sulfite (SO2–3).
Reducing agents like Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) have the ability to take up oxygen from the air and other substances that are rich in oxygen.
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
More Interesting Links
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Nh3 Molecular Geometry| Trigonal Pyramidal
Perchloric Acid| Is It Super Acid?
Hydrogen Bond| Definition & Easy Explanation
H2S Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Is Carbon Dioxide a Pure Substance?
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023