The molar mass of acetic acid is 60.052 g/mol. The acetic acid formula is CH3COOH and it is also known as Ethanoic acid. the pH of CH3COOH (1M solution) is 2.4. Keep reading to learn more about the properties and Lewis structure of CH3COOH, along with an explanation of glacial acetic acid.
Acetic Acid Lewis Structure

Atomic mass (CH3COOH)
(Atomic masses : C=12u; H=1u; O=16u)
Carbon atoms = 2;
Hydrogen atoms = 4;
Oxygen atoms = 2.
CH3COOH=1×C+3×H+1×C+2×O+1×H
=12+3+12+32+1 = 60u
Lewis Structure of CH3COOH (Ethanoic Acid)
From the structure, We can notice that CH3COOH has 8 bonds (or 16 shared electrons) and 4 lone pairs (8 unshared electrons). In order to draw the lewis structure of acetic acid, we need to follow the following steps:
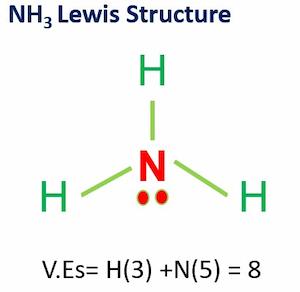
Step-1 (Determine the number of valence electrons in individual atoms)
Carbon has 4, oxygen has 6, and hydrogen has 1 valence electron.
Step-2 (Determine the number of valence electrons in CH3COOH )
Two carbon atoms times 4 electrons, plus two oxygen atoms times 6 electrons, plus four hydrogen atoms times 1 valence electron equals 24 valence electrons.
valence electrons in CH3COOH = 2(4)+2(6)+4(1)=24.
Step-3 (Place electron pairs between the atoms)
Draw lines between atoms. One electron pair between two atoms is equivalent to one line.
Step 4 (Place remaining electrons)
There are 8 bonds (16 shared electrons) and 4 lone pairs (8 unshared electrons).
Molar Mass Of CH3COOH
The molar mass of Oxygen =16.00 g/mol.
Hydrogen molar mass = 1.00794 g/mol.
Carbon molar mass = 12.011 g/mol.
Molar mass of acetic acid = 2(molar mass of C) + 4 (molar mass of H) + 2 (molar mass of O)
=2(12.011)+4(1.00794)+2(16.00)
=60.052 g/mol
Molar Mass of Acetic Acid-Key Points
- The molar mass of acetic acid is 60.052 g/mol.
Ethanoic acid (another name) - colorless liquid
- Unpleasant order.
- Soluble in water.
- 5-8% solution is called Vinegar.
- Also called Glacial acid.
- The melting point is 16.6 °C.
- The boiling point is 118 °C.
- The density is 1.05 g/cm³.
- pH of CH3COOH = 2.4 (1M solution).
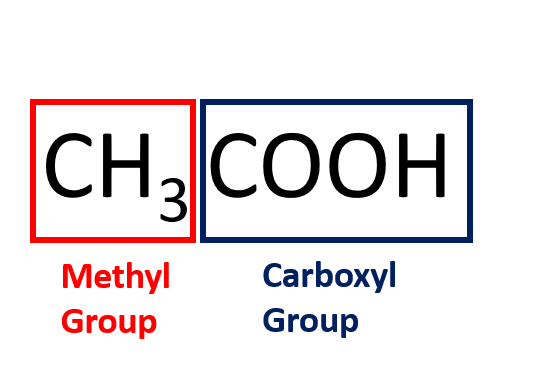
What is Acetic acid?
Acetic acid is also called ethanoic acid.
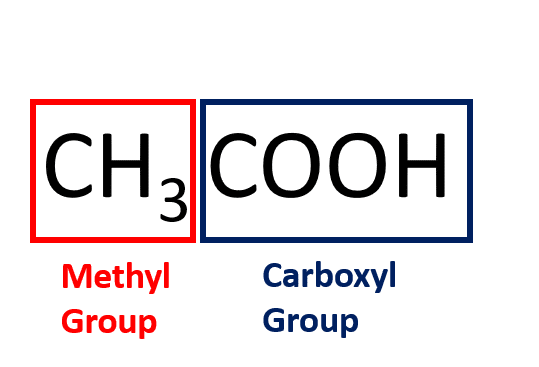
It is the most important of the carboxylic acids and consists of a methyl group attached to a carboxyl group.
It is made by methanol carbonylation, where methanol and carbon monoxide react to produce acetic acid.
CH3COOH is miscible with ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone, and benzene.
It is also soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide.
A dilute (5% by volume sol) CH3COOH is called vinegar.
Is Ethanoic acid a strong acid?
Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) is a very common weak acid because it doesn’t dissociate very much in solution. A weak acid is an acid that ionizes only slightly in an aqueous solution.

Acetic acid Uses
- 5-8 % CH3COOH solution is called vinegar and is widely used as a preservative in pickles.
- used in the manufacture of esters.
- It is sprayed on livestock silage to eliminate fungal and bacterial growth.
- CH3COOH is used in the preparation of metal acetates, which are used in some printing processes.
- Cellulose acetate is used in making photographic films and textiles.
- It is used as a solvent for resins, paints, and lacquers.
What is Glacial acetic acid?
Acetic acid is also called Glacial Acetic Acid in its anhydrous form. The name glacial acetic acid comes from the German name Eisessig (ice vinegar). Since CH3COOH forms ice-like crystals below room temperature (16.6 °C or 61.9 °F), it is also called “glacial acetic acid.”
Important Links
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
HCN Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
What is the Molar Mass of Nitrogen?
Author
Ms Sana Javed
Sana has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
She has a Mphil degree in pharmaceutics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Vinegar inhibits the growth of new bacteria. It is an ingredient in many chemical-based cleaning products.
It is a hazardous chemical if not used in a safe and appropriate manner.
Its 25% solution is highly corrosive to the skin and eyes and must be handled with extreme care.
CH3COOH can damage the internal organs if ingested or in the case of vapor inhalation.
CH3COOH is a very common weak acid because it doesn’t dissociate very much in the solution.
Molar mass of Acetic acid is= 60.052 g/mol.
More Links
- H2S Polar Or Nonpolar| Easy Explanation - April 5, 2021
- Atmospheric Pressure| Definition & Real-Life Examples - January 9, 2021
- Molar Mass of Acetic Acid| Easy-Explanation - January 8, 2021