O2 molar mass is 32 gram per mole. The molar mass of an element or molecule is the total mass in grams of all the atoms that comprise a mole of a certain molecule. Since oxygen (molar mass = 15.99 g/mol) does not exist as one atom, it is always O2 (32 g/mol).
Table of Contents
What is Oxygen (O2)?
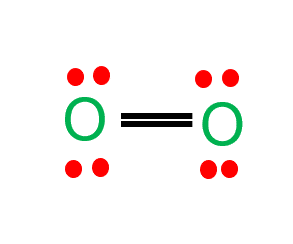
Oxygen (O2) is a diatomic, colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with 180-degree bond angles. The O2 Lewis structure is made up of two oxygen atoms linked in a pair. Many species rely on molecular oxygen to breathe, making it essential for survival. Oxygen (as a compressed gas) is also commonly used as an oxidizer in welding, metal cutting, and rocket engines.
| Name of molecule | Oxygen |
| Bond Angles | 180 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of Oxygen | Linear |
| The polarity of the O2 molecule | nonpolar |
| No of Valence Electrons in the O2 molecule | 12 |
| O2 molar mass | 32g/ml |
O2 Molecular Geometry
Oxygen is a diatomic molecule with linear molecular geometry and 180-degree bond angles.
Both oxygen atoms in the O2 molecule have identical electronegativity, and both atoms share equal ratios of bound shared electrons, resulting in a nonpolar molecule.
Oxygen Valence Electrons
Oxygen is in Group VI of the periodic table, so oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and four in the 2p subshell.
Key Points
- In the O2 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between two oxygen atoms.
- O2 is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas.
- Density of oxygen is 1.429 g/L.
- The boiling point is -183.0 C.
- Melting point −218.4 °C
- The O2 molar mass is 15.9994 g/mol.
- Oxygen has two allotropic forms, O2 and O3
- O2 molecule is nonpolar in nature.
Is O2 Polar or Nonpolar?
O2 is a nonpolar moleculele.
The four electrons that make up the double bond between the oxygen atoms in the O2 molecule are shared equally by both of them. Equal electronegativity indicates that each element has no partial charges.
Since neither atom pulls harder, it’s a non-polar covalent bond.
Oxygen Characteristics
- At room temperature, oxygen is a non-metal element that exists as a gas. It has two oxygen atoms in each of its molecules.
- Oxygen comprises about 50% of the earth’s crust.
- Respiration, the process of transferring energy from glucose to cells, requires oxygen.
- It is a gas at room temperature, and about 1/4 of the atmosphere by weight consists of oxygen.
- Water contains nearly 89% of combined oxygen.
- Calcium carbonate, which occurs in chalk and limestone marble, contains 48% oxygen.
- Silica, which is found in flint quartz, contains more than 50% oxygen.
- It is sparingly soluble in water and does not react with water.
- It is paramagnetic in nature and has two oxidation states.
- Burning requires the presence of oxygen. However, burning occurs only when the mixture of fuel and oxygen is sufficiently heated.
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- The O2 molar mass is 32 grams per mole.
- In the O2 Lewis structure, two oxygen atoms are connected together with a double bond.
- The bond angle is 180 degrees, and there are 12 valence electrons.
- O2 is a nonpolar molecule with linear geometry.
- There are four lone electron pairs in the oxygen molecule.
More Interesting Topics
Molar Mass of Acetic Acid| Easy-Explanation
Concentration Gradient Definition
Sodium Phosphate – Formula, Structure, Types, and Uses
Sulfurous Acid| Formula & Lewis Structure
Valence Electrons in Nitrogen
What is the Molar Mass of Nitrogen?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How to draw the lewis structure of SO2?
SO2 Lewis structure would be comprised of two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both S and O atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 12.
- The molecular geometry of SO2 is a trigonal planner.
- The three pairs of bonding electrons are arranged in the plane at an angle of 120 degrees.
- The sulfur’s valence electron is = 6
- The valence electrons of oxygen in SO2 are 6
2. What are unbonded pairs of electrons?
Unbonded pairs of electrons are unshared valence electrons.
They are also called lone pairs of electrons.
They are found in the outermost electron shell of atoms and can be identified by drawing lewis structure.
3. What is SO2?
SO2 (Sulfur dioxide) is the entity of a bond between sulfur and oxygen atoms.
It is a colorless, toxic, inorganic gas with a pungent smell like nitric acid.
SO2 gives a weak acid solution when dissolved in water.
It is naturally found in small amounts in the atmosphere and is a primary precursor of sulfuric acid.
4. What are the uses of oxygen?
Production of steel, plastics, and textiles, brazing, welding, and cutting of steel and other metals, rocket propellant, oxygen therapy, and life support systems in airplanes, submarines, spaceflight, and diving are all examples of common applications of oxygen.
5. Does oxygen have 6 or 8 valence electrons?
Because oxygen is in Periodic Group VI, it possesses six valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and four in the 2p subshell. Check out the full article here: oxygen valence electrons.
6. How many electrons does oxygen have?
A single oxygen atom has eight protons, eight electrons, and eight neutrons.
Oxygen is a stable isotope of oxygen with a nucleus of 8 neutrons and 8 protons. Its mass is 15.99491461956 u. Check the full topic “How many electrons does oxygen have?”.
Because of its linear, symmetrical form, carbon dioxide (CO2) is nonpolar. The electron density is drawn equally from both sides by the two oxygen atoms in either direction of the carbon atom. CO2 is nonpolar in nature because there is no uneven sharing of valence electrons.
The gas sulfur dioxide (SO2) has a polar character. It’s a polar molecule because of the electronegativity mismatch between the sulfur (2.58) and oxygen (3.44) atoms. Additionally, SO2 has a bent shape due to the existence of unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
SiO2 Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023


