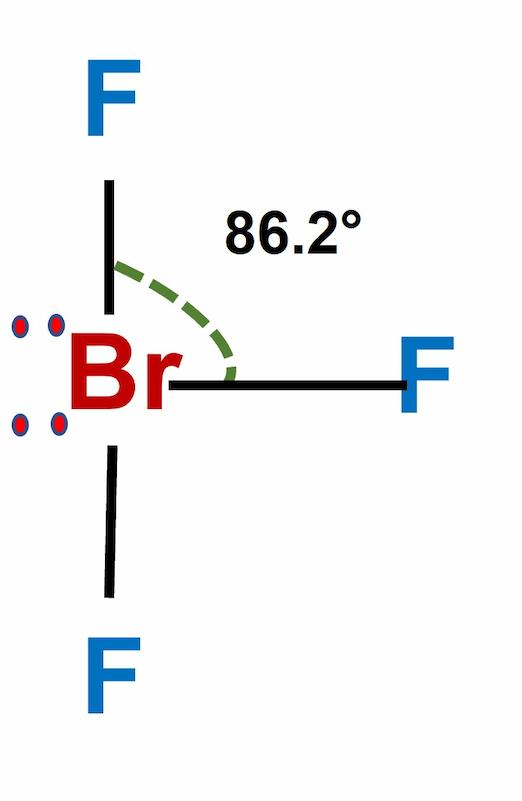
Bromine trifluoride (BrF3) is an interhalogen pale yellow liquid with a strong odor. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, although it interacts strongly with water and organic molecules. It’s an ionizing inorganic solvent and a strong fluorinating agent. BrF3 bond angle is 86.20.
| Name of molecule | Bromine trifluoride (BrF3) |
| BrF3 Bond Angle | 86.2 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry | T-shaped or Trigonal Bipyramidal |
| Hybridization | sp3d |
| The dipole moment | 1.19 D |
| molecular mass | 136.90 g/mol |
Table of Contents
BrF3 Bond Angle
BrF3 has a T-shaped or Trigonal Bipyramidal molecular geometry, with a bond angle of 86.2 °, which is somewhat less than the typical 90°. The repulsion created by the electron pairs is higher than that of the Br-F bonds, resulting in this angle.
Because the bromine atom has two lone pairs, the electrical repulsion between lone pairs and bound pairs produces shape distortion, resulting in the bent shape.
Is BrF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BrF3 is a polar molecule.
The polarity across the Br-F bond is generated by the difference in electronegativity of bromine and fluorine atoms, with bromine as the positive pole and fluorine as the negative pole.
Three fluorine atoms surround one bromine atom in bromine trifluoride.
The fluorine atom has an electronegativity of 3.98, while the bromine atom has an electronegativity of 2.96. The bromine atom occupies the center position due to its lower electronegative nature.
The electronic repulsion occurs because the bromine atom contains lone pairs on it.
According to the VSEPR theory, the repulsion between the lone pair and bond pairs creates a downward force on the Br-F bonds, bending the form of the molecule.
Important Points
- It reacts vigorously with water and other organic compounds.
- Due to the existence of three fluorine atoms linked together, it is a strong fluorinating agent.
- It occurs in a liquid form with a strong odor at typical temperature and pressure conditions.
- BrF3 dipole moment is non zero. Similarly, each of the three Br-F has a dipole with a non-zero value.
Polar versus Nonpolar Molecules
Polar molecules are formed when the electronegativity of the bonded atoms differs. When electrons are shared equally between atoms in a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other out, nonpolar molecules form (More details: Polar vs nonpolar molecules)
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In the BrF3 Lewis structure, the central sulfur atom has one lone pair and is bonded to four fluorine atoms
- The BrF3 bond angle is 86.2 degrees
- BrF3 is a polar molecule
- Due to the presence of three fluorine atoms linked together, it is a strong fluorinating agent.
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
Sulfurous Acid| Formula & Lewis Structure
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Hybridization of Bromine Trifluoride?
In its outermost shell, BrF3 has seven electrons. It contains two lone pairs and three Br—F covalent bonds after bond formation. The electron pair’s hybridization value is equal to 5, resulting in sp3d hybrid orbitals.
2. What is the Lewis structure for BrF3?
Bromine trifluoride is a compound that contains one bromine atom and three fluorine atoms. The center atom is bromine, which is surrounded by three fluorine atoms. Fluorine and bromine atoms have seven valence electrons. In their outermost shells, both atoms have seven electrons. (Read more: what is a lewis structure)
3. Does BrF3 have a dipole?
The polar covalent bond‘s dipole moment is always non-zero. Similarly, each of the three Br-F has a dipole with a non-zero value. The molecule’s net dipole also appears to be non-zero, with a direction that originates from the Br to the downward direction, i.e. the fluorine side.
4. Does BrF3 has a dipole moment?
The molecular dipole moment of bromine trifluoride is 1.19 D, where D stands for Debye.
5. Explain Chemical reactions?
Chemical reactions involve breaking chemical bonds between reactant molecules (particles) and establishing new bonds between atoms in product particles.
Examples of chemical reactions in everyday life include photosynthesis, rusting, baking, digestion, combustion, chemical batteries, fermentation, and washing with soap and water.
6. How to draw the lewis structure of SO2?
SO2 Lewis structure comprises two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both S and O atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 12.
- SO2 molecular geometry is a trigonal planner.
- The three pairs of bonding electrons are arranged in the plane at an angle of 120-degree.
- The sulfur’s valence electron = 6
- valence electrons of oxygen in SO2 are 6
7. What are unbonded pairs of electrons?
Unbonded pairs of electrons are unshared valence electrons.
They are also called lone pairs of electrons.
They are found in the outermost electron shell of atoms and can be identified by drawing Lewis structure.
8. What is SO2?
SO2 (Sulfur dioxide) is the entity of a bond between Sulfur and Oxygen atoms.
It is a colorless, toxic, and inorganic gas with a pungent smell like Nitric acid.
SO2 gives a weak acid solution when dissolved in water.
It is naturally found in small amounts in the atmosphere and is a primary precursor of Sulfuric acid.
9. H2S is polar or nonpolar?
Because of the tiny difference in electronegativity values of the Hydrogen (2.2) and Sulfur (2.58) atoms, H2S is a slightly polar molecule.
Furthermore, the existence of two lone pairs on opposing sides of the two Hydrogen atoms makes the molecule more polar and results in the bending shape geometrical structure of H2S. (Check full article H2S is polar or nonpolar).
10. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar compound. In BF3, the central boron atom has sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an unfilled p orbital on the Bron atom and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Because the Boron-Fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart, any net dipole in that plane is canceled out. Even if each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero because adding the bond vectors cancels everything out.
Check out the full article “Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”.
More Interesting Topics
H2S Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Perchloric Acid| Is It Super Acid?
Sulfurous Acid Formula & Lewis Structure
Nh3 Molecular Geometry| Trigonal Pyramidal
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
SO2 Polar Or Nonpolar
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023