Ozone (O3) is a gas that is naturally present in our atmosphere and is a highly reactive gas. Ozone is a very strong oxidizing agent and is highly unstable at higher concentrations. At high concentrations, ozone is decayed into diatomic oxygen.
O3 Lewis structure shows that the ozone molecule contains three oxygen atoms bound together by covalent bonds. This article explains step by step drawing of the O3 Lewis structure in detail.
| Name of molecule | Ozone (O3) |
| Bond Angles | 116.8 degrees |
| O3 molecular geometry | A bent trigonal planar shape |
| The polarity of the O3 molecule | Polar |
| No of Valence Electrons in the O3 molecule | 18 |
| Molar mass | 47.997 gmol-1 |
Table of Contents
Step by Step Construction of Lewis Structure
The following are the steps to construct the Lewis Structure.
Step-1: Count the valence electrons of atoms.
To draw the Lewis structure, we need to figure out the number of valence electrons in individual atoms as shown in the table below.
| Atom | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons (VEs) |
| 8O | 1S2 2S2 2P4 | 6 |
Valence electrons in O3 = 6+6+6 = 18 electrons
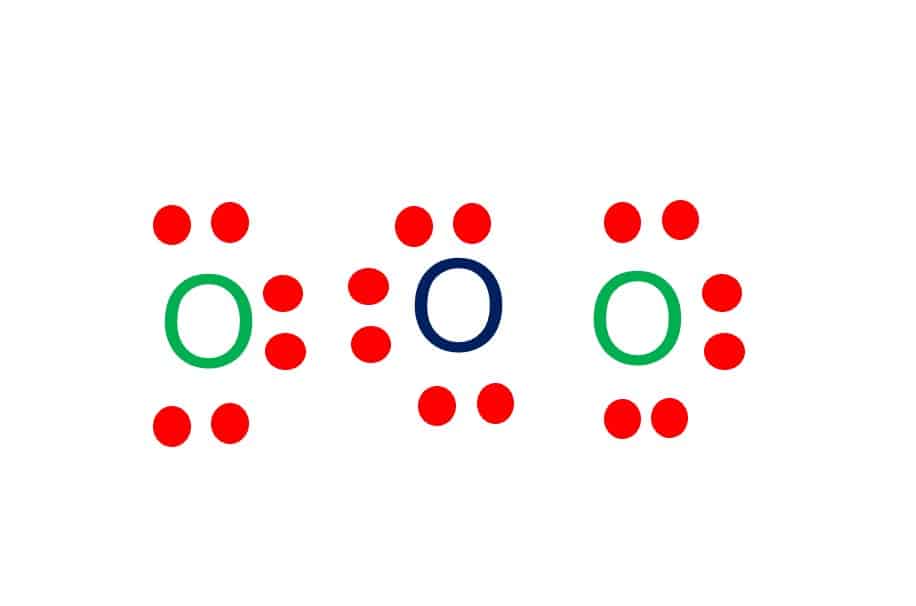
Step-2: Place electron pairs between the atoms
The Lewis diagram of O3 shows three oxygen atoms having eighteen dots, of valence electrons. Where six are arranged, around each oxygen atom.
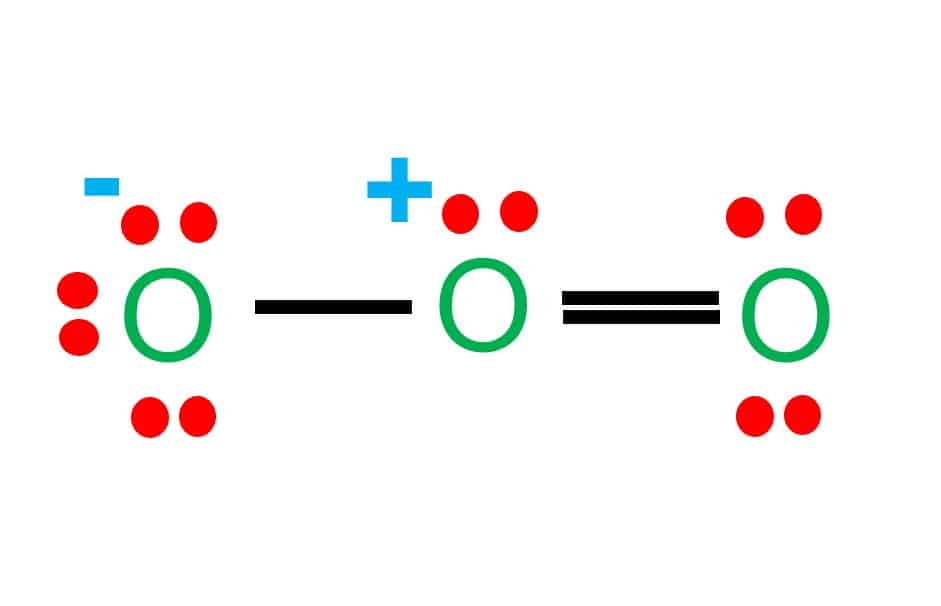
Step-3: Place remaining electrons around the other atoms
The lateral oxygen atoms have achieved octet as they have eight electrons surrounding them. But, the central atom only has six electrons around it.
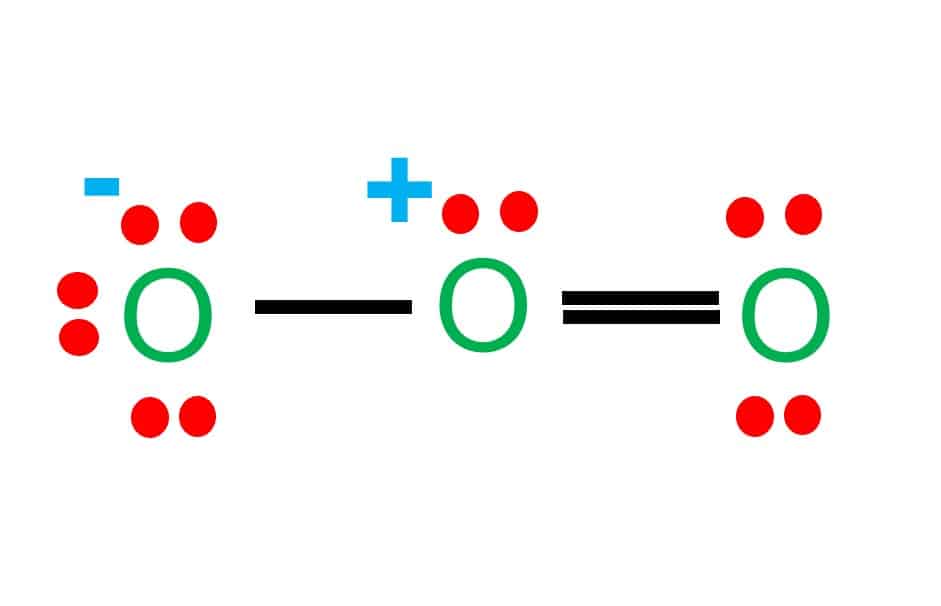
To complete the octet of the central atom, we must move two electrons from one of the lateral oxygen atoms and place them alongside the central oxygen atom.
Concerning the central oxygen atom, we now have one double bond and one single bond.
The resulting bond is a covalent bond.
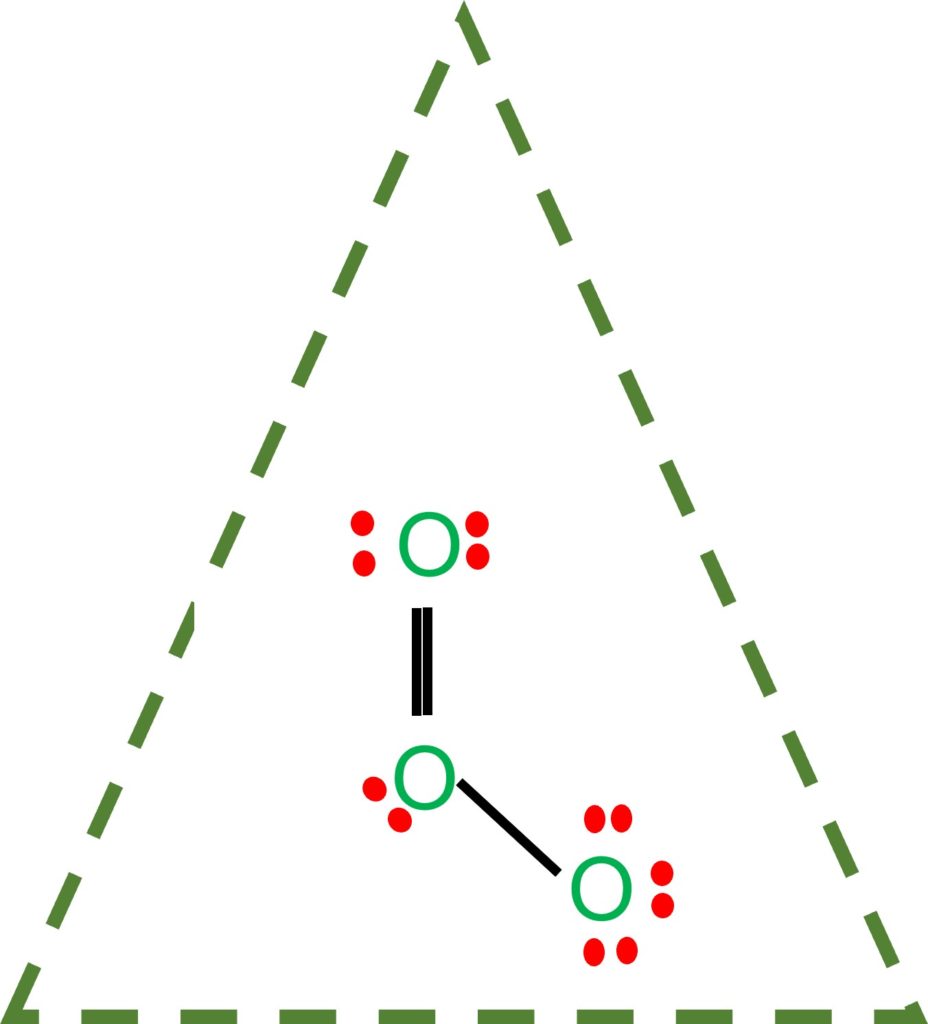
O3 Molecular Geometry
Ozone is a triatomic molecule with bent trigonal planar molecular geometry and bond angles of 116.8 degrees. In the O3 molecule, the central oxygen atom contains one lone pair of electrons.
O3 Lewis Structure- Key Points
- In the O3 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between the central oxygen atom and one lateral oxygen atom.
- O3 covers the whole globe and preserves life by absorbing the sun’s damaging ultraviolet-B (UV-B) rays.
- density = 2.14 kg/m3
- The boiling point is -112 °C.
- The molar mass of O3 is 47.997 g/mol.
- O3 molecule is polar in nature.

Uses of Ozone
- Ozone is used to deodorize air, purify water, and treat industrial wastes.
- Stratospheric ozone is “beneficial” because it shields living things from the sun’s UV rays. It naturally occurs in the high atmosphere, where it creates a protective barrier that protects humans from the sun’s damaging UV radiation.
Is O3 Polar or Nonpolar?
O3 is a polar molecule.
In an ozone molecule, the typical dipole moment value changes, and there are partial positive and negative charges present within the molecule.
The partial Positive charge will be carried by the ozone atom in the middle.
Dipole moments are then responsible for pushing the ozone molecule downward.
Because the lone electron pair produces a net dipole in O3, the ozone molecule is thought to be polar in nature.
Hybridization of Ozone (O3)
- The process of combining orbitals to produce hybrid orbitals is referred to as hybridization. The cornerstone of hybridization is how and why multiple atoms tend to interact with one another.
- The electronic configuration of the oxygen atom (Z = 8) is 1s22s22p4
- 2s orbital has two electrons and the rest six are present in 2px and 2py.
- Total no of orbitals= 1s and 2p
- Hence, the hybridization of the O3 molecule is sp2.
What is the Ozone layer?
Ozone, abbreviated as O3, is a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms. Ozone is created when heat and sunlight cause chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides (NOX) and volatile organic compounds (VOC), sometimes known as hydrocarbons.
The phrase “ozone layer” refers to the high concentration of ozone found in the stratosphere about 15–30 km above the earth’s surface. It covers the whole globe and preserves life by absorbing the sun’s damaging ultraviolet-B (UV-B) rays.
The ozone layer typically absorbs 97-99 percent of incoming UV-B radiation. Higher stratospheric ozone concentrations are thus important to ensure that life (including humans) on Earth’s surface is not exposed to hazardous UV-B radiation concentrations.
O2 Lewis Structure
Oxygen (O2) is a diatomic, colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with 180-degree bond angles. The O2 Lewis structure is made up of two oxygen atoms linked in a pair. Many species rely on molecular oxygen to breathe, making it essential for survival. Oxygen (as a compressed gas) is also commonly used as an oxidizer in welding, metal cutting, and rocket engines.
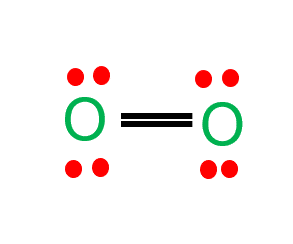
| Name of molecule | Oxygen |
| Bond Angles | 180 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of Oxygen | Linear |
| The polarity of the O2 molecule | nonpolar |
| No Valence Electrons in the O2 molecule | 12 |
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In the O3 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between the central oxygen atom and one lateral oxygen atom.
- The bond angle is 116.8 degrees and there are 18 valence electrons.
- O3 is a polar molecule with a bent trigonal planar shape.
More Links
Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
N2 Lewis Structure| Hybridization & Molecular Geometry
BF3 Lewis structure| Molecular geometry, Hybridization
Molar Mass of Acetic Acid
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How to draw the lewis structure of SO2?
SO2 Lewis structure would comprise two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both S and O atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 12.
- The molecular geometry of SO2 is a trigonal planner.
- The three pairs of bonding electrons are arranged in the plane at an angle of 120-degree.
- The sulfur’s valence electron = 6
- valence electrons of oxygen in SO2 are 6
2. What are unbonded pairs of electrons?
Unbonded pairs of electrons are unshared valence electrons.
They are also called lone pairs of electrons.
They are found in the outermost electron shell of atoms and can be identified by drawing lewis’s structure.
3. What is SO2?
SO2 (Sulfur dioxide) is the result of a link between the atoms of sulfur and oxygen.
It is a colorless, poisonous, inorganic gas with a strong odor similar to nitric acid.
When SO2 is dissolved in water, it produces a weak acid solution.
It is the main precursor of sulfuric acid and is naturally present in tiny levels in the environment.
4. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?
ClF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. According to the ClF3 Lewis structure, this molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. ClF3 is a polar compound.
5. What is the net charge of ozone molecules?
The ozone molecule has no net charge because the positive and negative charges cancel each other out. These charges keep rotating around the two atoms, forming the ozone molecule’s resonance structure.
6. What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the total number of electrons present on an atom’s outermost shell. Only the valence electrons participate in the formation of chemical bonds. For bond formation, they are either transmitted or shared (totally or partly).
Because of its linear, symmetrical form, carbon dioxide (CO2) is nonpolar. The electron density is drawn equally from both sides by the two oxygen atoms in either direction of the carbon atom. CO2 is nonpolar in nature because there is no uneven sharing of valence electrons.
The gas sulfur dioxide (SO2) has a polar character. It’s a polar molecule because of the electronegativity mismatch between the sulfur (2.58) and oxygen (3.44) atoms. Additionally, SO2 has a bent shape due to the existence of unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
Related Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) Lewis structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
BrF3 (Bromine trifluoride) Molecular Geometry, Bond Angles
How many electrons does oxygen have?
SiO2 Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023