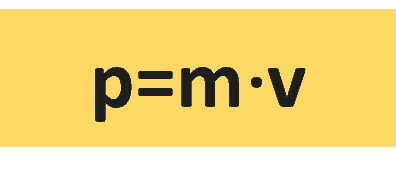Linear motion (also known as rectilinear motion) is a one-dimensional motion along a straight line that can be mathematically described using only one spatial dimension. In layman’s terms, linear motion is movement along a straight line, whereas nonlinear motion is any movement that is not along a straight line. Linear motion could be uniform or non-uniform. Some examples of linear motion are a bullet fired from a gun, a ball falling from a cliff, and a person walking straight.
Another interesting term is Linear momentum which is a vector quantity and is defined as the product of an object’s mass, m, and its velocity, v. Linear momentum is denoted by the letter p.

- Motion in physics is defined as a change in the position of an object with the passage of time.
- Translational motion is the motion in which all points of a moving body move uniformly in the same line or direction.
- Translational motion is classified into two types: rectilinear motion and curvilinear motion.
- Linear motion (or rectilinear motion) means moving in a straight line.
- Curvilinear motion is when the body moves in a curved path, similar to projectile motion.
Table of Contents
Daily Life Examples of Linear Motion
Linear motion is a type of motion in which an object moves in a straight line. Here are some examples of linear motion in daily life:
- A train moving down a track
- A person walking in a straight line
- A car driving down a road
- A ball rolling across a flat surface
- A pendulum swinging back and forth
- A person pushing a shopping cart in a straight line
- A roller coaster moving along a track
- A person jumping rope
- A race car driving on a straight track
- A spinning wheel with a bicycle.
Significance of Linear Motion Concept
Linear motion is important in many areas of science, engineering, and daily life because it is a basic form of motion that can be described and analyzed using simple mathematical models. Here are some reasons why linear motion is important:
- Understanding of basic physics: Linear motion is a fundamental concept in physics, and understanding how objects move in a straight line is essential for understanding more complex forms of motion, such as circular and elliptical motion.
- Engineering and design: Linear motion is used in many engineering and design applications, such as in the design of machines and mechanical systems. The ability to predict and control linear motion is crucial for the operation of many machines, including automobiles, trains, and elevators.
- Industrial processes: Linear motion is used in many industrial processes, such as in the production of goods, where objects are moved along a production line. A basic understanding of linear motion is necessary for optimizing the efficiency and productivity of these processes.
- Sports: Linear motion is important in many sports, such as running, jumping, and throwing. Athletes must be able to control their linear motion in order to perform at their best.
- Everyday life: Linear motion is also important in our everyday lives, as we move about and carry out our activities. Understanding linear motion helps us to move efficiently and safely, whether we are walking, driving, or riding a bicycle.
These are just a few examples of why linear motion is important in various fields and aspects of daily life. It is a fundamental concept that has wide-ranging applications and is essential for many areas of science and technology.
Related Topics
Relativistic Kinetic Energy
Power Units- The Basics
Mechanical Energy Formula & Examples
Can Momentum be Negative?
Velocity Time Graph
Can Displacement be Negative?
Can Work Be Negative?| Easy Explanation
Summary
Linear motion is a one-dimensional motion along a straight line that can be represented mathematically with only one spatial dimension. Linear motion can be both uniform and non-uniform. A bullet fired from a pistol, a ball falling from a cliff, and a person walking straight are all instances of linear motion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below
1. Can force be negative?
To answer the question “can force be negative”, we need to understand the concept of positive direction and negative direction.
- Force is negative If the applied force is in opposite direction to the displacement of the moving object.
- Forces that are aimed at the right are usually called positive forces.
- Forces that are aimed to the left are usually said to be in a negative direction.
2. What is instantaneous velocity?
The velocity of an object at any single instant or point is called instantaneous velocity.
It is similar to average velocity, except the time interval is infinitely small.
The formula for instantaneous velocity is the limit as the time approaches zero of the change in displacement over the change in time.

3. What is the momentum equation?
The momentum equation is simply the product of the mass and velocity of a moving object.
If an object is moving and has mass, then it has momentum.
The momentum of a body refers to the quantity of motion a body possesses due to its mass and velocity.
4. What is the kinetic energy formula?
A moving object’s kinetic energy equals half of the product of its mass and its velocity squared.
Because an object’s mass can never be zero and the square of velocity is positive, therefore kinetic energy is always positive.
5. What is energy definition science?
In physics, energy is the ability to perform work. It can take many forms, including potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, radioactive, and others. Furthermore, there is heat and work—that is, energy in the transmission of energy from one body to another.
6. What is the work-energy equation?
According to the work-energy theorem, the net work done on an item by forces equals the change in its kinetic energy.
7. What is the potential energy formula?
For the gravitational force, the formula of potential energy equals mgh, where m is the mass in kilograms, g is the gravity acceleration (9.8 m/sec2 at the earth’s surface), and h is the height in meters.
8. What is strain energy?
Strain energy is a form of potential energy which is stored within materials that have been subjected to strain deformation. When an item is deformed from its unstressed state, the external work done on it is transformed into (and is considered equivalent to) the strain energy contained in it. It is measured in N-m or Joules.
9. Can displacement be negative?
Displacement can be negative since it is a vector variable that depends on magnitude and direction. The negative sign just indicates the direction. Check the full article “can displacement be negative?”.
10. What is a state function?
A state function is a property that depends on the state of a system and is independent of the path taken to get it. Pressure and temperature, for example, are state functions.
11. Can momentum be negative?
Momentum is a vector quantity that is calculated by multiplying the mass of an item by its velocity. If the item’s velocity is negative, i.e. the object is travelling in the negative direction, the momentum will be negative as well. Check the full article “can momentum be negative?”.
W = mgh = 10 x 9.8 x 10 = 980J = 0.98kJ
mass = 1kg
height =1meter
W = mgh =1 x 9.8 x 1 = 9.8 J (Positive value)
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
More Interesting Topics
How Many Cups in a Gallon?
The Density of Water lbs/U.S gal
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Gravitational Potential Energy (w=mgh)
How Much Does a Gallon of Water Weigh?
Is Nh3 Polar?
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023