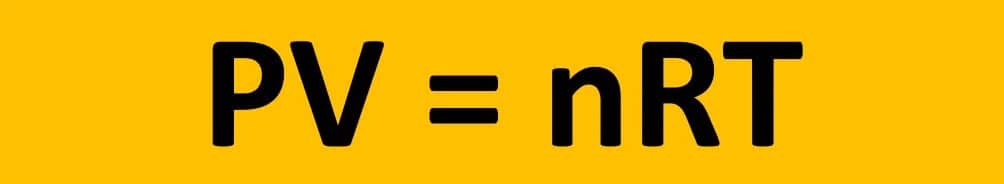Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been liquefied for transportation and storage.
Natural gas is almost entirely made of methane, while it does include trace amounts of other gases such as ethane, propane, butane, and pentane. Methane is made up of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms in a molecule.
Liquefying methane (natural gas) allows for the cost-effective transportation of gas across oceans or, in a few cases, by truck to tiny, dispersed users. In simple words, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state (liquefied), at about -260° Fahrenheit, for shipping and storage.
Although LNG takes up 600 times less space than natural gas, it must be stored at temperatures below 160 degrees Celsius and under pressure. When LNG arrives at its destination, it is converted back to a gaseous condition and used as an energy source. LNG is also utilized as a direct transportation fuel for ships and automobiles.

Table of Contents
Liquification of Natural Gas
Natural gas (methane) is a colorless, odorless, and highly combustible gas that is utilized to generate energy and heat houses all over the world. When the pressure on a natural gas increases, its molecules get closer together, and its temperature decreases, removing enough energy for it to transition from the gaseous to the liquid.
In addition, LNG is much denser than compressed natural gas (CNG). This means that significantly more gas may be transferred for the same volume flow. The LNG supply chain includes the following steps:
- Production
- Liquefaction
- Transportation
- Regasification.
LNG technology has enabled the utilization of natural gas from distant places of the world where it previously had no economic value and had to be flared (burned). LNG carriers, which are furnished with supercooled cryogenic tanks, transport LNG from far places.
Some heavy-duty vehicle fleets are switching to LNG as their preferred fuel. LNG enables more energy to be stored in a smaller container onboard a vehicle. Using LNG and natural gas to fuel automobiles decreases greenhouse gas emissions by 30-40% while also saving money on vehicle maintenance. (From www.fueleconomy.gov).
Molecular Structure of LNG
Natural gas is almost entirely composed of methane (CH4), the most basic hydrocarbon component. LNG is typically composed of 85 to 95 percent methane, a few percent ethane, even less propane and butane, and trace quantities of nitrogen.
Real Life Significance
| Real-Life Significance of LNG | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Security | Diversifies sources of natural gas supply, reducing dependence on any one supplier |
| Economic Benefits | Provides significant economic benefits, including job creation, increased investment, and improved trade balance |
| Reduced Emissions | Produces fewer emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter compared to other fossil fuels, making it a cleaner source of energy. Helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. |
| Transportation Sector | Use of LNG as a fuel in transportation, such as in heavy-duty trucks and marine vessels, can help reduce emissions and improve air quality in cities. |
| Power Generation | LNG can be used as a fuel for power generation, which can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve the efficiency of power production. |
| Energy Access | In remote areas where there is no access to natural gas pipelines, LNG can be transported by truck or ship to provide a reliable source of energy. |
| Backup Supply | LNG can serve as a backup supply of natural gas during periods of peak demand or supply disruptions. |
Summary
Natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state (liquefied) at roughly -260° Fahrenheit for transportation and storage is known as liquified natural gas (LNG). The volume of liquid natural gas in a natural gas pipeline is roughly 600 times smaller than the volume of gaseous natural gas. The major advantage of LNG is that it makes natural gas transportation from origin to endpoint easier.
Related Links
Heat Flux-An Overview
Thermite Welding- An Overview
Power Units- The Basics
Thermal Energy Equation- Simple Overview
Momentum Equation| Definition and Examples
Static Pressure| Definition, Meaning, and Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
| # | Question | Answer |
| 1 | What is Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)? | Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state, which makes it easier and safer to transport and store. |
| 2 | What is the process of liquefying natural gas? | The process of liquefying natural gas involves cooling the gas to approximately -260°F, at which point it condenses into a liquid form. |
| 3 | What are the benefits of using LNG as a fuel? | Benefits of using LNG as a fuel include lower emissions, reduced transportation costs, and increased energy security. |
| 4 | What are the safety considerations for handling LNG? | Safety considerations for handling LNG include proper training, use of appropriate equipment, and maintaining strict safety protocols. |
| 5 | What is the role of LNG in the US energy mix? | LNG plays an increasingly important role in the US energy mix, particularly in meeting peak demand for natural gas and in export markets. |
| 6 | What are the environmental benefits of using LNG as a fuel compared to other fossil fuels? | Environmental benefits of using LNG as a fuel include reduced emissions of greenhouse gases, sulfur dioxide, and other pollutants. |
| 7 | What is the potential for using LNG in the transportation sector? | The potential for using LNG in the transportation sector is significant, particularly for heavy-duty trucks and marine vessels. |
| 8 | What are the economic benefits of exporting LNG from the United States? | Economic benefits of exporting LNG from the United States include increased economic growth, job creation, and trade balance improvements. |
| 9 | What are the challenges associated with developing LNG infrastructure in the United States? | Challenges associated with developing LNG infrastructure in the United States include regulatory hurdles, high capital costs, and public opposition. |
| 10 | How is LNG stored and transported? | LNG is typically stored in insulated tanks and transported by specialized LNG carriers or in small containers using trucks or rail. |
1. Which is better LNG or LPG?
LNG is safer than LPG since it is neither refrigerated nor under pressure. CNG is safer than both LPG and LNG since it is lighter than air and hence releases into the atmosphere when it spills. LPG is commonly utilized in the refrigeration, agriculture, and industrial sectors.
2. What is liquid pressurized gas?
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), like coal, natural gas, and crude oil, is a fossil fuel. Unlike the others, LPG is never found on its own in nature; it is always found in combination with either natural gas or crude oil. In reality, LPG is a byproduct of the processing of these fuels. Approximately 60% of LPG is produced during natural gas extraction, with the remaining 40% recovered during crude oil refining.
3. What is the energy content of LNG?
LNG has an energy content ranging from 24 MJ/L to 21 MJ/L. LNG has an energy density of 0.41 kg/L to 0.5 kg/L, depending on temperature and pressure. LNG has a 2.4 times higher energy density than CNG. This makes transportation more cost-effective.
4. How can we increase the efficiency of the Otto cycle?
The efficiency of an Otto engine can be improved by running it on lean fuel (which consumes additional air) or by increasing the compression ratio.
5. What is the weight of LNG?
LNG has a density of 430 kg/m3 to 470 kg/m3 (3.5 to 4 lb/US gal). Because LNG has a density less than half that of water, it will float if spilled over water.
6. Do aerosols block sunlight?
Aerosols are microscopic particles that float in the Earth’s atmosphere. They have a cooling impact because they obstruct sunlight that would otherwise reach the globe.
7. How is static electricity useful for solar panels?
Researchers at MIT have invented a novel approach that utilizes static electricity to clear dust from solar panels, potentially saving 45 billion liters of water every year. Check the full article.
8. What are the disadvantages of LNG?
LNG releases considerable cold energy owing to the phase change of the natural gas, resulting in serious environmental pollution.
9. What are the advantages of natural gas?
- It is less expensive than others fossil fuels.
- Most environmentally friendly fossil fuel because it burns cleaner.
- Efficient storage and transportation flexibility compared to renewable energy.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023