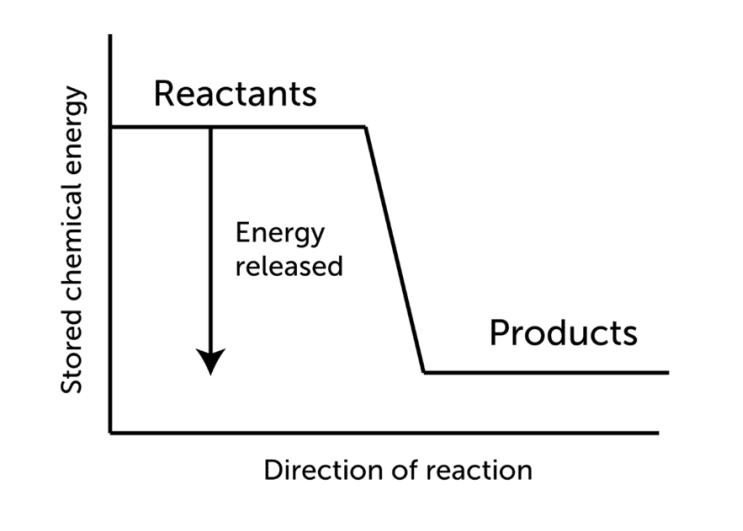
Hess’s law, also called Hess’s law of constant heat summation or Hess’s law of heat summation states that the heat absorbed or evolved (or the change in enthalpy) in every chemical reaction is a constant quantity that is independent of the reaction route or the number of steps needed to accomplish the reaction. In simple words, an overall chemical reaction’s energy change is equal to the total of the energy changes in the individual reactions that make it up.

Table of Contents
What Is Enthalpy in Simple Terms?
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic quantity that represents a system’s total heat content. It is the sum of the system’s internal energy as well as the product of pressure and volume. The enthalpy, H, is equal to the sum of the internal energy, E, and the product of the system’s pressure, P, and volume, V.
H = E + PV is the mathematical formula for it. Its unit is Jmol−1
Hess’s Law
The enthalpy change (heat of reaction at constant pressure) in a chemical reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states. The law is based on the first law of thermodynamics and energy conservation.
According to Hess’s law, It’s possible to break down a chemical reaction into numerous stages and calculate the overall energy of the process using standard enthalpies of formation.
Empirical data, generally obtained by calorimetry, is used to construct standard enthalpy tables. It is easy to calculate whether a more complicated reaction is thermodynamically favorable or not using these tables.
In addition to calculating the enthalpy of a reaction rather than directly measuring it, Hess’s law is used to:
- Determine electron affinities based on theoretical lattice energy.
- Calculate the heat transfer between phases.
- Calculate the heat change when material changes allotropes
- In a reaction, calculate the heat of formation of an unstable intermediate
- Find the lattice energy of ionic compounds.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics says that before and after any (physical or chemical) change, the total energy of the substances should be equal. The entire energy of the reactant must equal the total energy of the product, according to the law.
Importance Of Hess’s Law
- Every substance possesses internal energy. This energy is determined by the type of force present in the substance as well as the temperature.
- When a material goes through chemical processes, some bonds between atoms are broken and others are formed. Energy is used in the breaking and forming of bonds.
- As a result, product substances may have less, the same, or more energy than reacting substances in reactions.
- As a result, reactions can either release heat or absorb heat, making them exothermic or endothermic.
- Understanding the energy changes in every reaction is critical for manipulating the reactants and products in a chemical process to meet our needs.
- Internal energy change E denotes heat energy changes measured at constant volume, whereas enthalpy change H denotes heat energy changes measured at constant pressure.
- Only the net value of all reactions or products produced is determined by the experimental data. The enthalpy change of an intermediate reaction step or any intermediate product cannot be measured experimentally.
- Hess’s law is helpful for determining non-measurable enthalpy changes in physical and chemical processes, and it is the sole technique to do so.
Hess’s Law Applications in Daily Life
- This equation may theoretically be used in any chemical reaction, and companies that rely on reactions can determine if this is the most efficient way to generate the goods depending on the amount of energy required or released.
- To calculate the number of calories in a food, the quantity of energy generated by a body breaking down the bonds in the glucose must be calculated.
- Automobile manufacturers, for example, must determine how much energy the engine consumes or generates while burning fuel.
What is a Chemical Reaction?
When one or more compounds, known as reactants, are transformed into one or more distinct substances, known as products, a chemical reaction occurs. Substances include chemical elements and compounds. In a chemical reaction, the component atoms of the reactants are rearranged, resulting in the creation of different substances as products.
Summary
- The change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in different steps.
- The First law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be generated or destroyed in an isolated system.
- Hess’s law has applications in energy calculations of fuel, calories calculations of food, and feasibility of a chemical reaction
Important Links
Hydrogen Bond| Definition & Easy Explanation
Concentration gradient
Atmospheric Pressure
Perchloric Acid| Is It Super Acid?
Sulfurous Acid Formula & Lewis Structure
Malus Law- Definition, Concept, and Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an electron affinity?
Electron affinity (EA) is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom to produce a negatively charged ion.
2. What is atmospheric pressure?
The force exerted by the weight of the atmosphere per unit area is known as atmospheric pressure. One atmosphere equals 1,013 millibars of mercury, or 760 millimeters (29.92 inches). As height rises, atmospheric pressure decreases.
3. Room temperature definition in simple words?
The range of temperatures in which humans are comfortable is referred to as room temperature. A minimum room temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) is recommended for babies, children, the elderly, and those who are unwell, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). It has no set temperature, however, it is usually between 20 and 25 degrees Celsius (68 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit).
4. Enthalpy in simple words?
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic quantity that measures a system’s total heat content. It is the total of the system’s internal energy, as well as the product of pressure and volume.
The product of the system’s pressure, P, and volume, V, plus the internal energy, E, is the enthalpy, H.
H = E + PV is the mathematical formula for it.
5. Explain Chemical equilibrium?
Chemical equilibrium is a state in which no net change in the quantities of reactants and products occurs during a reversible chemical process.
There is no net change in the quantities of chemicals involved when the two opposing reactions occur at identical rates or velocities. At this point, the reaction can be regarded as complete; that is, the maximal conversion of reactants to products has been achieved for a given reaction state.
6. What is Hess’s law equation?
The heat absorbed or evolved (or the change in enthalpy) in every chemical reaction is a constant quantity that is independent of the reaction pathway or the number of steps required to complete the reaction, according to Hess’s law of heat summation.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023