Chemical reactions are classified as endothermic or exothermic based on the energy transfer between the surrounding environment and the system where the reaction is taking place. There are two methods for determining whether a chemical reaction is endothermic or exothermic:
a. observe the temperature change or the reaction
b. Determine the enthalpy change (ΔH) between the reactants and the products.
The primary distinction between endothermic and exothermic reactions is that endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, whereas exothermic reactions release energy into them. In addition, A chemical reaction with a positive ΔH is said to be endothermic, while a chemical reaction with a negative ΔH is said to be exothermic.
Table of Contents
What is an Exothermic Reaction?
The temperature of the products in endothermic reactions is typically lower than that of the reactants as shown in the figure below.
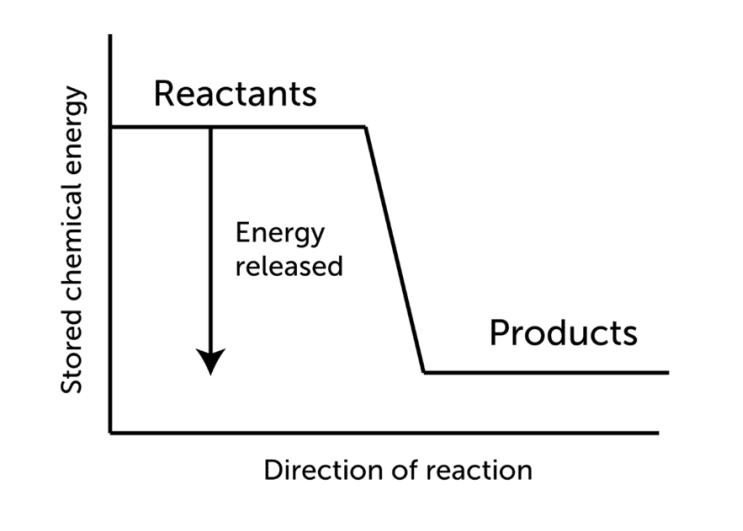
Exothermic reactions require additional energy to convert reactants into products. As a result, for exothermic reactions, the change in enthalpy, denoted by delta ΔH, will be negative.
Examples of Exothermic Reactions
- When water freezes into ice cubes, energy is released in the form of heat.
- The process of snow formation is an exothermic reaction
- Setting Cement And Concrete
- Combustion process
- Rusting of iron
- lighting a candle is an exothermic reaction
- phase transitions from the liquid to the solid state
- Digestion of food
- the reaction between quick lime and water is exothermic
- freezing of water in ice is an exothermic reaction
- Sponification process
- Thermite welding
What is an Endothermic Reaction?
The temperature of the products in exothermic reactions is typically above that of the reactants as shown in the figure below.
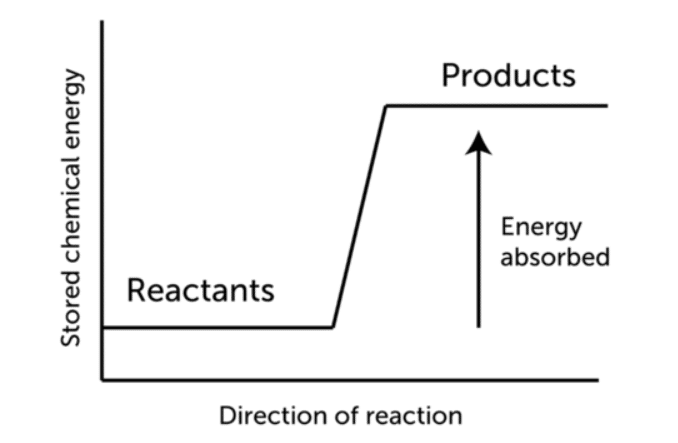
Enthalpy is absorbed from the surroundings as reactants are converted to products in an endothermic reaction. The reaction’s enthalpy change is positive. For instance, In the case of methane combustion, the enthalpy change (ΔH) is negative because heat is released by the system.
Examples of Endothermic Reactions
- Sweating is an endothermic process
- Boiling of Water
- photosynthesis
- evaporating liquids
- alkane cracking
- Cooking s an endothermic reaction
- Melting is an endothermic process
- dissolving table salt in water is endothermic
- vaporization (liquid to gas)
- Condensation reaction
- Sublimation process
Difference between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
| Endothermic | Exothermic |
| A reaction in which the system absorbs energy in the form of heat from its surroundings. | A reaction that releases heat as a type of energy from the system. |
| The energy from the surroundings is absorbed into the reaction. | The system’s energy is released into the environment. |
| Heat is released as a kind of energy. | Heat, electricity, light, and sound are released as a kind of energy. |
| Examples include ice melting, evaporation, cooking, gas molecules, and photosynthesis. | Examples include rusting iron, settling, chemical bonds, explosions, and nuclear fission. |
| entropy increases (ΔS > 0) | disorder decreases (ΔS < 0) |
| increase in enthalpy (+ΔH) | decrease in enthalpy (-ΔH) |
| Examples of an endothermic reaction: – Photosynthesis – Melting ice – Evaporating liquid water – Cracking alkanes – Cooking an egg | Examples of an exothermic reaction: – Combustion reaction – Respiration – Corrosion of metal (an oxidation reaction) – Dissolving an acid in water |
Summary
- Energy is constantly released during an exothermic reaction, often in the form of heat.
- Exothermic reactions characterise all combustion reactions. A substance burns when it combines with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
- Endothermic reactions require a constant input of energy, often in the form of heat.
- Photosynthesis is one of the most important endothermic reactions. Light provides the energy required for photosynthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How combustion is an exothermic reaction?
All combustion reactions are exothermic. A substance burns when it combines with oxygen during a combustion reaction. When substances burn, they usually emit energy in the form of heat and light.
For instance, The combustion of wood is an exothermic reaction that releases a lot of energy as heat and light.
2. Do exothermic reactions increase entropy?
The external entropy (entropy of the surroundings) increases during an exothermic reaction. The external entropy (entropy of the surroundings) decreases during an endothermic reaction.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023