Kinetic energy (K.E) is the energy that a moving object has due to its motion. The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The kinetic energy formula of a moving object equals one-half the product of its mass, and the square of its velocity.
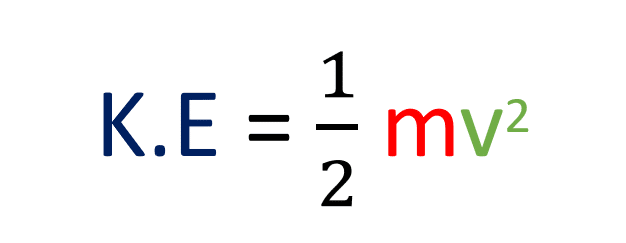
Table of Contents
Examples of Kinetic Energy
- Running water has kinetic energy
- Moving air has K.E and is used to derive windmills and push sailing boats.
- A bullet fired from a gun has kinetic energy and can penetrate a target.
- As the charges that cause the energy are moving, electrical energy is a form of kinetic energy.
Can Kinetic Energy be Negative?
A moving object’s kinetic energy is equal to half of the product of its mass and the square of its velocity.
Because an object’s mass can never be zero and the square of velocity is positive, the answer is positive.
Therefore, the answer to the question “Can kinetic energy be negative?” is no.
In addition, kinetic energy is the energy possessed by a body due to its motion.
The greater the speed and mass of the moving body, the greater its K.E.
The word “kinetic” comes from the word “kinesis,” which means motion.
For more insight, check out the full article “Can kinetic energy be negative?”.
Kinetic Energy Units
- Joules (MKS system).
- 1 erg (CGS system, 1 erg = 10-7Joules).
- Electron volt (atomic/subatomic scale).
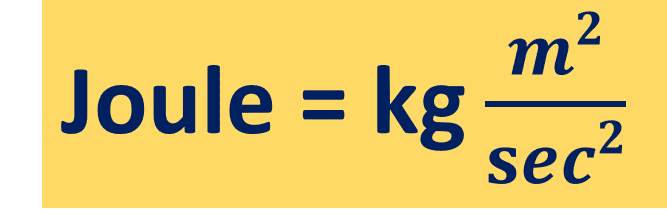
Key Points
| Kinetic energy definition | A moving object’s kinetic energy is equal to half of the product of its mass and the square of its velocity. |
| Kinetic energy formula | K.E = 0.5 m v2 |
| Kinetic energy unit | kg.m2/sec2 |
| Daily life examples of kinetic energy | Movement of cue ball rolling on a billiards table, working of a windmill, working of hydro turbines, and the movement of planets around the sun. |
| Can kinetic energy be negative? | Kinetic energy cannot be negative as it is equal to half of the product of an object’s mass and the square of its velocity. Since an object’s mass can never be zero and the square of velocity is positive, |
Kinetic Energy Types
Translation Kinetic Energy
Translational K.E = (1/2)(mass)(velocity)2.
Mass is the amount of matter contained within an object, and velocity is the speed of a moving object in a particular direction.
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Rotational K.E = (1/2)(Moment of Inertia)(angular velocity)2.
The moment of inertia is the angular mass or rotational inertia of a rigid body, and angular velocity is a vector measure of rotation rate.
Kinetic Energy Definitions in Simple Words
- Kinetic energy is defined as the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion.
- The translational K.E of a body is equal to one-half the product of its mass, m, and the square of its velocity, v, or (1/2)mv2.
- The rotational K.E of a body is equal to one-half the product of its moment of Inertia, I, and the square of its angular velocity, ω, or (1/2)Iω2.
What is Work?
Work is a force acting on an object in the direction of motion.
It is the product of force (F) and displacement (S) in the direction of the force.
It is a scalar quantity, and its unit is the joule.
Work done = force x displacement.
Please refer to the full article “Can work be negative?”.
What is 1 Joule?
1 Joule is the amount of work done when a force of 1 Newton is applied over 1 meter of distance.
Joule = N.m
Joule= kg*m2/sec2
Kinetic Energy Formula Derivation
Consider a body of mass “m” moving with velocity “v” on a rough surface.
The body stops after moving through a distance “S” due to frictional force on it.
As body possesses K.E and is capable to do work against opposing force F until it stops and loses all of its K.E. In this case, Kinetic energy equals the work done by the body.
The initial velocity (vi) of the body is v and the final velocity (vf) is zero.
K.E=Work = FS
F=ma and a= -F/m (acceleration is negative as motion is opposed)
2aS =vf2-vi2 (Newton law of motion)
2(-F/m)S= (0)2-(v)2
-2FS/m=-v2
FS =(1/2)(m)v2 = K.E
Quick Links
- Difference Between Kinetic and Potential Energy.
- Instantaneous Velocity| Easy Key Points
- Room Temperature| Comfortable Temperature
Can Velocity Be Negative?
Since velocity is a vector quantity, it can be negative. A positive velocity denotes that the object is traveling in the positive direction as defined by the coordinate system, whereas a negative velocity denotes that the object is moving in the opposite direction. Simply said, when velocity turns negative, it is the speed in the opposite direction.
To get more insight into the topic, please refer to the article “can velocity be negative?“
Work-Energy Theorem
According to the work-energy theorem, the work done by the sum of all forces acting on an object equals the change in kinetic energy of the object (or) the net work done on a system equals the change in kinetic energy. For equation and derivation of work-energy theorem check the full article “Work energy theorem”.
Related Topics
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
Ultimate Source of Energy
Relativistic Kinetic Energy
Power Units- The Basics
Work-Formula, Definition, & Units
Summary
The kinetic energy formula equals the half product of mass and the square of velocity.
The mass of an object is always positive and the square of velocity makes the total K.E a positive value.
The total kinetic energy of a body is the sum of the kinetic energies resulting from each type of motion.
The faster the motion, the more kinetic energy the object has.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a state function?
A state function is a property that depends on the state of a system and is independent of the path taken to get it. Pressure and temperature, for example, are state functions.
2. Can momentum be negative?
Momentum is a vector quantity that is calculated by multiplying the mass of an item by its velocity. If the item’s velocity is negative, i.e., the object is traveling in the negative direction, the momentum will be negative as well. Check the full article here“can momentum be negative?”.
3. What are the types of energy?
- Radiant energy (refers to the energy that travels by waves or particles)
- Thermal energy (refers to the energy among the atoms and molecules in an object.)
- Sound energy (deals with the energy caused by vibrations.)
- Electrical energy (related to the energy caused by the flow of negatively charged electrons around a circuit.)
- Mechanical energy (refers to the energy associated with the mechanical movement of an object.)
4. What is negative force?
Yes, the force can be negative as force is a vector quantity that depends upon magnitude and direction. The negative sign signifies only the direction.
5. Can displacement be negative?
Displacement can be negative as it is a vector quantity that depends upon magnitude and direction. The negative sign signifies only the direction.
6. What happens when gamma rays decay?
Gamma decay occurs when a nucleus transitions from a higher energy level to a lower energy one via emitting electromagnetic radiation (photons). Because the number of protons (and neutrons) in the nucleus remains constant during this process, the parent and daughter atoms are the same chemical element.
7. What is the difference between photonics and optics?
Optics is a broad field of physics that includes subjects such as physical optics, ray optics, and practical applications such as lasers and antenna theory. Photonics is an optical application field with a wide range of applications in fiber optics, signal processing, and wireless communication.
8. Stress in physics?
In physics, stress is defined as the force acting on a material’s unit area. Strain is the term used to describe the effect of stress on the body. The body can be deformed as a result of stress.
9. Do Quarks vibrate?
Atoms are the building blocks of all stuff. Atoms are made up of electrons that circle a nucleus of protons and neutrons, which are made up of quarks. According to string theory, electrons and quarks are basically microscopic vibrating loops of energy.
10. Kinetic energy formula?
Kinetic energy is related to the object’s mass and the square of its velocity. The Kinetic energy formula is 1/2 m v2. If the mass is measured in kilograms and the velocity is measured in meters per second, the kinetic energy is measured in kilograms-meters squared per second squared.
More Interesting Topics
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023