Liquid oxygen is a liquified form of oxygen gas that is used as an oxidant for liquid fuels in the propellant systems of missiles and rockets. Liquid oxygen is pale blue and extremely cold. Although non-flammable, it is a strong oxidizer. Oxygen is widely applied in the metal industries in conjunction with acetylene and other fuel gases for metal cutting, welding, scarfing, hardening, cleaning, and melting.
In addition, Liquid oxygen is extremely cold and boils at –297.3 degrees Fahrenheit (-182.9 degrees Celcius). Cold surfaces on liquid oxygen systems, such as valves, lines, or couplings, can cause severe frostbite or cryogenic burns if allowed to come into contact with skin or non-protective clothing. At cryogenic temperatures, the skin will adhere to cold surfaces, causing additional injury.

Liquid Oxygen is produced by an air separation unit (ASU) through liquefaction of
atmospheric air and separation of the oxygen by continuous cryogenic distillation. The oxygen is then removed and stored as a cryogenic liquid.
Table of Contents
Liquid Oxygen- Key Points
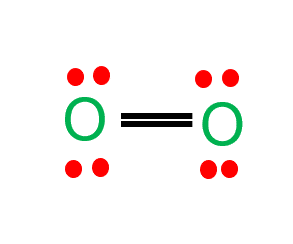
- Liquid oxygen is one of the forms of elementary oxygen abbreviated as LOX
- used in the submarine, aerospace, and gas industries.
- Liquid oxygen is pale blue in color and strongly paramagnetic i.e. can be an overhang between the powerful horseshoe magnet poles.
How Cold is Liquid Oxygen?
Cryogenic liquids, such as liquid oxygen, are extremely cold. Cryogenic liquids are liquefied gases with a normal boiling point of less than –130 degrees Fahrenheit (–90 degrees Celsius). The boiling point of liquid oxygen is –297°F (–183°C). Because the temperature difference between the product and the surrounding environment is significant—even in the winter—critical it’s to keep liquid oxygen insulated from the heat. Handling and storage of the product necessitate the use of specialized equipment. Liquid nitrogen is colder (−218.79 C at standard pressure) than liquid oxygen (−195.79°C at standard pressure).
How Cold Is Liquid Nitrogen?
Liquid nitrogen is simply extremely cold nitrogen with a temperature of − 196 °C [− 320 °F]. It’s so cold that anything it touches instantly freezes.
Large amounts of liquid nitrogen are produced in air separation plants, which liquefy and distill air into its constituent gases: nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. It is kept as a cryogenic liquid in a vacuum-insulated jar that may retain many days of material and can be utilized as a liquid or gas on demand.
Summary
- Liquid oxygen is simply extremely cold oxygen.
- Liquid oxygen is a pale blue band and extremely cold cryogenic liquid.
- Oxygen is often stored as a liquid, although it is used primarily as a gas
More Interesting Topics
NH3 Oxidation Number
Laminar Flow| Physics
Liquid Definition| Chemistry
NH3 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the molar mass of oxygen?
O2 molar mass is 32 gram per mole. The molar mass of an element or molecule is the total mass in grams of all the atoms that comprise a mole of a certain molecule. Since oxygen (molar mass = 15.99 g/mol) does not exist as one atom, it is always O2 (32 g/mol). There are 12 valence electrons in an oxygen molecule.
2. What is oxygen electronic configuration?
There are 8 protons, 8 electrons, and 8 neutrons in a single oxygen atom.
In the electron configuration for oxygen, the first two electrons will be in the 1s orbital. The next two electrons for O are placed in the 2s orbital because the 1s orbital can only hold two electrons. As a result, the O electron configuration is 1s22s22p4. There are 12 valence electrons in an oxygen molecule.
3. Is NH3 polar?
NH3 is polar due to its three N-H bond dipoles. nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. Charging differences between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms cause polarity.
4. Is carbon dioxide a pure substance?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a pure substance. It is a gas with a fixed composition that maintains its identity even when subjected to minor physical changes such as temperature and pressure.
5. Is HCL polar or nonpolar?
HCL is a polar molecule. Because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, it attracts the bound electron pair and gains a partial negative charge, whereas hydrogen gains a partial positive charge.
6. What is nitrogen fluoride?
Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is a colorless gas that has a moldy odor. It is extremely toxic when inhaled.
7. What is air?
Air is a homogeneous mixture of different gasses. The air in the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen, oxygen (which is required for animal and human life), carbon dioxide, water vapor, and trace amounts of other elements (argon, neon, etc.). At higher elevations, air contains ozone, helium, and hydrogen.
8. Density of oxygen?
Liquid oxygen is a liquified form of oxygen gas that is utilized as an oxidant for liquid fuels in missile and rocket propellant systems. It is incredibly cold and has a boiling point of –297.3 degrees Fahrenheit (-182.9 degrees Celcius).
Check the full article “Density of oxygen”.
9. Is helium a gas?
Helium (He) is an inert gas and chemical element in Periodic Group 18. (noble gases). Helium, the second lightest element (only hydrogen is lighter), is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that freezes at 268.9 degrees Celsius (452 degrees Fahrenheit).
10. At what temperature does water freeze?
Water’s normal freezing and melting points are 0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
11. Hydrogen cyanide polar or nonpolar?
HCN is a polar molecule.
As can be seen from the HCN lewis structure, the electronegativity difference between nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) makes it a polar molecule.
More Links
| How many electrons does Helium have? | Unit Weight of Water |
| What Happens If You Eat Silica Gel? | Molar Mass of Methanol| Easy-Explanation |
| How Many Cups in a Gallon? | Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar |
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023