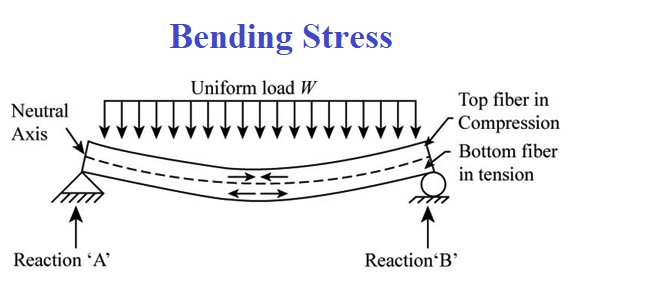
The flexural strength of a material refers to the maximum bending stress that can be applied to that material before it yields. The most common way of determining the flexural strength of a material is to do a transverse bending test using a three-point flexural test technique. Flexural strength is also known as bending strength, modulus of rupture, or transverse rupture strength.

In other words, Flexural strength is the capacity of a material to resist bending or breaking when a force is applied perpendicular to its surface. It is commonly measured in units of stress, such as psi or N/m², and is determined by applying force to the material until it either bends or fractures. In simpler terms, flexural strength describes how well a material can withstand forces that cause it to deform or bend.
Table of Contents
Why We Need to Know Flexural Strength
- The flexural strength of a Cured-in-Place Pipe (CIPP) liner determines how the liner will behave and how much force it may safely bear.
- Engineers can use flexural strength to assess the impact of external loads like soil fill, live traffic, and construction equipment on underground pipes.
- The flexural strength of hybrid carbon/glass composite sheets can be used to measure the bending strength of joints between two types of hybrid layers.
Testing Standards for Flexural Strength Measurement
Here are some standards for flexural strength measurement of a material:
- ASTM D790 – Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials.
- ISO 178 – Plastics – Determination of Flexural Properties.
- EN ISO 14125 – Fibre-reinforced plastic composites – Determination of flexural properties.
- JIS K 7171 – Testing method for flexural properties of plastics.
- DIN 53452 – Testing of plastics; determination of flexural properties.
Flexural Modulus
The flexural modulus (also known as the bending modulus) refers to the tendency of a material to bend or is described as a ratio of stress to strain.
How is flexural strength measured?
Material specimens are typically evaluated in a three-point bending configuration and a four-point bending arrangement.
The three-point bending arrangement produces the greatest bending moment in the specimen’s centre; nevertheless, this approach may not provide the best depiction of the material’s overall performance because bigger flaws around the support points do not affect the observed flexural strength.
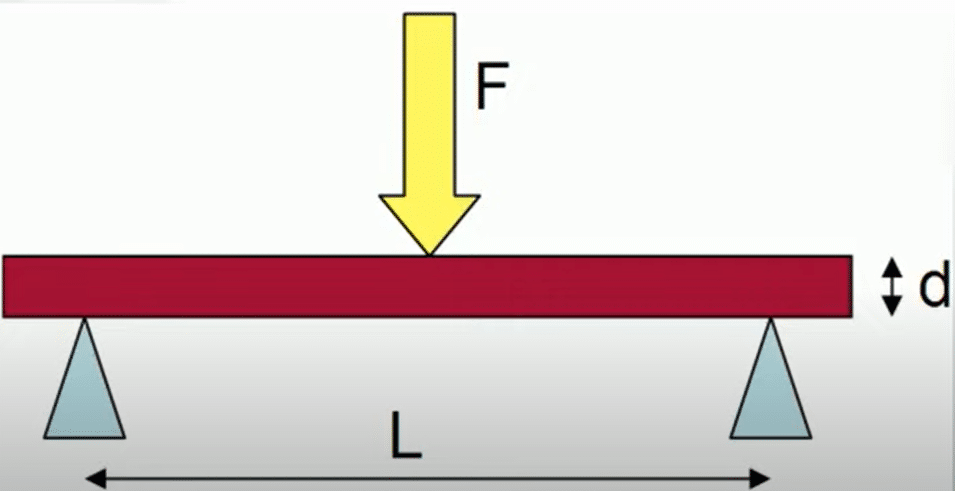
3-Point Bending Test
The three-point bend test is a classic mechanics experiment that measures a material’s Young’s modulus in the shape of a beam. The L-length beam is supported by two rollers and is subjected to a concentrated load of P at its center.

A load is applied to the center of the sample using a loading device, such as a hydraulic or mechanical press, and the sample is bent until it breaks.
During the test, the load and the deflection of the sample are recorded. From this data, the flexural strength can be calculated using the formula:
F = 3FL / 2bd2
where F is the maximum load applied to the sample before it breaks, L is the span length between the supports, b is the width of the sample, and d is the depth or thickness of the sample.
The flexural modulus, or the material’s stiffness, can also be calculated from the slope of the load-deflection curve.
4 Point Bending Test
It’s important to note that there are other methods to measure flexural strength, such as four-point bend tests or dynamic mechanical analysis, which may be more suitable for certain materials or applications. The specific testing method should be chosen based on the material being tested and the information needed for the application.
The four-point bending flexural test is identical to the three-point bending flexural test. The main difference is that with the addition of a fourth bearing, the section of the beam between the two loading points is subjected to maximum stress, whereas in the case of three-point bending, only the material directly beneath the central bearing is subjected to maximum stress.
Daily Life Examples of Flexural Strength
Some examples of flexural strength in daily life:
- Building materials: Structural components of buildings, such as beams, columns, and trusses, are designed to resist bending and buckling under loads.
- Furniture: Chairs, tables, and shelves are made to withstand the weight of people and objects without bending or breaking.
- Sporting goods: Items like tennis rackets, hockey sticks, and ski poles are designed to withstand the bending and twisting forces that occur during use.
- Automotive parts: Parts like car frames, suspension components, and engine mounts are engineered to resist bending and flexing under the weight and stresses of the vehicle.
- Electronics: The thin metal frames and covers of electronic devices, such as laptops and smartphones, must be able to flex without breaking under normal use and accidental drops.
In all of these examples, the flexural strength of the material is an important factor in ensuring that the structure or product is safe, durable, and reliable.
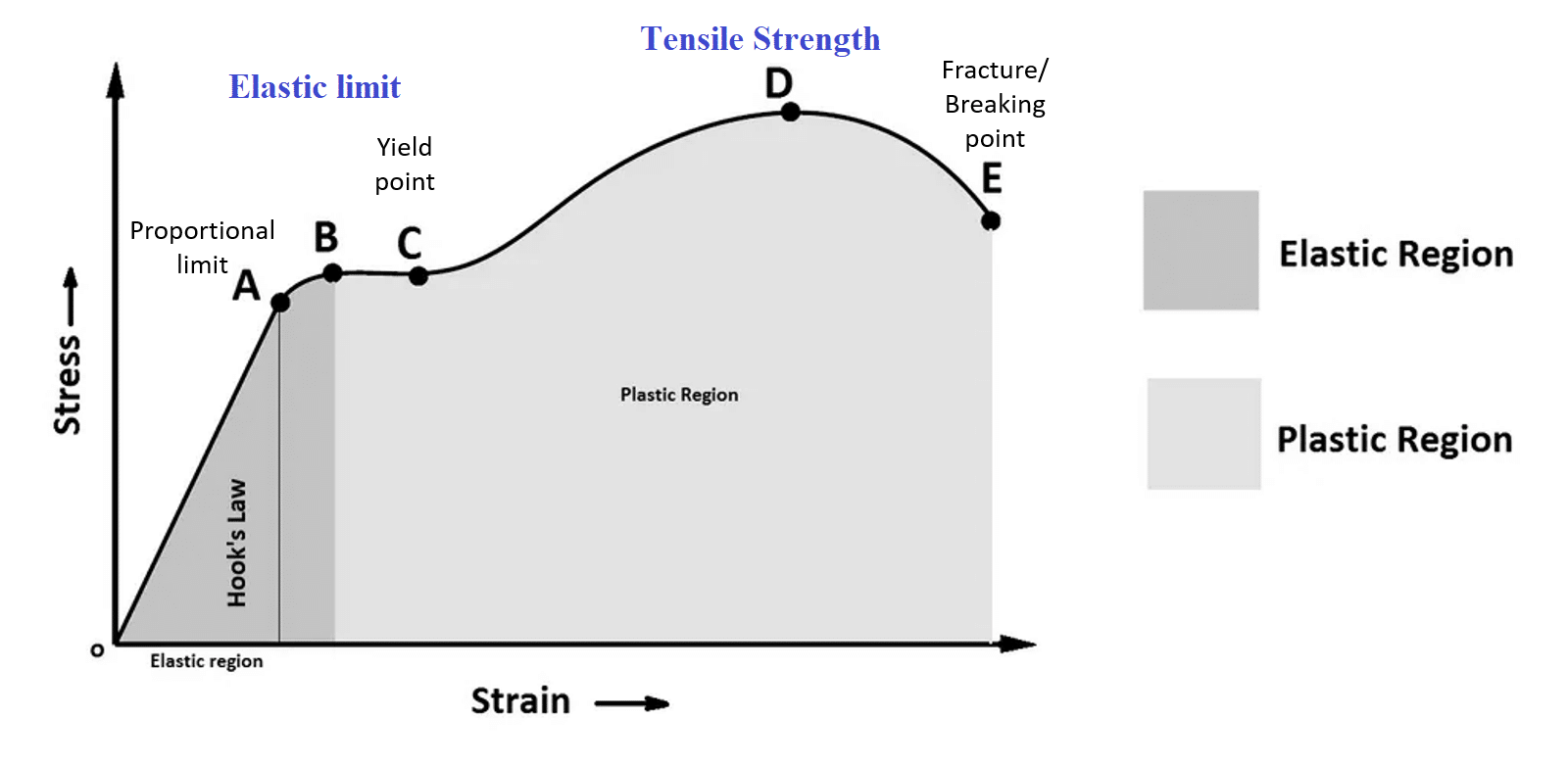
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is described as “the maximum load in weight per unit area pushing in the direction of length that a particular substance can sustain without ripping apart”

Stiffness vs Strength
The tendency of an element to return to its original shape after being exposed to a force is indicated by stiffness. Strength is the amount of stress that may be given to an element before it irreversibly deforms or breaks.

Related Links
Mass Vs Weight| 5 Easy Examples
Can Force Be Negative?| Easy Explanation
Energy-The Ability to do Work
Metal Definition & Meaning| Daily Life Examples
Elastic Limit| Definition, Formula, and Simple Explanation
Solved Numerical Problem
A rectangular beam made of steel with a length of 1 meter, width of 10 cm, and height of 2 cm is subjected to a load of 5000 N at its midpoint. The beam deflects by 5 mm under this load. What is the flexural strength of the steel beam?
Solution: The flexural strength of a material is calculated by using the formula:
Flexural strength = 3FL / 2bd^2
where F is the load applied at the midpoint, L is the length of the beam, b is the width of the beam, and d is the height of the beam.
Plugging in the given values, we get:
Flexural strength = (3 x 5000 N x 1 m) / (2 x 0.1 m x (0.05 m)^2) = 600 N/mm^2
Therefore, the flexural strength of the steel beam is 600 N/mm^2.
Multiple Choice Questions-Flexural Strength
- Which of the following materials would typically have the highest flexural strength?
a) Rubber b) Wood c) Steel d) Aluminum
Answer: c) Steel
- What is the formula for calculating flexural strength?
a) F = ma b) F = mg c) F = 3FL / 2bd^2 d) F = kx
Answer: c) F = 3FL / 2bd^2
- Which of the following testing methods is commonly used to measure flexural strength of plastics?
a) Tensile test b) Compression test c) Shear test d) Three-point bend test
Answer: d) Three-point bend test
- Flexural strength is a measure of a material’s ability to resist which of the following types of loads?
a) Compression b) Tension c) Shear d) Bending
Answer: d) Bending
- In flexural testing, the distance between the supports is known as the:
a) Span length b) Load capacity c) Strain rate d) Yield point
Answer: a) Span length
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Define strength?
The strength of a material is defined in material mechanics as its capacity to sustain an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. The field of material strength is concerned with the forces and deformations that occur as a result of their action on a material.
2. What is Ultimate tensile strength?
The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of a material is the greatest stress that it can endure when stretched or pulled. The ultimate tensile stress (UTS) is the amount of stress sustained in a tensile test at the exact instant the item ruptures.
3. What is the modulus of elasticity?
The modulus of elasticity is just the stress-strain ratio. Young’s modulus, shear modulus, and bulk modulus are the three forms of elastic moduli.
4. What is strain energy?
Strain energy is a form of potential energy that is stored within materials that have been subjected to strain deformation. When an item is deformed from its unstressed state, the external work done on it is transformed into (and is considered equivalent to) the strain energy contained in it. It is measured in N-m or Joules.
More Interesting Links
What Is Malleability in Metal?
Fatigue Testing of Thermoset Composites
Engineering Stress vs True Stress
Yield Point| Definition and Stress-Strain Relation
Compressive Stress – Definition, Formula, SI Unit, and FAQs
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023