Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG, LP Gas, propane gas, or autogas) is a clean-burning alternative fuel that has been used for decades to power propane vehicles, as well as for cooking. LPG is a tri-carbon alkane that is in gaseous form at atmospheric pressure but becomes a liquid at normal temperatures and low pressure.
Furthermore, LPG is not natural gas since it is propane, whereas natural gas is methane.
In addition. LPG is less harmful to the ozone layer than chlorofluorocarbons.

Table of Contents
Composition of Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG)
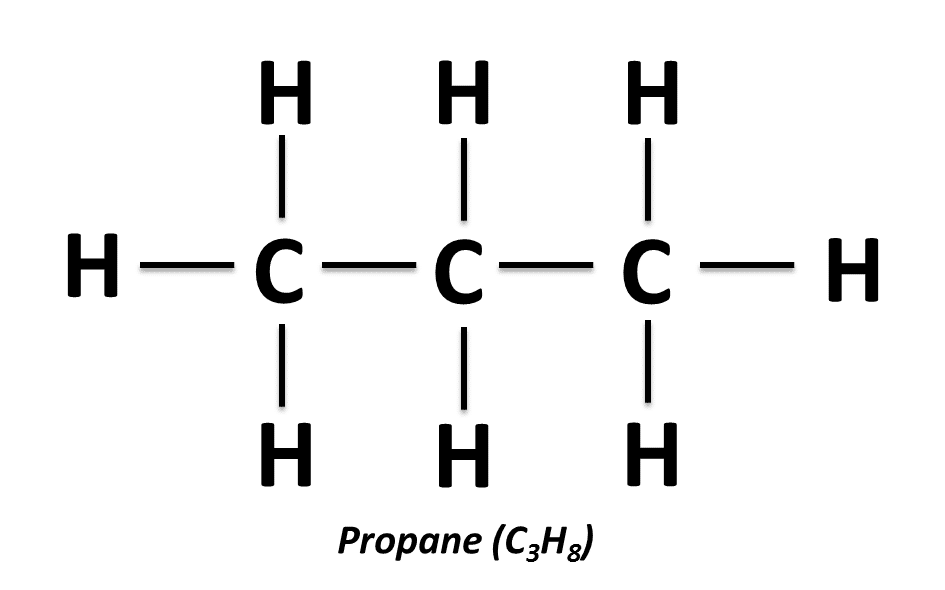
LPG is made up of two elements: hydrogen and carbon, often known as hydrocarbons. In scientific terms, LPG is a combination of Propane (C3H8) and Butane (C4H10) that can be produced as a byproduct of crude oil processing at refineries or collected from natural gas streams from oil and gas sources. Propane and Butane are both gases at room temperature and pressure, but they may be liquified under certain pressure and temperature circumstances. Furthermore, LPG may be stored securely and readily at room temperature.
Uses of LPG
- LPG has a larger energy content and calorific value per unit than several other regularly used fuels, including coal, natural gas, diesel, gasoline, fuel oils, and biomass-derived alcohols.
- Because of its versatility, LPG is utilized in over a thousand applications, including cooking, heating, air conditioning, and cars, as well as aerosol propellant and foam manufacture. It is also utilized in the production of Synthetic Natural Gas (SNG).
- LPG is reasonably easy to transport and store, and it may be utilized in almost any place. It does not necessitate the use of a fixed network and will not deteriorate with time.
- As LPG is easily interchangeable with natural gas, it is an excellent backup fuel for the industry in times of natural gas shortages. When utilized as SNG, no changes to the pipeline network or diameters are required, and it enables the convenience of switching between natural gas and LPG without adjusting equipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LPG
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| LPG will mix with air at any temperature | The ignition temperature of LPG is higher than petrol |
| Nontoxic and Non-corrosive nature | The LPG is heavier than air, so it gets collected at the lowest spot in the case of leakage, which causes suffocation. It is more hazardous in the case of fire. |
| Contain less content carbon than petrol fuel, so it produces less carbon monoxide pollution. | Proper ventilation and detection system is required for indoor storage |
| High octane value leads to the high thermal efficiency of the engine | Low vapor pressure may cause the engine to start trouble at low temperature |
| Less noise and vibration when compared to a diesel engine. | Since LPG is odorless an odorant should be added to it for quick detection of leakage. |
Propane Molecule
Propane molecules are made up of three carbon atoms linked together in a chain, with eight hydrogen atoms attached to these carbon atoms. A methane molecule, on the other hand, is made up of just one carbon atom connected to four hydrogen atoms.
Summary
Liquefied petroleum gas (propane gas) is a combustible mixture of hydrocarbon gases, the most common of which are propane, butane, and propylene. LPG is frequently used as a fuel source for gas barbecue grills, gas cooktops and ovens, gas fireplaces, and portable heaters. LPG water heaters are widely used throughout Europe. It is also used as a fuel for engines and backup generators.
Related Links
Heat Flux-An Overview
Thermite Welding- An Overview
Power Units- The Basics
Thermal Energy Equation- Simple Overview
Momentum Equation| Definition and Examples
Absolute Alcohol| Definition, and Formula
Pressure-Volume Diagram|PV Diagram
Chemical Reactions| Examples in Daily Life
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is LPG the same as natural gas?
LPG is not natural gas since it is propane, whereas natural gas is methane. LPG is formed during the natural gas processing and crude oil refining processes. LPG is kept as a liquid under pressure in gas bottles or tanks once it has been processed.
2. What is compressed natural gas?
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a more environmentally friendly alternative to gasoline. CNG fuel is safer than gasoline and diesel since it is non-toxic and does not harm groundwater. It is produced by compressing methane (natural gas) to less than 1% of its volume.
3. What are the advantages of liquified natural gas?
Natural gas is less expensive than other fossil fuels, it is the most ecologically beneficial fossil fuel since it burns cleaner, and is more efficient in storage and transmission than renewable energy.
Liquified natural gas (LNG) enables the cost-effective transfer of gas across seas or, in certain situations, by truck to small, scattered customers. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid condition (liquefied) at around -260° Fahrenheit for transit and storage.
More Interesting Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023