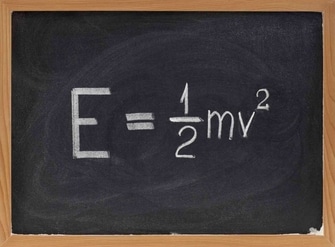Mechanical energy is the energy that an object possesses as a result of its motion or location. It is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy. Mechanical energy is calculated using the formula:
Mechanical energy = kinetic energy + potential energy.
Keep reading to learn more about mechanical energy, including its definition, mechanical energy formula, and mechanical energy examples.

Table of Contents
Mechanical Energy Definition
Mechanical energy (M.E.) is the sum of potential and kinetic energy in physical sciences.
It’s the macroscopic energy that a system has.
The principle of M.E conservation holds that if an isolated system is solely subjected to conservative forces, the M.E will remain constant.
This energy enables something to do tasks.
Energy is frequently defined as the ability to perform work.
Any object with M.E, whether in the form of potential or kinetic energy, has the ability to perform work.
An object’s M.E allows it to exert a force on another object, causing it to move.
Mechanical Energy Formula
The M.E of an object is the sum of its kinetic (K.E) and potential energy (U).
Its formula is
Emech = 0.5mv2 + mgh
m is the mass of an object, v is the velocity, h is the height, and g is the gravitational force.

Types of Energy
An object’s M.E is equal to the sum of its potential and kinetic energy.
Kinetic Energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy it has due to its movement.
It is the amount of work required to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to a specified velocity. Here are a few examples:
- Turbines use the kinetic energy of falling water to rotate their fans.
- A fast-moving car possesses K.E due to its mass and velocity.
- Because of its motion, flowing water has a K.E.
- A strong windstorm blows off the leaves from its tree due to K.E.
- A fast-hitting hammer drives the nail into the board due to its K.E.
Potential Energy
The potential is contained in an object due to its position.
We can think of it as the energy that can do work.
A rock perched on the edge of a cliff is one of its example. The potential energy in the rock will be transformed into kinetic energy as it falls.
Examples of Mechanical Energy
- A moving car possesses energy due to its motion (kinetic energy).
- Because of its high speed (kinetic energy) and vertical position above the ground (gravitational potential energy), a travelling baseball has M.E.
- A dart gun has an Emech when it is loaded and the springs are compressed.
- In windmills, moving air (wind) contains kinetic energy, which is a form of energy (due to motion). The air can function on the fan blades because of this capacity. The moving air exerts a force on the blades, causing them to rotate.
- A person riding a bicycle possesses some amount of energy in the form of chemical potential energy. This energy is utilized by the cyclist to do work on the paddles of the bicycle by applying some force and enabling the bicycle to move forward.
- A rider converts chemical potential energy into Emech to operate on the paddles of the bicycle by exerting force and allowing the bicycle to travel forward.
- Another everyday example is a bow and arrow. As an arrow is drawn, it has elastic potential energy, and when it is shot, the bow imparts kinetic energy to the arrow by pulling and propelling it toward the target. When all of these energies are combined, the arrow has enough mechanical movement to travel and strike its target.
Kinetic Energy Formula
The kinetic energy formula of a moving object equals one-half the product of its mass, and the square of its velocity.
Since the mass of an object can never be zero, and the square of velocity makes the answer positive.
Therefore, kinetic energy can never be negative.
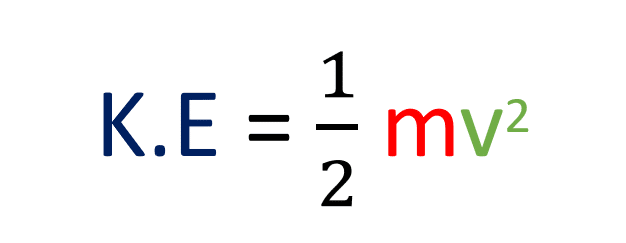
What is work?
“Work” is a force acting on an object in the direction of motion.
It is the product of Force (F) and displacement (S) in the direction of the force.
It is a scalar quantity, and its unit is the joule.
Work done = force x displacement.
What is 1 joule?
A Joule is the amount of work done when a force of 1 Newton is applied over a distance of 1 meter.
Joule = N.M
Joule= kg*m2/sec2
Related Topics
Instantaneous Velocity| Easy Key Points
Displacement| Physics
Elastic Limit| Definition, Formula, and Simple Explanation
How Many Water Bottles Is A Gallon| Examples
Can Momentum be Negative?
Velocity Formula & Definition
Power Units- The Basics
Summary
The mechanical energy formula is the sum of its kinetic energy( 0.5mv2) and potential energy (mgh).
The total kinetic energy of a body is the sum of the kinetic energies resulting from each type of motion.
The faster the motion, the more M.E the object has.
The Emech of an object is due to its position and movement.
Frequently Asked Question
1. What are examples of converting heat energy to mechanical energy?
- Steam engines convert thermal energy into mechanical movement in a train.
- Our body converts chemical potential to M.E
- During the combustion process in a car engine, the engine converts heat energy to mechanical movement.
2. What is a device that converts electricity into mechanical movement?
An electric motor converts electricity to mechanical movement.
3. State the Principle of Conservation of Mechanical Energy
The principle of mechanical energy conservation states that as long as the only forces acting are conservative forces, the total M.E in a system (i.e., the sum of the potential and kinetic energies) remains constant.
4. What is strain energy and how is it different from resilience?
Strain energy is elastic, which means that when the stress is removed, the material tends to recover. Resilience is the property of a material that allows it to hold energy without permanent distortion; the energy is released as soon as the load is removed, so the body does not deform permanently.
5. What is thermite welding?
Thermite welding is a type of welding that involves reducing metal oxides with aluminum powder and releasing a large quantity of heat. The thermite reaction is used to repair railway rails or broken machine components.
6. What is a state function?
A state function is a property that depends on the state of a system and is independent of the path taken to get it. Pressure and temperature, for example, are state functions.
7. What is water potential?
Water Potential is a gradient of free water molecule concentration. The water potential increases with the number of free water molecules. Water moves from a high potential to a low potential region by osmosis. Due to the low water potential, few forces are driving the water to move, so it tends to stay put. Because there is no solute and no pressure, pure water has no water potential.
8. What are examples of mechanical energy?
Following are some examples of mechanical energy
- Movement of windmill blades.
- Working on the hydropower plant.
- Cycling
- Working of electric motor
- Releasing an arrow from a bow
- Hammering a nail
Bottom Line
This article explains the mechanical energy formula and definition along with daily life examples. We hope that after reading this article you have a better idea of M.E and its uses in our daily lives. Please feel free to comment if you have any questions or suggestions.

Interesting Links
Momentum Equation| Definition And Examples
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
Relativistic Kinetic Energy| Easy Explanation
The density of water in g/mL-Accurate Value
The Density of Water lbs/U.S gal
Work Formula, Definition, & Units
15-Types of Energy and Examples| Simple and Short
What is Green Energy?| Importance and Examples
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023