Hydrosulfuric acid, often known as hydrogen sulphide, is a colourless, flammable, very dangerous gas with a “rotten egg” odour. Sewer gas, smelly damp, swamp gas, and manure gas are some of the more popular names for gas. It can be found in crude petroleum, natural gas, and hot springs.
| Name of molecule | Hydrosulfuric acid, Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfane (H2S) |
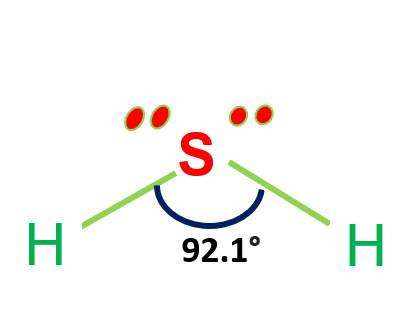
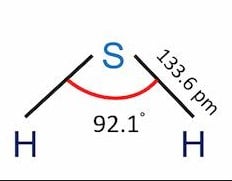
| Bond Angles | 92.1° |
| Molecular Geometry of Hydrosulfuric Acid | Bent shape |
| Molar mass | 34.1 g/mol |
| Valence electrons | 8 |
| Hydrogen sulfide (Hydrosulfuric acid) formula | H2S |
Table of Contents
Hydrosulfuric Acid Formula and Molecular Geometry
Hydrosulfuric Acid formula is H2S and the molecule is sp3 hybridized. the Sulfur atom is in the centre connecting with two Hydrogen atoms, producing a bond angle smaller than 180 degrees.
The existence of two unbonded electron pairs causes the molecule to bend.
Because sulphur is more electronegative than hydrogen, the molecule is somewhat polar.
In H2S, the vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments results in a non-zero total dipole moment.
As a result, Hydrogen sulfide shows dipole-dipole interactions.
Hydrosulfuric Acid Formula – Key Points
- Hydrosulfuric acid formual is H2S
- H2S is a colorless toxic gas
- It is produced by sewers and as a byproduct of industrial activities.
- In low concentrations, it smells like rotten eggs
- Soluble in water and many other liquids.
- When subjected to a relatively cold heat source of 232 degrees Celsius, it is extremely explosive and only takes a concentration of 4% to cause a flash fire.
- It is heavier and 1.136 times denser than air. This means it is likely to be found in low-lying areas with little to no ventilation
- H2S is a polar molecule
Molar Mass of Hydrosulfuric Acid
Molar mass of Hydrogen = 1.00794 g/mol
Sulfur molar mass = 32.06 g/mol
Molar mass of H2S is 34.1 g/mol

Uses of Hydrosulfuric Acid
- It is the main precursor for elemental Sulfur.
- It plays a vital role in signaling pathways in the human body.
- H2S is used primarily to produce sulfuric acid and sulfur.
- Hydrogen sulphide is used as an agricultural disinfectant by farmers, and it is present in some cutting oils, which are coolants and lubricants developed particularly for metalworking and machining operations.
H2S Polar or Nonpolar?
H2S is a slightly polar molecule because of the small difference in electronegativity values of Hydrogen (2.2) atoms Sulfur (2.58) atoms.
The molecular geometry of Hydrogen sulfide is polar but the bonds are not polar.
Electronegativity determines polarity. If a molecule’s structure is not symmetric, the molecule is polar.
In the case of symmetric structure, the dipole vectors on each molecule cancel each other out, resulting in the molecule’s nonpolar nature.
Furthermore, the existence of two lone pairs on opposing sides of the two Hydrogen atoms makes the molecule more polar and results in the bending shape geometrical structure of H2S.
A detailed explanation can be found at the link “h2s polar or nonpolar“.
Summary
To summarize everything in this article, the following are some important points:
- In the hydrosulfuric acid molecular geometry , two hydrogen forms a single covalent bond with the sulfur atom.
- The bond angle is 92.1 degrees and there are 8 valence electrons.
- H2S is a polar molecule with bent geometry.
- Exposure to Hydrogen sulfide can be dangerous.
Imprtant Links
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Acid
Hydrogen Molar Mass – What’s Insight
H2S Polar Or Nonpolar| Easy Explanation
Sulfurous Acid Formula & Lewis Structure
Hydrogen Cyanide-A Simple Overview
Hydrogen Electronegativity
Hydrogen Ion | Definition, Charge & Formula
Is HCl Polar or Nonpolar?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below
1. What is Polarity?
The distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond causes polarity.
It is known, for example, that bonds between atoms of various elements are electrically inequivalent.
In hydrogen chloride, for example, the H atom is slightly positively charged, whereas the Cl atom is slightly negatively charged.
The existence of minor electrical charges on dissimilar atoms is referred to as partial charges, and the presence of partial charges indicates the presence of a polar bond.
Some examples of polar molecules are Water (H2O), Ethanol, Ammonia, and SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide).
2. Explain Hydrogen sulfide Lewis Structure in simple words
In the H2S lewis structure, there is a single link between two hydrogen and sulphur atoms.
The structure is curved and has bond angles of 92.1 degrees.
3. H2S is acid or base?
In its gaseous form, H2S is neither acidic nor basic, i.e. it is neutral, but when it is made into an aqueous solution, it releases the hydronium ions H+ and S2- ions.
4. What is sulfur electronic configuration?
Sulfur electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
Imprtant Links
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
SiO2 Lewis Structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CO Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
NH3 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
O2 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
SO2 Lewis Structure| 4 Simple Steps
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023