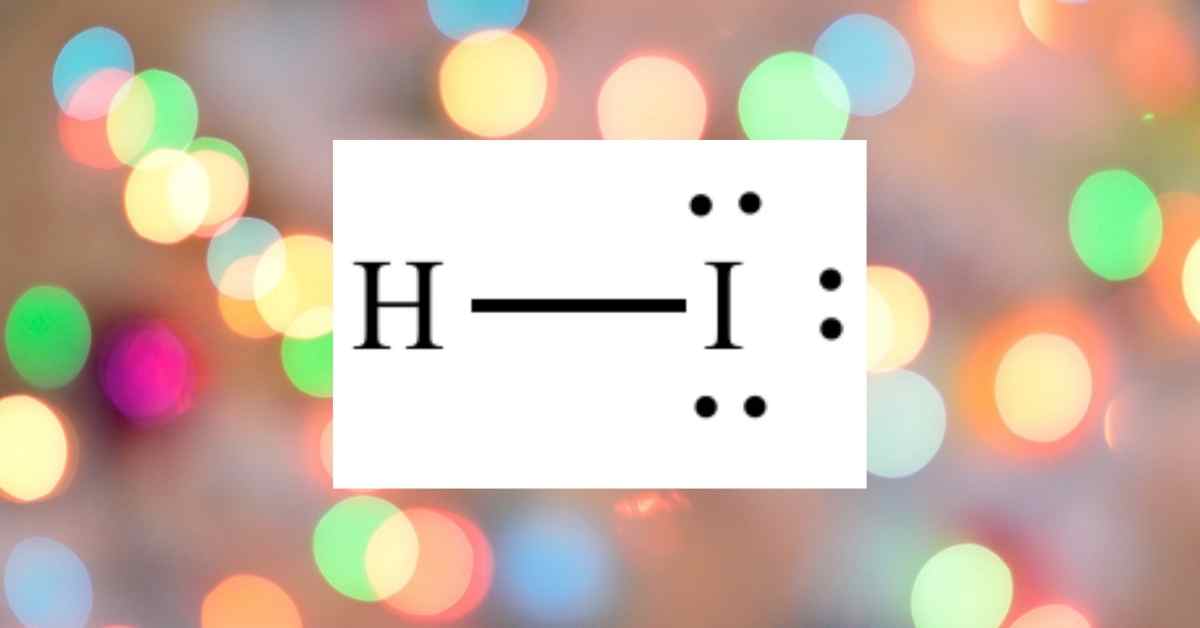
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is made up of a single sulfur atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. It is a highly poisonous, flammable gas with the odor of rotten eggs that are frequently produced by bacterial decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. When hydrogen sulfide is dissolved in water, it forms a weak acid (H2S acid).
H2S (g)+H2O(l)→ H3O(aq)+HS(aq)
The generation of H3O (hydronium) is indicative of the fact that it is an acid.

| Name of molecule | Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) |
| Polarity | Polar nature |
| Structure | Bent shape |
| No of lone pairs | Two |
| H2S Valence electrons | Eight |
| The molar mass of Hydrogen sulfide | 34.1 g/mol |
H2S bonds are covalent because H has an electronegativity of about 2.2 and sulfur has a value of 2.56. A covalent bond is formed by two H atoms and the central Sulfur atom. These bonds take up four valence electrons out of the eight available, leaving four valence electrons available. The molecule is sp3 hybridized as a result of this arrangement.
Table of Contents
Frequently Asked Questions
Some of the frequent questions are given below. If you have any questions please feel free to post a comment.
1. What is h2s acid’s name?
H2S (hydrogen sulfide) is a colorless, very deadly gas with a foul stench similar to rotten eggs. It is soluble in carbon disulfide and mildly soluble in water. When it dissolves in water, it generates a very weak acid.
2. What is a Polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is a kind of covalent bond that lies between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Such bonds are formed when the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7, they form.
3. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar compound. In BF3, the central boron atom has sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an unfilled p orbital on the Bron atom and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Because the Boron-Fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart, any net dipole in that plane is canceled out. Even if each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero because adding the bond vectors cancels everything out. Check the full article “Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”.
4. Is MgCl2 Ionic or Covalent?
When the magnesium atom loses two electrons to create the Mg2+ ion and each chlorine receives one electron to form the Cl– ion, an ionic connection is formed between the magnesium and chlorine atoms.
Check “Is MgCl2 ionic or covalent?”.
5. Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?
SiCl4 (silicon tetrachloride) is a nonpolar molecule. Because the four chemical bonds between silicon and chlorine are uniformly distributed, SiCl4 is non-polar. A polar covalent bond is a type of covalent link that is intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. When the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7, such bonds occur.
Check the full article “Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?”.
6. What is nitrogen fluoride?
Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is a colorless gas that has a moldy odor. It is extremely toxic when inhaled.
7. What is air?
Air is a homogeneous mixture of different gasses. The air in the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen, oxygen (which is required for animal and human life), carbon dioxide, water vapor, and trace amounts of other elements (argon, neon, etc.). At higher elevations, air contains ozone, helium, and hydrogen.
8. What is liquid oxygen?
Liquid oxygen is a liquified form of oxygen gas that is utilized as an oxidant for liquid fuels in defense systems. It is incredibly cold and has a boiling point of –297.3 degrees Fahrenheit (-182.9 degrees Celcius).
9. Density of oxygen?
Liquid oxygen is a liquified form of oxygen gas that is utilized as an oxidant for liquid fuels in missile and rocket propellant systems. It is incredibly cold and has a boiling point of –297.3 degrees Fahrenheit (-182.9 degrees Celcius).
Check the full article “Density of oxygen”.
10. Is helium a gas?
Helium (He) is an inert gas and chemical element in Periodic Group 18. (noble gases). Helium, the second lightest element (only hydrogen is lighter), is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that freezes at 268.9 degrees Celsius (452 degrees Fahrenheit).
11. At what temperature does water freeze?
Water’s normal freezing and melting points are 0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
12. Hydrogen cyanide polar or nonpolar?
HCN is a polar molecule.
As can be seen from the HCN lewis structure, the electronegativity difference between nitrogen (3.04) and hydrogen (2.2) makes it a polar molecule.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023