Solar power-based technologies turn sunlight into electrical energy by using photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors that concentrate solar radiation. This solar-based energy can be utilized to create power or saved in batteries or thermal storage. A solar panel, also known as a solar module, is a component of a photovoltaic system. It is made of a series of photovoltaic cells organized in a panel. Solar panels are available in a number of rectangular designs and are used in conjunction to generate power.
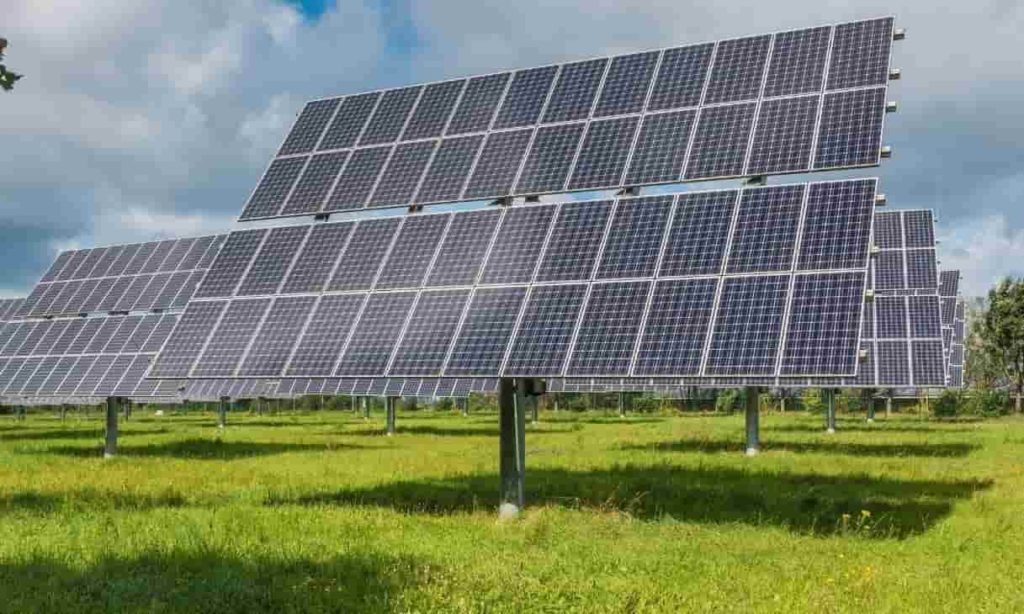

Table of Contents
What are Solar Panels Made of?
Solar panels (also known as “PV panels”) are used to convert sunlight’s light, which is made up of energy particles known as “photons,” into electricity that may be utilized to power electrical loads. These panels capture clean renewable energy in the form of sunshine and convert it into electricity, which can subsequently be utilized to power loads.
Solar panels are made up of individual solar cells that are made up of layers of silicon, phosphorous (which gives the negative charge), and boron (which provides the positive charge).
How do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels absorb photons from the Sun and generate an electric current as a result.
The energy released by photons impacting the surface of the solar panel knocks electrons out of their atomic orbits and releases them into the electric field formed by the solar cells, which subsequently pulls these liberated electrons into a directed current.
This entire process is known as the Photovoltaic Effect.
An inverter is a device that converts the direct current produced by a solar panel into alternating power. In addition, When installing a solar panel, the optimum orientation is chosen so that the solar panel faces in the most appropriate direction for the specified purpose.
Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic (PV) effect is the conversion of absorbed solar energy into electricity by a PV cell. PV systems produce no carbon dioxide emissions, which is beneficial to the environment. Nanomaterials absorb photon energy, which is then transmitted to the electrons in the atoms.
Light is made up of photons, which are tiny bundles of electromagnetic radiation or energy. These photons may be absorbed by a photovoltaic cell, which is the type of cell utilized in solar panels.
When the light of an appropriate wavelength is incident on these cells, the energy from a photon is transmitted to an atom of the semiconducting material at the p-n junction. The energy is sent to the electrons in the material in a precise way. As a result, the electrons jump to a higher energy state known as the conduction band, leaving behind a hole in the valence band. This process results in the formation of two charge carriers, electrons, and holes. These excited electrons and holes move in opposite directions.
Summary
Solar power methods use photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors called solar panels to convert sunlight into electrical energy. A solar panel is made up of a collection of photovoltaic cells that are arranged in a grid.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does solar power work?
Solar energy is transformed into power by converting the sun’s energy. The sunlight helps us to produce two forms of energy for human use: electricity and heat. Both are made possible by the usage of solar panels, which range in size from residential rooftops to acre-long “solar farms” on rural terrain.
2. What is liquid pressurized gas?
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), like coal, natural gas, and crude oil, is a fossil fuel. Unlike the others, LPG is never found on its own in nature; it is always found in combination with either natural gas or crude oil. In reality, LPG is a byproduct of the processing of these fuels. Approximately 60% of LPG is produced during natural gas extraction, with the remaining 40% recovered during crude oil refining.
3. What is energy density in physics?
The quantity of energy stored in a specific system or region of space per unit volume is referred to as energy density in physics.
4. How can we increase the efficiency of the Otto cycle?
The efficiency of an Otto engine can be improved by running it on lean fuel (which consumes additional air) or by increasing the compression ratio.
5. Why is thermal mass important for passive solar?
Thermal mass is an important and complementary component of passive solar design. Thermal mass refers to a material’s ability to receive, store, and release heat energy from the sun.
6. Do aerosols block sunlight?
Aerosols are microscopic particles that float in the Earth’s atmosphere. They have a cooling impact because they obstruct sunlight that would otherwise reach the globe.
7. How is static electricity useful for solar panels?
Researchers at MIT have invented a novel approach that utilizes static electricity to clear dust from solar panels, potentially saving 45 billion liters of water every year. Check the full article.
More Links
Power Units- The Basics
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023