How do domain names work?
The domain name’s primary purpose is to act as your website address. Every computer including the server that hosts your website has an IP address made of a string of numbers. Without domain names, users would have to enter your server’s IP address to access your site. Instead, your web address provides an easy to recall alternative, users can quickly enter your domain name to reach your content.
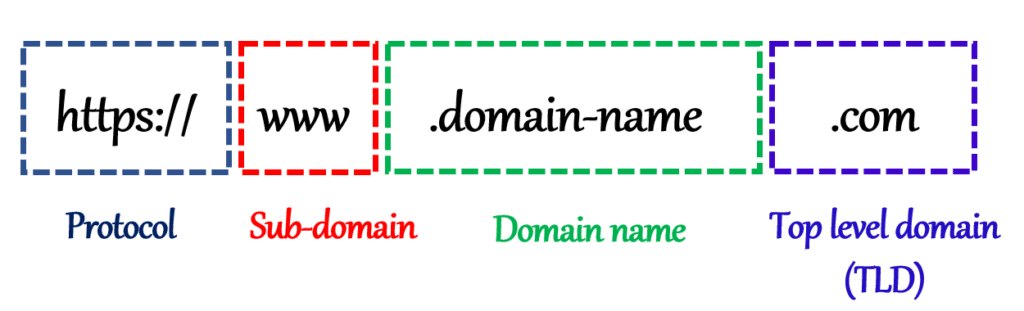
In order to understand how a domain name works, you need to know about the Domain name system (DNS). This is a decentralized system that stores information about which domains are connected to which IP addresses.
When a user enters your domain name in their browser it then checks the DNS for the corresponding IP address and directs the visitor to the right page. In this sense, you can think of DNS as the directory of the internet. Top-level domain (TLD) is the end portion of domain name such as .com
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



