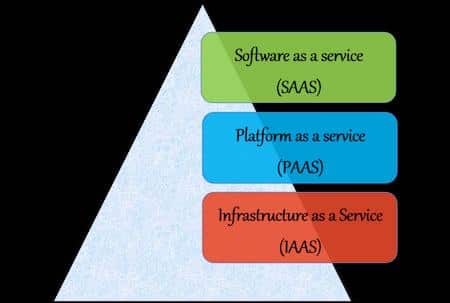
Cloud computing refers to highly optimized virtual data centers that provide various hosted services via the internet, with pay-as-you-go pricing. It’s a model for managing, storing, and processing data online via the internet. Major types are Software as a service (SAAS), model platform as a service (PAAS), and Infrastructure as a service (IASS).

Table of Contents
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a paradigm shift that provides computing over the internet. It consists of highly optimized virtual data centres that provide various softwares, hardware, and information resources for use when needed.
Three different models are listed below:
- Software as a service (SAAS) model
- Platform as a service (PAAS)
- Infrastructure as a service (IASS)
Software as a service (SAAS) model
It is a service that offers on-demand pay per use of application software to users.
This service is platform-independent and you don’t need to install the software on your PC.
The cloud runs a single instance of the software and makes it available for multiple end-users.
All the computing resources responsible for delivering SAAS are entirely managed by the vendor.
This service is accessible via a web browser or lightweight client application.
Some major examples of applications using the SAAS model are Gmail, google jamboard, Google docs and google drive, Microsoft office 365, Salesforce.
Platform as a service (PAAS)
This service provides an organization with a platform or a runtime environment to create and deploy applications. Its made up of a Programming language, execution environment, an operating system, a web server, and a database.
In this model, the organization is only responsible for the development, maintenance, and management of the applications.
Example products and services for PAAS are Amazon web service Elastic beanstalk, Google App Engine, Windows Azure, and Heroku.
Infrastructure as a service (IASS)
This service offers computing architecture and infrastructure.
It offers all computing resources in a virtual environment so that multiple users can access them.
These resources include data storage, virtualization, servers, and networking.
Most vendors are responsible for managing the above resources.
If you use this service, you will be responsible for handling other resources such as applications, data runtime, and middleware. IAAS is mainly for system administrators.
Some examples based on this model are Amazon EC2, GoGrid, and Rackspace.
Cloud Computing Benefits
Cloud computing is the driver behind the most advanced technologies of our time: artificial intelligence, machine learning, data science, blockchain, and the internet of things.
To meet ever-changing business needs, organizations need to invest time and budget to scale up their IT infrastructures such as hardware, software, and services.
However, with on-premises IT infrastructure, the scaling process can be slow and organizations are frequently unable to achieve optimal utilization of the IT infrastructure.
Organizations can simply connect to the cloud (virtual data centre) and use the available resources on a pay-per-use basis.
This helps them to avoid capital expenditure on additional on-premises infrastructure resources and instantly scale up or scale down according to business requirements.
What is cloud storage?
The cloud means the services delivered over a network like an internet.
Cloud storage is a service model in which data is backed up, managed, and accessed remotely, usually over the internet.
Users typically pay for their cloud data storage at a per-gigabyte monthly rate.
So the more data you have, the more you will have to pay to keep it stored in the cloud and vice versa. Consumers are probably familiar with cloud services like Dropbox or Google Drive typically for photos and documents.
For enterprises, cloud storage is more often used for data backups, disaster recovery, archiving, and DevOps projects.
Uses
Every day each business in the world has to deal with heaps of records, data, and paperwork.
It’s not just the big corporations but small businesses too that need to keep track of a lot of data.
Cloud computing keeps all this information safely stored in a cloud.
A cloud refers to a remote server on the internet.
The greatest disadvantage of storing information on your computer is that you cannot access it from any other place but when you store your valuable data on internet service, you can access it anytime from anywhere through any of your smart devices.
Cloud computing also gives you the facility to share your information with others so if you want to discuss a project with the customer, you can share the project details with them from anywhere.
Some benefits are as follows:
- Automatic software update
- Better reach (scattered groups of individuals can get together virtually and effortlessly share information efficiently through cloud resources)
- Flexibility in storage capacity (storage requirements can be scaled up and down easily)
- Reliable resources are always available from any internet connection)
- Back up and quick recovery of cloud-based data
- Cost-effective ( huge capital is not required)
- Redundancy (if one server goes down, others automatically kicks in)
- Security (Cloud platforms have several layers of built-in security, such as communication and data encryption, spam and virus filtering, monitored antivirus, active cybersecurity monitoring)
Cloud Services
Cloud services are services for allowing convenient, on-demand access from anywhere, to a shared pool of computing resources. These can include servers, storage, networking, applications, and services.
All types of cloud computing include five essential services
- On-demand self-service (This allows users to quickly and automatically get access to the IT resources)
- Broad network access (This is the ability to access a service from any standard device that’s connected to the network including PCs, laptops, mobile phones or tablets)
- Resource pooling (Computer network and storage are pooled and shared across multiple customers)
- Rapid Elasticity (This allows you to quickly scale or shrink the capabilities of your cloud to match the level of user demand)
- Metering (This tracks and controls the level of resource usage or the cost of that usage
Related Links
What Is A Search Engine?
How do domain names work?
Alliteration Definition
Technical Writing
Chemical Weathering
Crest of a Wave| Wave Properties|
Energy of Light
Au Pair Meaning & Definition
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023