Lewis structures, also known as Lewis-dot diagrams, show the bonding interactions between atoms in a molecule and lone pairs of electrons in the molecule. Lewis structures can also be used to predict molecular geometry when combined with hybrid orbitals.
This article explains the Lewis structure of hydrogen (H2) and the Lewis structure of water (H2O).
Table of Contents
Lewis structure definition
A Lewis structure is a molecule’s structural representation in which dots represent electron locations surrounding the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent interactions between atoms.
Other names for Lewis structures are Lewis dot diagrams, electron dot diagrams, Lewis dot formulas, and electron dot formulas. The steps for drawing Lewis structures are listed below:
- Count the valence electrons of atoms.
- Determine the central atom.
- Place electron pairs between the atoms.
- complete octet of the molecule.
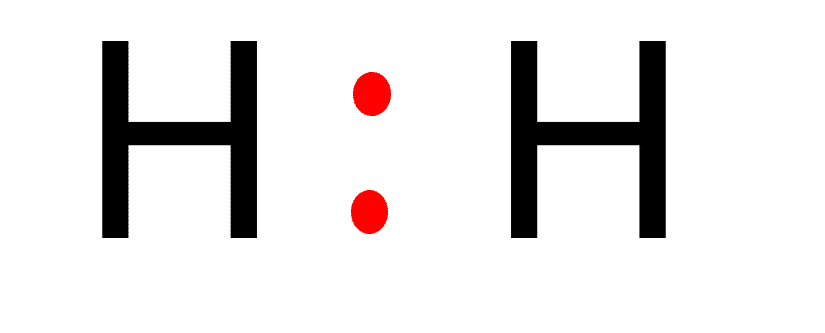
The Lewis Structure of Hydrogen (H2)
Step: 1
To sketch the Lewis structure of H2, we must first determine the total number of valence electrons present in the H2 molecule. Hydrogen is a group 1 element on the periodic table. Hence, the number of valence electrons present in a hydrogen molecule is two.
Step: 2
The H2 molecule has two identical atoms. Therefore, any of the atoms can be considered a center atom.
Step: 3
Two hydrogen atoms form a chemical bond by sharing one electron each.
In the Lewis structure, you put two electrons between each hydrogen atom to show a chemical bond between both atoms.
Step: 4
According to the octet rule, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have a full valence shell of eight electrons. Hydrogen is an exception since it can only hold two electrons in its valence state.
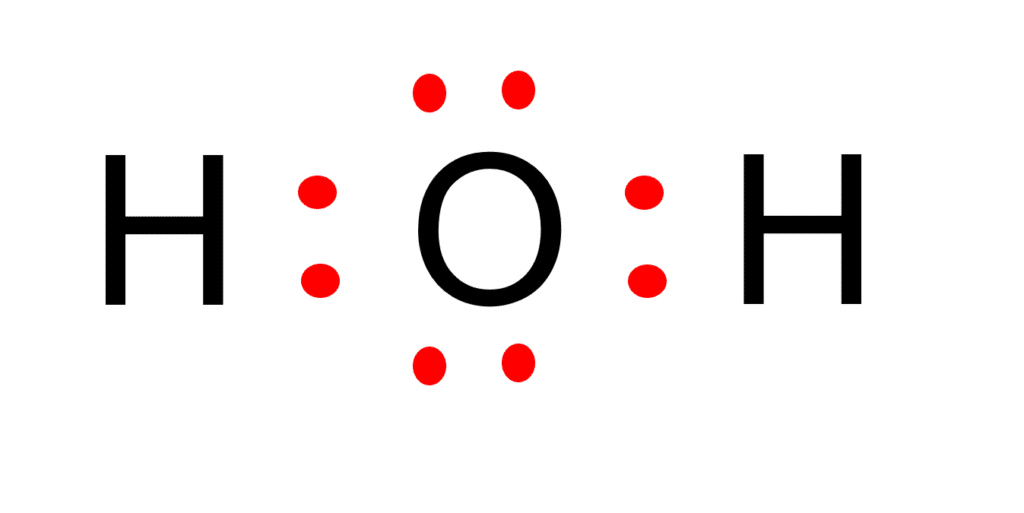
The Lewis Structure of Water (H2O)
Water has the chemical formula H2O. In a water molecule, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to one oxygen atom, and the outer electron shell of oxygen is filled. The following are the steps to draw the Lewis structure of H2O.
Step: 1
In a water molecule, hydrogen is a Group IA element with one electron in its outermost shell (valence shell). The oxygen in Group VIA has six electrons in its final shell.
The total number of valence electrons in the H2O Lewis structure is eight.
Step: 2
The oxygen atom in a water molecule is more electronegative than the hydrogen atom. As a result, electrons in the water molecule spend slightly more time near the oxygen atomic center and somewhat less time near the hydrogen atomic center.
In addition, the ability to have a higher valence is important for being the center atom.
Therefore, oxygen will be the central atom.
Step: 3
In a water molecule, oxygen has six valence electrons and therefore requires two more electrons from two hydrogen atoms to complete its octet. This also leaves two pairs of lone electrons that are not bound to any other atoms.
Step: 4
The H2O Lewis structure contains four electron pairs in total, with two H-O bonds already present.
The Molecular Geometry of H2O
In the H2O molecule, the oxygen atom forms two single sigma bonds with the hydrogen atoms. The oxygen atom still possesses two electron pairs. These lone electron pairs and hydrogen atoms are as far apart as possible, forming a tetrahedral geometry.
A water molecule’s bond angle (104.5°).
Hybridization of H2O
A water molecule (H2O) has one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
During the formation of a water molecule, one 2S orbital and three 2p orbitals of oxygen combine to form four hybrid orbitals of equivalent energy. These four new equivalent orbitals are called sp3 hybrid orbitals.
The two hybrid orbitals are nonbonding orbitals with paired electrons.
The other two orbitals are bonding orbitals and are half-filled.
The nonbonding pairs of hybridized orbitals are called lone pairs.
These hybridized orbitals are in the direction of the four corners of regular tetrahedrons.
| Type of hybridization in a water molecule | sp3 |
| The ground state electronic configuration of oxygen (Z = 8) | 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1 |
| Number of bonds in a water molecule | 2 |
| Number of sigma bonds in a water molecule | 2 sigma bonds |
| The bond angle of a water molecule | 104.5o |
More Lewis Structures
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Is B2 Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic?
BF3 Lewis structure| Molecular geometry, Hybridization
SiO2 Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
H2S Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CLF3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, and Polarity
CH4 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023