The molar mass of sulfur dioxide is 64.1 g/mol because the molar mass of sulfur is 32.1 g/mol and the molar mass of oxygen is 16.0 g/mol.
| Name of molecule | Sulfur dioxide |
| Bond Angles | 119 degrees |
| Molecular Geometry of SO2 | Trigonal planar |
| Hybridization of SO2 | sp2 hybridization |
| No Valence Electrons in the molecule | 18 |
| SO2 Polar or Nonpolar | Polar |
| The dipole moment of SO2 | 1.61 debye |
| molar mass for sulfur dioxide | 64.1 g/mol |
Table of Contents
Sulfur dioxide molar mass
Molar mass of Sulfur =32.066 g/mol.
O2 molar mass = 16.00 x 2 = 32.00 g/mol.
Molar mass of SO2 = 64.066 g/mol
The polarity of SO2 molecule
In SO2 molecules, the electronegative potential of oxygen is higher than that of sulfur.
As a result, oxygen exerts a stronger pull on sulfur dioxide’s covalent bonds.
The side of the molecule containing both oxygen atoms is somewhat negatively charged.
Whereas, the portion which has the sulfur atom has a slightly positive charge.
This makes SO2 a polar molecule.
In addition, the unbonded electrons on the sulfur and oxygen create repulsion between atoms.
This is another cause of the polarity of the sulfur dioxide molecule.
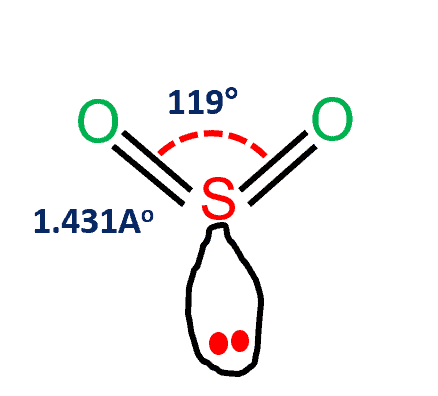
SO2 Molecular Geometry
Sulfur dioxide has a bent molecular shape, with a bond angle of 120°. The charge distribution on the central atom is asymmetric. The portion of the molecule that contains both oxygen atoms is somewhat negatively charged. The sulfur atom, on the other hand, has a slightly positive charge. On the sulfur, there is also a single pair of electrons.
Between sulfur and each oxygen atom, one sigma and one pi bond are formed. To reduce repulsions, the double bonds and the lone pair are separated as much as possible, and so the molecule is bent.
What is Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Sulfur Dioxide (American English), also known as Sulphur Dioxide (Commonwealth English), is a bond formed by the elements Sulfur and Oxygen. It’s a colorless, deadly inorganic gas with a terrible stench that reminds me of nitric acid. This gas is naturally released by volcanic activity.
When dissolved in water, it produces a weak acid solution.
Sulfur dioxide, a major precursor of sulfuric acid, is present in trace amounts in the environment.
Key Points
- SO2 Lewis structure would comprise two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both S and O atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 12.
- The electron geometry of SO2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner.
- The three pairs of bonding electrons are arranged in the plane at an angle of 120-degree.
- The sulfur’s valence electron = 6
- valence electrons of oxygen = 6 (There are 2 oxygen atoms in the compound)
Similarities between Sulfur and Oxygen atoms
- Both Oxygen and Sulfur have the same outer electric configuration of ns2 and np4
- O and S are usually divalent
- Both exhibit allopatric form
- O and S are non-metals
- In reaction with metals, both react with the oxidation state of -2
- While reacting with nonmetals, both form covalent compounds, for instance, H2O, H2S, CO2, and CS2.
Dissimilarities between oxygen and sulfur
| Oxygen | Sulfur |
| Two allotropic forms | 3 allotropic forms |
| Gas at ordinary temperature | Solid at ordinary temperature |
| Sparingly soluble in water | Not soluble in water |
| Helps in combustion | Combustible itself |
| Paramagnetic in nature | diamagnetic in nature |
| Does not react with water | When steam is passed through boiling sulfur, a little hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide is formed. |
| Does not react with acids | It is readily oxidized by concentrated sulfuric acid or nitric acid. |
Sulfur dioxide Effects on Humans
Sulfur dioxide is a toxic gas that can be harmful to one’s health.
It can irritate the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs.
Its excessive amounts might irritate and induce inflammation in the respiratory system.
Sulfur dioxide emissions in the atmosphere can result in the formation of additional sulfur oxides (SOx).
Small particles can develop when SOx reacts with other chemicals in the environment.
These tiny particles can penetrate far into the lungs and, in large enough quantities, can cause health issues.
Summary
- The molar mass of sulfur dioxide is 64.1 g/mol.
- Sulfur to the Oxygen ratio in Sulfur dioxide is 1:2.
- The sulfur dioxide molecule has two double bonds between the Sulfur atom and Oxygen atoms.
- There are 5 lone pairs of electrons in the molecule of SO2.
- Molar mass of sulfur dioxide = 64.066 g/mol.
- SO2 gives a weak acid solution when dissolved in water.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are given below. If you have any questions, feel free to comment or send an email to [email protected]
1. How many lone pairs of electrons are present in the SO2 lewis structure?
In the SO2 lewis structure, there are two double bonds between the sulfur and oxygen atoms. Sulfur atoms have one lone pair, while Oxygen atoms have two.
2. What is the biggest source of SO2?
Burning fossil fuels are the largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere.
Because sulfur and oxygen are both non-metals, the formation of sulfur dioxide is a covalent bonding process. Two oxygen atoms encircle the sulfur atom in the middle.
Related Links
SiO2 Lewis Structure
N2O Lewis Structure| Laughing Gas
HCN Lewis Structure
Hydrogen Molar Mass
Chemical Reactions| Examples in Daily Life
What is the Molar Mass of Nitrogen?
| Paramagnetic Materials | N2O Molecular Geometry |
| CO2 Lewis Structure and Molecular Geometry | Is Titanium Magnetic? |
| is water a pure substance? | The Otto Cycle| A Simple Overview |
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



