Weathering and erosion are geological processes that help shape the Earth’s surface.
The breakdown of rocks, soils, and minerals as a result of direct contact with the Earth’s atmosphere is known as weathering. Erosion, on the other hand, is the downward or down-slope movement of solids (soil, mud, rock, and other particles) caused by current agents such as wind, water, or ice responding to gravity or by living organisms.
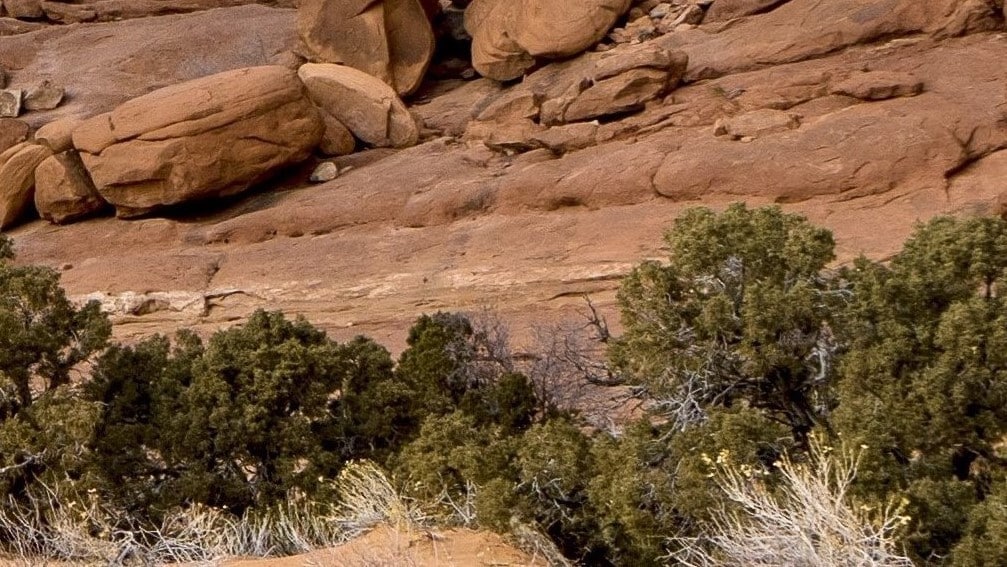

Weathering can be chemical, physical, or biological, whereas erosion is simply the movement of sediments from one location to another. Explicitly, physical weathering usually leads to erosion because it reduces the size of rock particles to sizes that natural forces can transport. Weathering is unstoppable, but humans have discovered ways to mitigate erosion by building gabions or planting trees.
Weathering and erosion both result in the formation of new geological features by reshaping the surface. Weathering produces particles that eventually form sedimentary rocks such as limestone and sandstone, and chemical weathering aids in the reduction of atmospheric CO2. If weathering did not exist, the earth would be a barren wasteland devoid of flora and fauna. The weathering process is responsible for the majority of fertile soils. Soil erosion transports mineral-rich soil to previously infertile areas, transforming them into agriculturally productive areas.
Weathering is a major cause of the deterioration of man-made structures such as roads, bridges, and houses. Chemical weathering also results in oxidation, which is responsible for rusting. Weathering and erosion can cause natural disasters such as rockslides and mudslides, which kill hundreds of people each year. The same weathering and erosion processes that create and deposit fertile soils are also responsible for removing fertile soils from an area, rendering it agriculturally crippled.
Table of Contents
Summary
- Weathering and erosion are geological processes.
- Weathering is the breakdown of rocks, soils, and minerals due to the influence of the earth’s atmosphere
- Erosion is the downward movement of soil, mud, or rocks due to gravity.
More Interesting Links
Physical Weathering| Short Overview
How many electrons does Helium have?
Valence Electrons in Nitrogen
Is HCl Polar or Nonpolar?| Simple Explanation
CH4 Polarity| Simple Explanation
Is HCN Polar or Nonpolar?
Is MgCl2 Ionic or Covalent?
Chemical Weathering
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023