Oxygen (O2) is a diatomic, colorless, odorless, tasteless gas with bond angles of 180 degrees. O2 Lewis structure comprises two oxygen atoms connected in a pair. Many species require molecular oxygen for breathing, making it vital for life. Oxygen (as a compressed gas) is also frequently employed in welding, metal cutting, and rocket engines as …
Lewis Structure
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a poisonous gas that has no odor or color. It has two distinct atoms in its Lewis structure: carbon and hydrogen. It’s a polar molecule with 180-degree bond angles. There is a triple bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The CO molecule has a total of ten valence electrons. Name …
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a colorless toxic gas. In its Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms on both sides of the central sulfur atom. Around the sulfur atom, there are also two lone pairs. H2S forms hydro-sulfuric acid when dissolved in water. Name of molecule Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) Bond Angles 92.1° Molecular Geometry of …
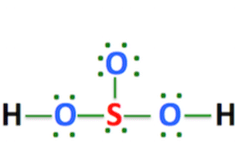
The sulfurous acid formula is H2SO3. It is a colorless weak dibasic acid, forms when sulfur dioxide is dissolved in water. It is the conjugate acid of hydrogensulfite. Sulfurous Acid Formula H2SO3 Other names Sulfur dioxide solution or Dihydrogen tri-oxosulfate Structure trigonal Pyramidal structure Valence electrons 26 Molar mass 82.07 g/mol. Sulfurous Acid Sulfurous acid …
A Lewis Structure of a Molecule is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons.It shows how the electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule. Electrons are represented as “dots” or “bonding electrons” as a line between the two atoms. The objective of drawing the Lewis structure is to obtain the “best” …
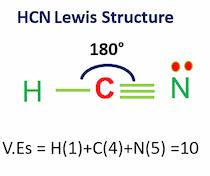
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) is a colorless, flammable, and poisonous liquid. The HCN Lewis structure comprises three different atoms: hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. It is a polar molecule with a bond angle of 180 degrees. HCN is used in electroplating, mining, and as a precursor for several compounds. Name of molecule Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) Bond Angles 180 …
In the N2O Lewis structure, nitrogen (N) and oxygen (O) atoms are covalently bonded. The number of valence electrons in N and O is five and six, respectively. The total number of valence electrons in N2O is 16. N2O or nitrous oxide is commonly known as a laughing gas. Also, several other names by which this …
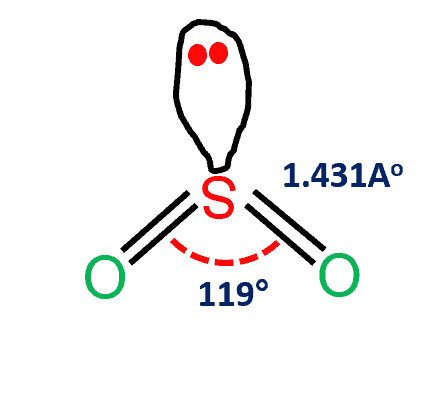
The SO2 Lewis structure would be comprised of two atoms of oxygen (O) and one sulfur atom. The number of valence electrons in both sulfur and oxygen atoms is six. The total number of SO2 valence electrons is 18. Name of molecule Sulfur dioxide (SO2) Bond Angles 119 degrees Molecular Geometry of SO2 Bent-V shaped Hybridization …
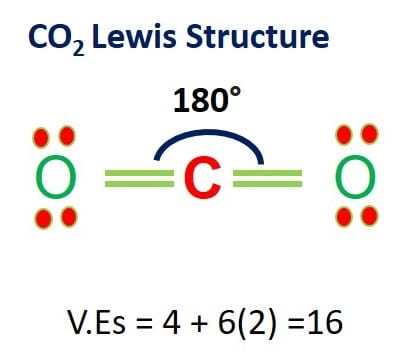
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a colorless, odorless, incombustible gas resulting from the oxidation of carbon. Its Lewis structure comprises two different atoms: carbon and oxygen. It is a nonpolar molecule with a bond angle of 180 degrees. CO2 is used as the refrigerant in fire extinguishers and it is a significant greenhouse gas in the Earth’s …
In the SiO2 Lewis structure, there is one atom of silicon (Si) atom and two atoms of Oxygen (O). The number of valence electrons in Si is 4 and the number of valence electrons in O is 6. The total number of valence electrons is 16. SiO2 Lewis Structure (Step by Step Construction) In the SiO2 …
Sulfurous acid is a colorless weak dibasic acid, forms when sulfur dioxide is dissolved in water. It is the conjugate acid of hydrogensulfite. Like sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, it is an oxoacid since it is an acid with oxygen atoms in its chemical formula. The sulfurous acid formula is H2SO3.Pure anhydrous H2SO3 has never been isolated or …
Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless, pungent gas and is made up of nitrogen and hydrogen. In the NH3 Lewis structure, three hydrogen atoms are bound to a nitrogen atom. NH3 molecular geometry is trigonal-pyramidal. Name of molecule Ammonia (NH3) Bond Angles 107.3 degrees Molecular Geometry of NH3 Trigonal-Pyramidal Hybridization of NH3 SP3 hybridization Electronic configuration …