Sodium hydrogen sulfate (NaHSO4) is an acid salt formed when sulfuric acid is partially neutralized with an equal amount of sodium hydroxide or sodium chloride (table salt). Additionally, it can also be synthesized through the reaction of Sodium Hydroxide and Sulphuric acid. Sodium hydrogen sulfate is also known as sodium bisulfate. Other synonyms include sodium hydrogen sulfate monohydrate, sodium bisulfate monohydrate, and sodium bisulfate monohydrate.
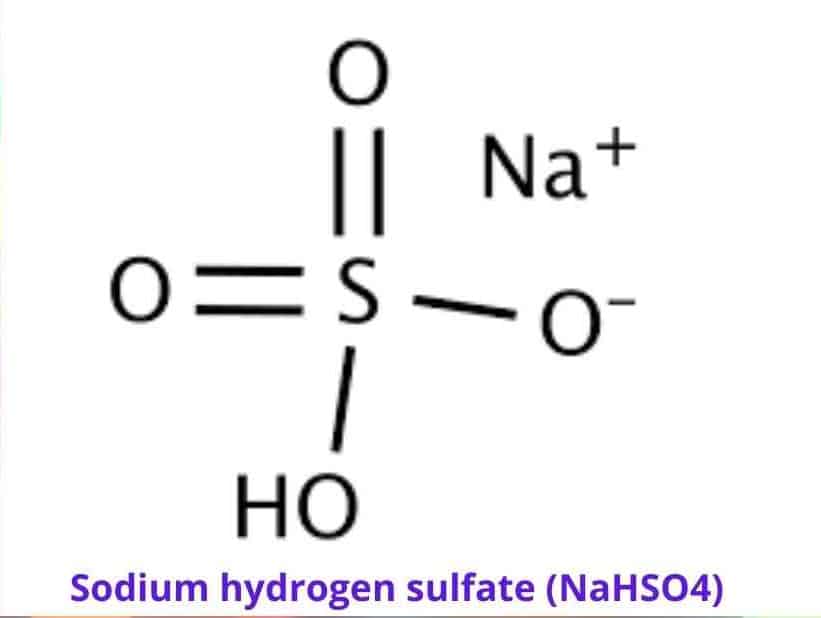
Sodium hydrogen sulfate (NaHSO4) is a dry acid in crystal, granular, or powder form that is used in a variety of industries such as household cleaning and swimming pool maintenance as a pH adjuster, fungicide, herbicide, or microbicide (a product that kills microbes).
Table of Contents
More Interesting Topics
Sodium Phosphate – Formula, Structure, Types, and Uses
Sodium Sulfate- Miraculous salt
Zinc Hydroxide
Hydrogen oxide-An Overview
Is MgCl2 Ionic or Covalent?
Sulfurous Acid Formula & Lewis Structure
Frequently Asked Questions
Some of the frequent questions are given below. If you have any questions please feel free to post a comment.
1. What is h2s acid’s name?
H2S (hydrogen sulfide) is a colorless, very deadly gas with a foul stench similar to rotten eggs. It is soluble in carbon disulfide and mildly soluble in water. When it dissolves in water, it generates a very weak dibasic acid known as hydro sulfuric acid.
Check the full article “Hydrogen sulfide acid”.
2. Is h2s ionic or covalent?
Because hydrogen has an electronegativity of around 2.2 and sulfur has an electronegativity of 2.56, H2S bonds are covalent. Hydrogen is a reducer and sulfur oxidizer due to its lower electronegativity.
3. What are the effects of the presence of hydrogen sulfide in water?
The presence of hydrogen sulfide in water may cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, coma, blurred vision, hemorrhage
4. What is the Polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is a kind of covalent bond that lies between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Such bonds are formed when the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7, they form.
5. Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BF3 is a non-polar compound. In BF3, the central boron atom has sp2 hybridized orbitals, resulting in an unfilled p orbital on the Bron atom and trigonal planar molecular geometry. Because the Boron-Fluorine bonds are all 120 degrees apart, any net dipole in that plane is canceled out. Even if each B-F bond is polar, the net dipole moment is zero because adding the bond vectors cancels everything out. Check the full article “Is BF3 polar or nonpolar?”.
6. Is MgCl2 Ionic or Covalent?
When the magnesium atom loses two electrons to create the Mg2+ ion and each chlorine receives one electron to form the Cl– ion, an ionic connection is formed between the magnesium and chlorine atoms.
Check “Is MgCl2 ionic or covalent?”.
7. Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?
SiCl4 (silicon tetrachloride) is a nonpolar molecule. Because the four chemical bonds between silicon and chlorine are uniformly distributed, SiCl4 is non-polar. A polar covalent bond is a type of covalent link that is intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. When the difference in electronegativity between the anion and the cation is between 0.4 and 1.7, such bonds occur.
Check the full article “Is SiCl4 polar or nonpolar?”.
8. What is h2s acid’s name?
H2S (hydrogen sulfide) is a colorless, very deadly gas with a foul stench similar to rotten eggs. It is soluble in carbon disulfide and mildly soluble in water. When it dissolves in water, it generates a very weak dibasic acid known as hydro sulfuric acid.
Check the full article “Hydrogen sulfide acid”.
More Interesting Topics
Ideal Gas Law| Simple Overview
Zinc Metal| Properties and Uses
Thermal Diffusivity
Energy Stored in a Capacitor
The pH of Distilled/ De-Ionized Water
Conduction in Physics| Easy Examples
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023