Photosynthesis is the chemical process by which plants and other organisms combine carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar (glucose) and oxygen using energy from the Sun. In this process, plants absorb sunlight energy, take in carbon dioxide from the air via their leaves, absorb water via their roots, and produce glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis occurs on land as well as in shallow water where sunlight can reach seaweed.

Table of Contents
Daily Life Significance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen. It is an essential process that supports life on Earth, and its significance can be seen in our daily lives in the following ways:
- Oxygen production: Photosynthesis is responsible for producing around 70% of the oxygen in our atmosphere, which is essential for all forms of life to survive.
- Food production: Photosynthesis is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems and is responsible for producing the food that we eat. Crops such as grains, fruits, and vegetables all rely on photosynthesis to produce the energy they need to grow and develop.
- Carbon dioxide absorption: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, which helps to mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing the amount of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere.
- Energy production: Photosynthesis is the foundation of many renewable energy sources such as biomass, biofuels, and solar energy. These energy sources are becoming increasingly important in our efforts to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
- Aesthetic value: Plants are an important part of our natural environment, and their beauty and diversity provide aesthetic value to our daily lives. Photosynthesis is responsible for producing the colours and fragrances that make flowers, trees, and other plants so appealing.
Photosynthesis Simple Definition
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and some bacteria to convert sunlight energy into sugar (glucose) and oxygen. The word photosynthesis is derived from the Greek words photo, which means “light,” and synthesis, which means “putting together.”
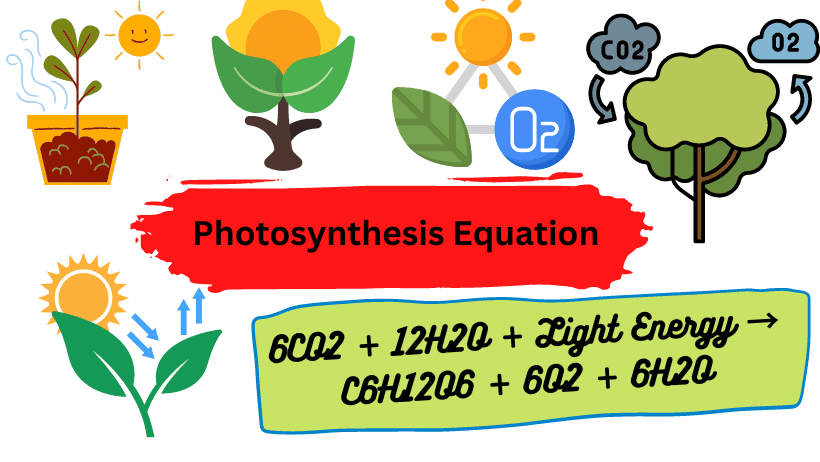
Photosynthesis Equation
Light energy transfers electrons from water to carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, resulting in carbon dioxide reduction, water oxidation, and the production of carbohydrates and oxygen.
This type of photosynthesis (also known as Oxygenic photosynthesis) balances respiration by absorbing CO2 produced by all breathing organisms and reintroducing oxygen into the atmosphere.
6CO2 + 12H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 (carbohydrate) + 6O2 + 6H2O
In the above equation, we can see six molecules of carbon dioxide combine with twelve molecules of water using light energy. As a result, a single carbohydrate molecule (C6H12O6, or glucose) is formed, along with six oxygen and water molecules.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the reactants needed for photosynthesis to occur, and where do they come from?
Answer: The reactants needed for photosynthesis to occur are carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is obtained from the air, while water is absorbed from the soil through the roots of the plant. - What are the two main types of chlorophyll, and what is their role in photosynthesis?
Answer: The two main types of chlorophyll are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis and is responsible for absorbing light energy. Chlorophyll b is an accessory pigment that helps to transfer light energy to chlorophyll a. - What is the role of light in photosynthesis, and how does it influence the process?
Answer: Light is an essential component of photosynthesis, as it provides the energy needed to power the process. The pigments in chloroplasts, including chlorophyll, absorb light energy and convert it into chemical energy, which is then used to synthesize glucose and other organic molecules. The intensity, duration, and quality of light all influence the rate of photosynthesis, with optimal conditions varying depending on the specific plant species and environmental factors. - What is the difference between the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, and where do they occur?
Answer: The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light energy and the conversion of this energy into ATP and NADPH, which are used to power the light-independent reactions. The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into glucose using the ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions.
5. What is the main product of photosynthesis, and how is it used by plants?
Answer: The main product of photosynthesis is glucose (sugar), which is synthesized from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. Glucose is used by plants as a source of energy to fuel various cellular processes, such as growth and reproduction. Additionally, excess glucose can be stored in the form of starch for later use, or used to produce other organic molecules such as cellulose, which forms the structural components of plant cell walls.
More Links
Ultimate Source of Energy
Chemical Reactions| Examples in Daily Life
Condensation Definition| Chemistry
Combustion Reactions| Introduction, Reaction, & Facts
The density of Water in g/ml-Accurate Value
How Many Cups in a Gallon? Cups to Pints, Quarts, and More
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023