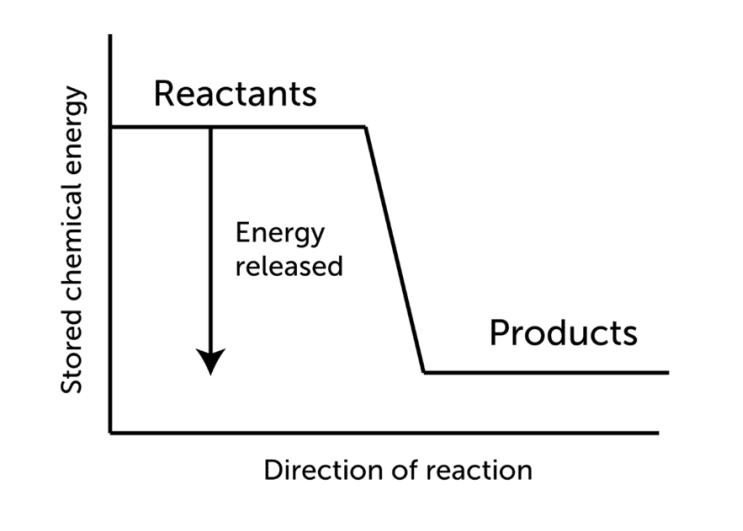
When molecular hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) are combined and allowed to react, energy is released and the molecules of hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form either water or hydrogen peroxide. However, hydrogen does not react with oxygen at room temperature, a source of energy is required to break the covalent bonds that hold the H2 and O2 molecules together. The hydrogen cations and oxygen anions are then free to react with each other due to electronegativity differences. The net reaction is highly exothermic, meaning a reaction that is accompanied by the release of heat.
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
Table of Contents
Fuel Cell Basics
A fuel cell is a device that produces electricity via an electrochemical reaction rather than combustion. In a fuel cell, Hydrogen and oxygen are combined to produce electricity, heat, and water. Fuel cells are used in a variety of applications, including providing power to homes and businesses, maintaining critical facilities such as hospitals, grocery stores, and data centres, and moving a variety of vehicles such as cars, buses, trucks, forklifts, trains, and more.
Catalysts (mostly nickel) are used in fuel cells to reduce the activation energy of the hydrogen-oxygen reaction, making it easier to initiate. Hydrogen fuel cells are used for backup power generation, powering spacecraft and remote facilities, and in hydrogen cars. Some advantages of fuel cells are listed below:
- Fuel cells that run on pure hydrogen are completely carbon-free, with only electricity, heat, and water as byproducts.
- Fuel cells can be scaled up. This means that individual fuel cells can be connected to form stacks. These stacks can then be combined to form larger systems.
Working of Fuel Cells-Hydrogen and Oxygen Reaction
- In a fuel cell, the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen is exothermic. The hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell efficiently converts the energy released by the reaction into electrical energy.
- A catalyst on the anode side splits the hydrogen molecules into electrons and protons.
- The protons pass through the porous electrolyte membrane, while the electrons are forced through a circuit, generating an electric current and excess heat. At the cathode, the protons, electrons, and oxygen combine to produce water molecules.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023